Abstract
Purpose
There is a lack of data on the role of sleep in the development of metabolic syndrome (MetS) in older adults. We aimed to examine the associations of sleep durations at night and other sleep-related parameters with the presence of MetS in older Chinese adults.
Methods
Data of 4579 individuals aged 60 years or older from the Weitang Geriatric Disease Study were analyzed. MetS was diagnosed based on the Adult Treatment Panel III (ATP III) criteria. Information regarding sleep durations and other sleep-related parameters was collected by questionnaires.
Results
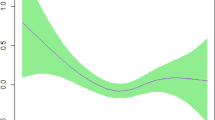
Compared with those with daytime napping, individuals without daytime napping were at an increased risk of MetS (odds ratio [OR] = 1.23; 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.03–1.47). Each hour increase in daytime napping increased the risk of MetS by 33% (OR = 1.33; 95% CI = 1.15–1.52). After adjusting for the effect of age and gender, a J-shaped association between sleep durations at night and the presence of MetS was observed. The risk of MetS was lowest among those who slept 7–8 h at night. Gender-stratified analysis indicated that the J-shaped relationship between sleep durations at night and MetS remained significant in men but not in women.
Conclusions
In older Chinese adults, sleep durations at night might have a dual effect on the risk of MetS and this effect was particularly pronounced in men. The results indicated that circadian rhythm might play an important role in the development of MetS in older populations.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.A. Batsis, R.E. Nieto-Martinez, F. Lopez-Jimenez, Metabolic syndrome: from global epidemiology to individualized medicine. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 82(5), 509–524 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.clpt.6100355
M. Mongraw-Chaffin, M.C. Foster, C.A.M. Anderson, G.L. Burke, N. Haq, R.R. Kalyani, P. Ouyang, C.T. Sibley, R. Tracy, M. Woodward, D. Vaidya, Metabolically healthy obesity, transition to metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular risk. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 71(17), 1857–1865 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2018.02.055
T.P. Ng, L. Feng, M.S. Nyunt, L. Feng, Q. Gao, M.L. Lim, S.L. Collinson, M.S. Chong, W.S. Lim, T.S. Lee, P. Yap, K.B. Yap, Metabolic syndrome and the risk of mild cognitive impairment and progression to dementia: follow-up of the Singapore longitudinal ageing study cohort. JAMA Neurol. 73(4), 456–463 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.4899
V. Xanthakis, J.H. Sung, T.E. Samdarshi, A.N. Hill, S.K. Musani, M. Sims, K.A. Ghraibeh, P.R. Liebson, H.A. Taylor, R.S. Vasan, E.R. Fox, Relations between subclinical disease markers and type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and incident cardiovascular disease: the Jackson Heart Study. Diabetes Care 38(6), 1082–1088 (2015). https://doi.org/10.2337/dc14-2460
T. Ma, G. Shi, Y. Zhu, Y. Wang, X. Chu, X. Jiang, Z. Liu, J. Cai, H. Wang, L. Jin, Z. Wang, X. Wang, Sleep disturbances and risk of falls in an old Chinese population-Rugao Longevity and Ageing Study. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 73, 8–14 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archger.2017.07.003
C.L. Lin, C.P. Lin, S.W. Chen, H.C. Wu, Y.H. Tsai, The association between sleep duration and overweight or obesity in Taiwanese adults: a cross-sectional study. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 12(4), 384–388 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orcp.2016.07.005
R. Liu, Y. Li, Z. Mao, X. Liu, H. Zhang, K. Yang, H. Zhang, R. Tu, X. Qian, J. Jiang, R. Bie, C. Wang, Gender-specific independent and combined dose-response association of napping and night sleep duration with type 2 diabetes mellitus in rural Chinese adults: the RuralDiab study. Sleep Med. 45, 106–113 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2017.12.017
Y. Zhan, R. Chen, J. Yu, Sleep duration and abnormal serum lipids: the China Health and Nutrition Survey. Sleep Med. 15(7), 833–839 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2014.02.006
X. Li, L. Lin, L. Lv, X. Pang, S. Du, W. Zhang, G. Na, H. Ma, Q. Zhang, S. Jiang, H. Deng, T. Han, C. Sun, Y. Li, U-shaped relationships between sleep duration and metabolic syndrome and metabolic syndrome components in males: a prospective cohort study. Sleep Med. 16(8), 949–954 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2015.03.024
L. Pulido-Arjona, J.E. Correa-Bautista, C. Agostinis-Sobrinho, J. Mota, R. Santos, M. Correa-Rodriguez, A. Garcia-Hermoso, R. Ramirez-Velez, Role of sleep duration and sleep-related problems in the metabolic syndrome among children and adolescents. Ital. J. Pediatr. 44(1), 9 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13052-018-0451-7
M.H. Hall, M.F. Muldoon, J.R. Jennings, D.J. Buysse, J.D. Flory, S.B. Manuck, Self-reported sleep duration is associated with the metabolic syndrome in midlife adults. Sleep 31(5), 635–643 (2008)
T. Ohkuma, H. Fujii, M. Iwase, S. Ogata-Kaizu, H. Ide, Y. Kikuchi, Y. Idewaki, T. Jodai, Y. Hirakawa, U. Nakamura, T. Kitazono, U-shaped association of sleep duration with metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes: the Fukuoka Diabetes Registry. Metabolism 63(4), 484–491 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2013.12.001
K.M. Choi, J.S. Lee, H.S. Park, S.H. Baik, D.S. Choi, S.M. Kim, Relationship between sleep duration and the metabolic syndrome: Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey 2001. Int. J. Obes. 32(7), 1091–1097 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2008.62
C.E. Kim, S. Shin, H.W. Lee, J. Lim, J.K. Lee, A. Shin, D. Kang, Association between sleep duration and metabolic syndrome: a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 18(1), 720 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-018-5557-8
K.M. Stefani, H.C. Kim, J. Kim, K. Oh, I. Suh, The influence of sex and age on the relationship between sleep duration and metabolic syndrome in Korean adults. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 102(3), 250–259 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2013.10.003
D. Saleh, I. Janssen, Interrelationships among sedentary time, sleep duration, and the metabolic syndrome in adults. BMC Public Health 14, 666 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-14-666
S.D. Youngstedt, E.E. Goff, A.M. Reynolds, D.F. Kripke, M.R. Irwin, R.R. Bootzin, N. Khan, G. Jean-Louis, Has adult sleep duration declined over the last 50+ years? Sleep Med. Rev. 28, 69–85 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2015.08.004
O.E. Titova, E. Lindberg, S. Elmstahl, L. Lind, H.B. Schioth, C. Benedict, Associations between the prevalence of metabolic syndrome and sleep parameters vary by age. Front. Endocrinol. 9, 234 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00234
A. Martocchia, M. Stefanelli, G.M. Falaschi, L. Toussan, C. Ferri, P. Falaschi, Recent advances in the role of cortisol and metabolic syndrome in age-related degenerative diseases. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 28(1), 17–23 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-015-0353-0
M. Kumari, E. Badrick, T. Chandola, N.E. Adler, E. Epel, T. Seeman, C. Kirschbaum, M.G. Marmot, Measures of social position and cortisol secretion in an aging population: findings from the Whitehall II study. Psychosom. Med. 72(1), 27–34 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1097/PSY.0b013e3181c85712
X. Chen, R. Wang, P. Zee, P.L. Lutsey, S. Javaheri, C. Alcantara, C.L. Jackson, M.A. Williams, S. Redline, Racial/ethnic differences in sleep disturbances: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). Sleep 38(6), 877–888 (2015). https://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.4732
X. Hou, J. Lu, J. Weng, L. Ji, Z. Shan, J. Liu, H. Tian, Q. Ji, D. Zhu, J. Ge, L. Lin, L. Chen, X. Guo, Z. Zhao, Q. Li, Z. Zhou, G. Shan, Z. Yang, W. Yang, W. Jia, Impact of waist circumference and body mass index on risk of cardiometabolic disorder and cardiovascular disease in Chinese adults: a national diabetes and metabolic disorders survey. PLoS ONE 8(3), e57319 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0057319
W. Li, F. Song, X. Wang, L. Wang, D. Wang, X. Yin, S. Cao, Y. Gong, W. Yue, F. Yan, H. Zhang, Z. Sheng, Z. Wang, Z. Lu, Prevalence of metabolic syndrome among middle-aged and elderly adults in China: current status and temporal trends. Ann. Med. 50(4), 345–353 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/07853890.2018.1464202
J. Lu, L. Wang, M. Li, Y. Xu, Y. Jiang, W. Wang, J. Li, S. Mi, M. Zhang, Y. Li, T. Wang, M. Xu, Z. Zhao, M. Dai, S. Lai, W. Zhao, L. Wang, Y. Bi, G. Ning, Metabolic syndrome among adults in China: the 2010 China noncommunicable disease surveillance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 102(2), 507–515 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2016-2477
C.W. Pan, X.L. Cong, H.J. Zhou, X.Z. Wang, H.P. Sun, Y. Xu, P. Wang, Evaluating health-related quality of life impact of chronic conditions among older adults from a rural town in Suzhou, China. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 76, 6–11 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archger.2018.01.008
Y.J. Gu, C.H. He, S. Li, S.Y. Zhang, S.Y. Duan, H.P. Sun, Y.P. Shen, Y. Xu, J.Y. Yin, C.W. Pan, Tea consumption is associated with cognitive impairment in older Chinese adults. Aging Ment. Health 22(9), 1232–1238 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/13607863.2017.1339779
C.W. Pan, X. Wang, Q. Ma, H.P. Sun, Y. Xu, P. Wang, Cognitive dysfunction and health-related quality of life among older Chinese. Sci. Rep. 5, 17301 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep17301
C. Sabanayagam, J.J. Wang, P. Mitchell, A.G. Tan, E.S. Tai, T. Aung, S.M. Saw, T.Y. Wong, Metabolic syndrome components and age-related cataract: the Singapore Malay eye study. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 52(5), 2397–2404 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.10-6373
B. Xi, D. He, M. Zhang, J. Xue, D. Zhou, Short sleep duration predicts risk of metabolic syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep. Med. Rev. 18(4), 293–297 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2013.06.001
J.Y. Kim, D. Yadav, S.V. Ahn, S.B. Koh, J.T. Park, J. Yoon, B.S. Yoo, S.H. Lee, A prospective study of total sleep duration and incident metabolic syndrome: the ARIRANG study. Sleep Med. 16(12), 1511–1515 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2015.06.024
J.P. Chaput, J. McNeil, J.P. Despres, C. Bouchard, A. Tremblay, Seven to eight hours of sleep a night is associated with a lower prevalence of the metabolic syndrome and reduced overall cardiometabolic risk in adults. PLoS ONE 8(9), e72832 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0072832
L.X. Yan, X.R. Chen, B. Chen, Y.M. Bai, J.H. Li, X.W. Zhang, Z. Dong, H. Wang, S.Q. Mi, W.H. Zhao, Gender-specific association of sleep duration with body mass index, waist circumference, and body fat in Chinese adults. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 30(3), 157–169 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3967/bes2017.023
H.B. Deng, T. Tam, B.C. Zee, R.Y. Chung, X. Su, L. Jin, T.C. Chan, L.Y. Chang, E.K. Yeoh, X.Q. Lao. Short sleep duration increases metabolic impact in healthy adults: a Population-Based Cohort Study. Sleep 40(10) (2017). https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/zsx130
J. Xiao, C. Wu, G. Xu, J. Huang, Y. Gao, Q. Lu, T. Hua, H. Cai, Association of physical activity with risk of metabolic syndrome: findings from a cross-sectional study conducted in rural area, Nantong, China. J. Sports Sci. 34(19), 1839–1848 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/02640414.2016.1140221
K.V. Hjerkind, J.S. Stenehjem, T.I. Nilsen, Adiposity, physical activity and risk of diabetes mellitus: prospective data from the population-based HUNT study, Norway. BMJ Open 7(1), e013142 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-013142
M.L. Andersen, T.F. Alvarenga, R. Mazaro-Costa, H.C. Hachul, S. Tufik, The association of testosterone, sleep, and sexual function in men and women. Brain Res. 1416, 80–104 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2011.07.060
J.R. Carter, J.J. Durocher, R.A. Larson, J.P. DellaValla, H. Yang, Sympathetic neural responses to 24-hour sleep deprivation in humans: sex differences. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 302(10), H1991–H1997 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.01132.2011
A.E. Reschke-Hernandez, K.L. Okerstrom, A. Bowles Edwards, D. Tranel, Sex and stress: men and women show different cortisol responses to psychological stress induced by the Trier social stress test and the Iowa singing social stress test. J. Neurosci. Res. 95(1–2), 106–114 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.23851
C.W. Pan, Q. Ma, H.P. Sun, Y. Xu, N. Luo, P. Wang, Tea Consumption and Health-Related Quality of Life in Older Adults. J. Nutr. Health Aging 21(5), 480–486 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-016-0784-0
M. Liu, J. Wang, B. Jiang, D. Sun, L. Wu, S. Yang, Y. Wang, X. Li, Y. He, Increasing prevalence of metabolic syndrome in a Chinese elderly population: 2001–2010. PLoS ONE 8(6), e66233 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0066233
S.M. Johari, S. Shahar, Metabolic syndrome: the association of obesity and unhealthy lifestyle among Malaysian elderly people. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 59(2), 360–366 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archger.2014.04.003
N. Okubo, M. Matsuzaka, I. Takahashi, K. Sawada, S. Sato, N. Akimoto, T. Umeda, S. Nakaji, Relationship between self-reported sleep quality and metabolic syndrome in general population. BMC Public Health 14, 562 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-14-562
E.N. Georgousopoulou, N.M. D’Cunha, D.D. Mellor, S. Tyrovolas, N. Naumovski, A. Foscolou, V. Bountziouka, E. Gotsis, G. Metallinos, D. Tyrovola, S. Piscopo, G. Valacchi, N. Tsakountakis, A. Zeimbekis, J.-A. Tur, A.-L. Matalas, E. Polychronopoulos, C. Lionis, L. Sidossis, D.B. Panagiotakos, M.S. Group, The Association Between sleeping time and metabolic syndrome features, among older adults living in Mediterranean region: the MEDIS Study. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 16(1), 20–28 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1089/met.2017.0113
Y. Cao, R.H. Wang, Associations among metabolism, circadian rhythm and age-associated diseases. Aging Dis. 8(3), 314–333 (2017). https://doi.org/10.14336/ad.2016.1101
A.J. Pyykkonen, B. Isomaa, A.K. Pesonen, J.G. Eriksson, L. Groop, T. Tuomi, K. Raikkonen, Sleep duration and insulin resistance in individuals without type 2 diabetes: the PPP-Botnia study. Ann. Med. 46(5), 324–329 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3109/07853890.2014.902226
V.H. Goh, T.Y. Tong, Sleep, sex steroid hormones, sexual activities, and aging in Asian men. J. Androl. 31(2), 131–137 (2010). https://doi.org/10.2164/jandrol.109.007856
D. Morgan, S.C. Tsai, Sleep and the endocrine system. Crit. Care Clin. 31(3), 403–418 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccc.2015.03.004
S.W. Lockley, D.J. Skene, J. Arendt, Comparison between subjective and actigraphic measurement of sleep and sleep rhythms. J. Sleep Res. 8(3), 175–183 (1999)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Science and Technology Bureau of Xiangcheng District in Suzhou, China under grant no. XJ201706 and the Health Commission of Suzhou under grant no. GSWS2019090.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was conducted abide by the tenets of the Helsinki Declaration, and with the approval of the Institutional Review Board of Soochow University.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
These author contributed equally: Yu-Xi Qian, Jing-Hong Liu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, YX., Liu, JH., Ma, QH. et al. Associations of sleep durations and sleep-related parameters with metabolic syndrome among older Chinese adults. Endocrine 66, 240–248 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-019-02064-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-019-02064-y