Abstract
Purpose
Emerging data demonstrate that type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is associated with right ventricular (RV) dysfunction. A cutoff point of 155 mg/dL for the 1-hour (h) post-load plasma glucose, during oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), identifies patients with normal glucose tolerance (NGT) at high risk to develop T2DM and cardiovascular (CV) disease. We investigated if 1-h post-load glucose may affect RV geometry and function in a group of never-treated hypertensive individuals.
Methods
We enrolled 446 Caucasian newly diagnosed hypertensive outpatients. All patients underwent an OGTT and a standard echocardiography. The tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE) and the RV fractional area change (RVFAC) were measured together with systolic pulmonary arterial pressure (s-PAP) and pulmonary vascular resistances (PVR). Insulin sensitivity was evaluated using the Matsuda index.
Results
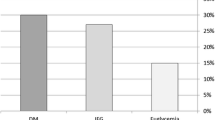
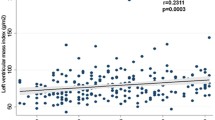
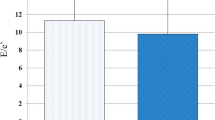
Among all partecipants, 296 had NGT, 100 impaired glucose tolerance (IGT), and 50 T2DM. Considering the cutoff point of 155 mg/dl for 1-h glucose, NGT subjects were stratified into two groups: NGT < 155 (n = 207), NGT ≥ 155 (n = 89). Subjects NGT ≥ 155 presented a worse metabolic and inflammatory profile than NGT < 155. RV functional parameters (TAPSE, RVFAC, TAPSE/s-PAP, and TAPSE/PVR) were significantly reduced in NGT ≥ 155 subjects compared with NGT < 155 patients. On the contrary, s-PAP and PVR were significantly higher. At multiple regression analysis, 1-h glucose was the strongest predictor of TAPSE in NGT ≥ 155, IGT, and T2DM.
Conclusions
The presence of RV impairment in hypertensive NGT ≥ 155 subjects further complicates their CV burden and it may, at least in part, justify the worse clinical outcome in this setting of patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Gaede, P. Vedel, N. Larsen, G.V. Jensen, H.H. Parving, O. Pedersen, Multifactorial intervention and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 348(5), 383–393 (2003)
S. Boudina, E.D. Abel, Diabetic cardiomyopathy revisited. Circulation 115(25), 3213–3223 (2007)
L. Zhou, W. Deng, L. Zhou, P. Fang, D. He, W. Zhang et al. Prevalence, incidence and risk factors of chronic heart failure in the type 2 diabetic population: systematic review. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 5(3), 71–84 (2009)
A. Dei Cas, S.S. Khan, J. Butler, R.J. Mentz, R.O. Bonow, A. Avogaro et al. Impact of Diabetes on Epidemiology, Treatment, and Outcomes of Patients With Heart Failure. JACC Heart Fail. 3(2), 136–145 (2015)
M.L. Ward, D.J. Crossman, Mechanisms underlying the impaired contractility of diabetic cardiomyopathy. World J. Cardiol. 6(7), 577–584 (2014)
R. Muniyappa, M. Montagnani, K.K. Koh, M.J. Quon, Cardiovascular actions of insulin. Endocr. Rev. 28(5), 463–491 (2007)
G. Frati, L. Schirone, I. Chimenti, D. Yee, G. Biondi-Zoccai, M. Volpe, An overview of the inflammatory signalling mechanisms in the myocardium underlying the development of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc. Res. 113(4), 378–388 (2017)
S.R. Mittal, Right ventricular functions in patients with type 2 diabetes below 50 years. J. Assoc. Physicians India 55, 599–600 (2007)
W. Kosmala, P. Colonna, M. Przewlocka-Kosmala, W. Mazurek, Right ventricular dysfunction in asymptomatic diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 27(11), 2736–2738 (2004)
W. Kosmala, M. Przewlocka-Kosmala, W. Mazurek, Subclinical right ventricular dysfunction in diabetes mellitus--an ultrasonic strain/strain rate study. Diabet. Med. 24(6), 656–663 (2007)
M.R. Movahed, N. Milne, Presence of biventricular dysfunction in patients with type II diabetes mellitus. Congest. Heart Fail. 13(2), 78–80 (2007)
R.L. Widya, R.W. van der Meer, J.W. Smit, L.J. Rijzewijk, M. Diamant, J.J. Bax, A. de Roos et al. Right ventricular involvement in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetes Care 36(2), 457–462 (2013)
M.M. Tumuklu, U. Erkorkmaz, A. Ocal, The impact of hypertension and hypertension-related left ventricle hypertrophy on right ventricle function. Echocardiography 24(4), 374–384 (2007)
S. Ghio, A. Gavazzi, C. Campana, C. Inserra, C. Klersy, R. Sebastiani, Independent and additive prognostic value of right ventricular systolic function and pulmonary artery pressure in patients with chronic heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 37(1), 183–188 (2001)
E.F. Aziz, M. Kukin, F. Javed, D. Musat, A. Nader, B. Pratap et al. Right ventricular dysfunction is a strong predictor of developing atrial fibrillation in acutely decompensated heart failure patients, ACAP-HF data analysis. J. Card. Fail. 16(10), 827–834 (2010)
J. West, K.D. Niswender, J.A. Johnson, M.E. Pugh, L. Gleaves, J.P. Fessel et al. A potential role for insulin resistance in experimental pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 41(4), 861–871 (2013)
G. Hansmann, R.A. Wagner, S. Schellong, V.A. Perez, T. Urashima, L. Wang et al. Pulmonary arterial hypertension is linked to insulin resistance and reversed by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ activation. Circulation 115(10), 1275–1284 (2007)
L. Benson, E.L. Brittain, M.E. Pugh, E.D. Austin, K. Fox, L. Wheeler et al. Impact of diabetes on survival and right ventricular compensation in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pulm. Circ. 4(2), 311–318 (2014)
M.K. Rutter, H. Parise, E.J. Benjamin, D. Levy, M.G. Larson, J.B. Meigs et al. Impact of glucose intolerance and insulin resistance on cardiac structure and function: sex-related differences in the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 107(3), 448–454 (2003)
R.M. Henry, O. Kamp, P.J. Kostense, A.M. Spijkerman, J.M. Dekker, R. van Eijck et al. Left ventricular mass increases with deteriorating glucose tolerance, especially in women: independence of increased arterial stiffness or decreased flow-mediated dilation: the Hoorn study. Diabetes Care 27(2), 522–529 (2004)
A. Ilercil, R.B. Devereux, M.J. Roman, M. Paranicas, M.J. O’grady, T.K. Welty et al. Relationship of impaired glucose tolerance to left ventricular structure and function: the Strong Heart Study. Am. Heart J. 141(6), 992–998 (2001)
M.A. Abdul-Ghani, T. Abdul-Ghani, N. Ali, R.A. Defronzo, One-hour plasma glucose concentration and the metabolic syndrome identify subjects at high risk for future type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 31(8), 1650–1655 (2008)
T.V. Fiorentino, M.A. Marini, F. Andreozzi, F. Arturi, E. Succurro, M. Perticone et al. One-Hour Post load Hyperglycemia Is a Stronger Predictor of Type 2 Diabetes Than Impaired Fasting Glucose. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 100(10), 3744–3751 (2015)
G. Sesti, T.V. Fiorentino, E. Succurro, M. Perticone, F. Arturi, A. Sciacqua et al. Elevated 1-h post-load plasma glucose levels in subjects with normal glucose tolerance are associated with unfavorable inflammatory profile. Acta Diabetol. 51(6), 927–932 (2014)
A. Sciacqua, R. Maio, S. Miceli, A. Pascale, G. Carullo, N. Grillo et al. Association between one-hour post-load plasma glucose levels and vascular stiffness in essential hypertension. PLoS ONE 7(9), e44470 (2012)
E. Succurro, M.A. Marini, F. Arturi, A. Grembiale, M. Lugarà, F. Andreozzi et al. Elevated one-hour post-load plasma glucose levels identifies subjects with normal glucose tolerance but early carotid atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 207(1), 245–249 (2009)
E. Succurro, F. Arturi, M. Lugarà, A. Grembiale, T.V. Fiorentino, V. Caruso et al. One-hour postload plasma glucose levels are associated with kidney dysfunction. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 5(11), 1922–1927 (2010)
A. Sciacqua, S. Miceli, G. Carullo, L. Greco, E. Succurro, F. Arturi et al. One-Hour Postload Plasma Glucose Levels and Left Ventricular Mass in Hypertensive Patients. Diabetes Care 34(6), 1406–1411 (2011)
A. Sciacqua, S. Miceli, L. Greco, F. Arturi, P. Naccarato, D. Mazzaferro et al. One-hour postload plasma glucose levels and diastolic function in hypertensive patients. Diabetes Care 34(10), 2291–2296 (2011)
ESH/ESC guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension, The Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Heart J. 34(28), 2159–2219 (2013)
American Diabetes Association: Standards of medical care in diabetes–2017. Diabetes Care 40(Suppl. 1), S1–S135 (2017)
M. Matsuda, R.A. DeFronzo, Insulin sensitivity indices obtained from oral glucose tolerance testing: comparison with the euglycemic insulin clamp. Diabetes Care 22(9), 1462–1470 (1999)
A.S. Levey, L.A. Stevens, C.H. Schmid, Y.L. Zhang, A.F. Castro 3rd, H.I. Feldman et al. CKD-EPI (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration). A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 150(9), 604–612 (2009)
R.M. Lang, L.P. Badano, V. Mor-Avi, J. Afilalo, A. Armstrong, L. Ernande et al. Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: an update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 28(1), 1–39.e14 (2015)
S.F. Nagueh, C.P. Appleton, T.C. Gillebert, P.N. Marino, J.K. Oh, O.A. Smiseth et al. Recommendations for the evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function by echocardiography. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 22(2), 107–133 (2009)
L.G. Rudski, W.W. Lai, J. Afilalo, L. Hua, M.D. Handschumacher, K. Chandrasekaran et al. Guidelines for the echocardiographic assessment of the right heart in adults: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography endorsed by the European Association of Echocardiography, a registered branch of the European Society of Cardiology, and the Canadian Society of Echocardiography. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 23(7), 685–713 (2010)
A.E. Abbas, F.D. Fortuin, N.B. Schiller, C.P. Appleton, C.A. Moreno, S.J. Lester, A simple method for non invasive estimation of pulmonary vascular resistance. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 41(6), 1021–1027 (2003)
M. Guazzi, F. Bandera, G. Pelissero, S. Castelvecchio, L. Menicanti, S. Ghio et al. Tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion and pulmonary arterial systolic pressure relationship in heart failure: an index of right ventricular contractile function and prognosis. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 305(9), H1373–H1381 (2013)
A. Lopez López-Candales, F.R. Lopez, S. Trivedi, J. Elwing, Right ventricular ejection efficiency: a new echocardiographic measure of mechanical performance in chronic pulmonary hypertension. Echocardiography 31(4), 516–523 (2014)
T.V. Fiorentino, F. Sesti, F. Andreozzi, E. Pedace, A. Sciacqua, M.L. Hribal et al. One-hour post-load hyperglycemia combined with HbA1c identifies pre-diabetic individuals with a higher cardio-metabolic risk burden. Atherosclerosis 253, 61–69 (2016)
T.V. Fiorentino, E. Succurro, F. Andreozzi, A. Sciacqua, F. Perticone, G. Sesti, One-hour post-load hyperglycemia combined with HbA1c identifies individuals with higher risk of cardiovascular diseases: Cross-sectional data from the CATAMERI study. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 30, e3096 (2018)
M. Tadic, B. Ivanovic, I. Grozdic, Metabolic syndrome impacts the right ventricle: true or false? Echocardiography 28(5), 530–538 (2011)
M. Tadic, B. Ivanovic, C. Cuspidi, Metabolic syndrome and right ventricle: an updated review. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 24(7), 608–616 (2013)
V. Chavali, S.C. Tyagi, P.K. Mishra, Predictors and prevention of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 6, 151–160 (2013)
G. Sesti, A. Sciacqua, A. Scozzafava, M. Vatrano, E. Angotti, C. Ruberto et al. Effects of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-1 on cardiac hypertrophy of hypertensive patients. J. Hypertens. 25(2), 471–477 (2007)
O.L. Klein, J.A. Krishnan, S. Glick, L.J. Smith, Systematic review of the association between lung function and Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet. Med. 27(9), 977–987 (2010)
K. Sakata, H. Yoshino, H. Kurihara, K. Iwamori, H. Houshaku, A. Yanagisawa et al. Prognostic significance of persistent right ventricular dysfunction as assessed by radionuclide angiocardiography in patients with inferior wall acute myocardial infarction. Am. J. Cardiol. 85(8), 939–944 (2000)
M. Bergman, A. Chetrit, J. Roth, R. Dankner, One-hour post-load plasma glucose level during the OGTT predicts mortality: observations from the Israel Study of Glucose Intolerance, Obesity and Hypertension. Diabet. Med. 33(8), 1060–1066 (2016)
M. Bergman, M. Manco, G. Sesti, R. Dankner, M. Pareek, R. Jagannathan et al. Petition to replace current OGTT criteria for diagnosing prediabetes with the 1-hour post-load plasma glucose≥ 155 mg/dl (8.6 mmol/L). Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 146, 18–33 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures, that have been performed in humans, were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional ethic committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sciacqua, A., Perticone, M., Miceli, S. et al. Elevated 1-h post-load plasma glucose is associated with right ventricular morphofunctional parameters in hypertensive patients. Endocrine 64, 525–535 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-019-01873-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-019-01873-5