Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study is to summarize the effectiveness and safety of metreleptin in patients with congenital or acquired generalized lipodystrophy.
Methods
Patients (n = 66) aged ≥6 months had lipodystrophy, low circulating leptin, and ≥1 metabolic abnormality (diabetes mellitus, insulin resistance, or hypertriglyceridemia). Metreleptin dose (once or twice daily) was titrated to a mean dose of 0.10 mg/kg/day with a maximum of 0.24 mg/kg/day. Means and changes from baseline to month 12 were assessed for glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), fasting triglycerides (TGs), and fasting plasma glucose (FPG). Additional assessments included the proportions of patients achieving target decreases in HbA1c or fasting TGs at months 4, 12, and 36, medication changes, and estimates of liver size. Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were recorded.
Results
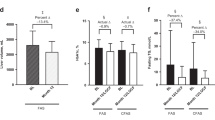
Significant mean reductions from baseline were seen at month 12 for HbA1c (–2.2%, n = 59) and FPG (–3.0 mmol/L, n = 59) and mean percent change in fasting TGs (–32.1%, n = 57) (all p ≤ 0.001). Reductions from baseline over time in these parameters were also significant at month 36 (all p < 0.001, n = 14). At month 4, 34.8% of patients had a ≥1% reduction in HbA1c and 62.5% had a ≥30% reduction in fasting TGs; at month 12, 80% of patients had a ≥1% decrease in HbA1c or ≥30% decrease in TGs, and 66% had a decrease of ≥2% in HbA1c or ≥40% decrease in TGs. Of those on medications, 41%, 22%, and 24% discontinued insulin, oral antidiabetic medications, or lipid-lowering medications, respectively. Mean decrease in liver volume at month 12 was 33.8% (p < 0.001, n = 12). Most TEAEs were of mild/moderate severity.
Conclusions
In patients with generalized lipodystrophy, long-term treatment with metreleptin was well tolerated and resulted in sustained improvements in hypertriglyceridemia, glycemic control, and liver volume.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.J. Brown, D. Araujo-Vilar, P.T. Cheung, D. Dunger, A. Garg, M. Jack, L. Mungai, E.A. Oral, N. Patni, K.I. Rother, J. von Schnurbein, E. Sorkina, T. Stanley, C. Vigouroux, M. Wabitsch, R. Williams, T. Yorifuji, The diagnosis and management of lipodystrophy syndromes: a multi-society practice guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 101, 4500–4511 (2016)
W.A. Haque, I. Shimomura, Y. Matsuzawa, A. Garg, Serum adiponectin and leptin levels in patients with lipodystrophies. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 87, 2395 (2002)
Y. Zhang, R. Proenca, M. Maffei, M. Barone, L. Leopold, J.M. Friedman, Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 372, 425–432 (1994)
Y. Handelsman, E.A. Oral, Z.T. Bloomgarden, R.J. Brown, J.L. Chan, D. Einhorn, A.J. Garber, A. Garg, W.T. Garvey, G. Grunberger, R.R. Henry, N. Lavin, C.D. Tapiador, C. Weyer, The clinical approach to the detection of lipodystrophy—an AACE consensus statement. Endocr. Pract. 19, 107–116 (2013)
A. Bingham, G. Mamyrova, K.I. Rother, E. Oral, E. Cochran, A. Premkumar, D. Kleiner, L. James-Newton, I.N. Targoff, J.P. Pandey, D.M. Carrick, N. Sebring, T.P. O’Hanlon, M. Ruiz-Hidalgo, M. Turner, L.B. Gordon, J. Laborda, S.R. Bauer, P.J. Blackshear, L. Imundo, F.W. Miller, L.G. Rider, Predictors of acquired lipodystrophy in juvenile-onset dermatomyositis and a gradient of severity. Medicine 87, 70–86 (2008)
E.A. Oral, Lipoatrophic diabetes and other related syndromes. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 4, 61–77 (2003)
A. Garg, Acquired and inherited lipodystrophies. N. Engl. J. Med. 350, 1220–1234 (2004)
C.A. Meehan, E. Cochran, A. Kassai, R.J. Brown, P. Gorden, Metreleptin for injection to treat the complications of leptin deficiency in patients with congenital or acquired generalized lipodystrophy. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 9, 59–68 (2016)
N. Patni, A. Garg, Congenital generalized lipodystrophies—new insights into metabolic dysfunction. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 11, 522–534 (2015)
M. Miller, N.J. Stone, C. Ballantyne, V. Bittner, M.H. Criqui, H.N. Ginsberg, A.C. Goldberg, W.J. Howard, M.S. Jacobson, P.M. Kris-Etherton, T.A. Lennie, M. Levi, T. Mazzone, S. Pennathur, Triglycerides and cardiovascular disease: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 123, 2292–2333 (2011)
K. Chou, C.M. Perry, Metreleptin: first global approval. Drugs 73, 989–997 (2013)
Myalept [Package Insert] (Aegerion Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Cambridge, MA, 2015)
J.L. Chan, K. Lutz, E. Cochran, W. Huang, Y. Peters, C. Weyer, P. Gorden, Clinical effects of long-term metreleptin treatment in patients with lipodystrophy. Endocr. Pract. 17, 922–932 (2011)
A.Y. Chong, B.C. Lupsa, E.K. Cochran, P. Gorden, Efficacy of leptin therapy in the different forms of human lipodystrophy. Diabetologia 53, 27–35 (2010)
J.D. Christensen, A.O. Lungu, E. Cochran, M.T. Collins, R.I. Gafni, J.C. Reynolds, K.I. Rother, P. Gorden, R.J. Brown, Bone mineral content in patients with congenital generalized lipodystrophy is unaffected by metreleptin replacement therapy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 99, E1493–E1500 (2014)
T. Diker-Cohen, E. Cochran, P. Gorden, R.J. Brown, Partial and generalized lipodystrophy: comparison of baseline characteristics and response to metreleptin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 100, 1802–1810 (2015)
J. Joseph, R.D. Shamburek, E.K. Cochran, P. Gorden, R.J. Brown, Lipid regulation in lipodystrophy versus the obesity-associated metabolic syndrome: the dissociation of HDL-C and triglycerides. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 99, E1676–E1680 (2014)
F. Kamran, K.I. Rother, E. Cochran, E. Safar Zadeh, P. Gorden, R.J. Brown, Consequences of stopping and restarting leptin in an adolescent with lipodystrophy. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 78, 320–325 (2012)
R. Muniyappa, B.S. Abel, A. Asthana, M.F. Walter, E.K. Cochran, A.T. Remaley, M.C. Skarulis, P. Gorden, R.J. Brown, Metreleptin therapy lowers plasma angiopoietin-like protein 3 in patients with generalized lipodystrophy. J. Clin. Lipidol. 11, 543–550 (2017)
E.A. Oral, V. Simha, E. Ruiz, A. Andewelt, A. Premkumar, P. Snell, A.J. Wagner, A.M. DePaoli, M.L. Reitman, S.I. Taylor, P. Gorden, A. Garg, Leptin-replacement therapy for lipodystrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 346, 570–578 (2002)
K. Ebihara, T. Kusakabe, M. Hirata, H. Masuzaki, F. Miyanaga, N. Kobayashi, T. Tanaka, H. Chusho, T. Miyazawa, T. Hayashi, K. Hosoda, Y. Ogawa, A.M. DePaoli, M. Fukushima, K. Nakao, Efficacy and safety of leptin-replacement therapy and possible mechanisms of leptin actions in patients with generalized lipodystrophy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 92, 532–541 (2007)
C. Vatier, S. Fetita, P. Boudou, C. Tchankou, L. Deville, J. Riveline, J. Young, L. Mathivon, F. Travert, D. Morin, J. Cahen, O. Lascols, F. Andreelli, Y. Reznik, E. Mongeois, I. Madelaine, M. Vantyghem, J. Gautier, C. Vigouroux, One-year metreleptin improves insulin secretion in patients with diabetes linked to genetic lipodystrophic syndromes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 18, 693–697 (2016)
D. Araujo-Vilar, S. Sanchez-Iglesias, C. Guillin-Amarelle, A. Castro, M. Lage, M. Pazos, J.M. Rial, J. Blasco, E. Guillen-Navarro, R. Domingo-Jimenez, M.R. del Campo, B. Gonzalez-Mendez, F.F. Casanueva, Recombinant human leptin treatment in genetic lipodystrophic syndromes: the long-term Spanish experience. Endocrine 49, 139–147 (2015)
C. Musso, M.L. Major, E. Andres, V. Simha, Metreleptin treatment in three patients with generalized lipodystrophy. Clin. Med. Insights Case Rep. 9, 123–127 (2016)
J. Beltrand, M. Beregszaszi, D. Chevenne, G. Sebag, M. De Kerdanet, F. Huet, M. Polak, N. Tubiana-Rufi, D. Lacombe, A.M. De Paoli, C. Levy-Marchal, Metabolic correction induced by leptin replacement treatment in young children with Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipoatrophy. Pediatrics 120, e291–e296 (2007)
R.J. Brown, J.L. Chan, E.S. Jaffe, E. Cochran, A.M. DePaoli, J.F. Gautier, C. Goujard, C. Vigouroux, P. Gorden, Lymphoma in acquired generalized lipodystrophy. Leuk. Lymphoma 57, 45–50 (2016)
A.V. Hernandez, V. Pasupuleti, V.A. Benites-Zapata, P. Thota, A. Deshpande, F.R. Perez-Lopez, Insulin resistance and endometrial cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 51, 2747–2758 (2015)
B. Arcidiacono, S. Iiritano, A. Nocera, K. Possidente, M.T. Nevolo, V. Ventura, D. Foti, E. Chiefari, A. Brunetti, Insulin resistance and cancer risk: an overview of the pathogenetic mechanisms. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2012, 789174 (2012)
X. Wang, M.F. Haring, T. Rathjen, S.M. Lockhart, D. Sorensen, S. Ussar, L.M. Rasmussen, M.M. Bertagnolli, C.R. Kahn, C. Rask-Madsen, Insulin resistance in vascular endothelial cells promotes intestinal tumour formation. Oncogene 36, 4987–4996 (2017)
Acknowledgements
All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this manuscript and take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole. Aegerion Pharmaceuticals provided funding for medical writing and/or editing support in the development of this manuscript; Jennifer L. Giel, Ph.D., of inScience Communications, Springer Healthcare (Philadelphia, PA, USA), based on input from authors, wrote the first draft and revised subsequent drafts of the manuscript, and Adrienne M. Schreiber of inScience Communications, Springer Healthcare (Philadelphia, PA, USA) copyedited and styled the manuscript per journal requirements. Aegerion Pharmaceuticals reviewed and provided feedback to the authors. The authors had full editorial control of the manuscript and provided their final approval of all content. Jean-Karl Sirois provided statistical analyses on behalf of Veristat LLC, Montreal, Canada, which was funded by Aegerion Pharmaceuticals, Inc. The authors acknowledge the services of the Clinical Core Laboratory of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health for measurement of leptin levels.
Funding
This work was supported by the intramural research program of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. E.A.O. is supported by NIH grant RO-1 DK-088114 as well as UM Lipodystrophy Fund donated by the Sopha Family and White Point Foundation of Turkey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
E.A.O. has served as a consultant to Aegerion, Akcea, AstraZeneca, and Regeneron, received grants from Aegerion, Akcea, AstraZeneca, Gemphire, GIDynamics, and received non-material support from Aegerion and Boehringer Ingelheim. D.A.V. and D.B.S. have served as consultants to Aegerion Pharmaceuticals. A.L. and G.F. are employees of Aegerion Pharmaceuticals. T.S. is a former employee of Aegerion Pharmaceuticals. R.J.B., E.C., and P.G. declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brown, R.J., Oral, E.A., Cochran, E. et al. Long-term effectiveness and safety of metreleptin in the treatment of patients with generalized lipodystrophy. Endocrine 60, 479–489 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-018-1589-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-018-1589-1