Abstract
Purpose
During follow-up of acromegaly patients, there is a discordance rate of 30% between the measurements of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-1 levels. Further tests are required to determine disease activity in patients with discordant results. This study was planned to investigate an association of serum levels of matrix metalloproteinase-2, matrix metalloproteinase-9, and cathepsin B with disease activity in acromegaly patients.
Methods
In this study, 64 acromegaly patients followed in our clinic were divided into two groups according to the 2010 consensus criteria for cure of acromegaly as patients with active disease (n = 24) and patients with controlled disease (n = 40). Serum matrix metalloproteinase-2, matrix metalloproteinase-9, and cathepsin B levels were measured by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay method.
Results
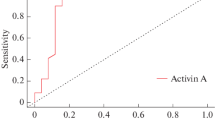
The mean serum matrix metalloproteinase-2 level was significantly higher in the active acromegaly patients than in the controlled acromegaly patients (150.1 ± 54.5 ng/mL vs. 100.2 ± 44.6 ng/mL; p < 0.0001). There was no significant difference between the active and controlled acromegaly patients regarding serum matrix metalloproteinase-9 and cathepsin B levels (p = 0.205 and p = 0.598, respectively). Serum matrix metalloproteinase-2 levels of 118.3 ng/mL and higher had a sensitivity of 75% and a specificity of 77.5% in determining active disease. The risk of active acromegaly was 3.3 fold higher in the patients with a matrix metalloproteinase-2 level of >118.3 ng/mL than in the patients with a matrix metalloproteinase-2 level of <118.3 ng/mL.
Conclusions
In this study, serum matrix metalloproteinase-2 level is increased in the active acromegaly patients and a threshold value in determining active disease was defined for serum matrix metalloproteinase-2 level. This study is the first to compare acromegaly patients having active or controlled disease in terms of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 levels. The results need to be confirmed by a study that will be conducted in a larger patient group also including a healthy control group to demonstrate the value of this novel marker in disease activity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Melmed, Medical progress: acromegaly. N. Eng. J. Med. 355, 2558–2573 (2006)
S. Melmed, A. Colao, A. Barkan, M. Molitch, A.B. Grossman, D. Klienberg, D. Clemmons, P. Chanson, E. Laws, J. Schlechte, M.L. Vance, K. Ho, A. Giustina; Acromegaly Consensus Group., guidelines for acromegaly management: an update. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 94, 1509–1517 (2009)
E.O. Machado, G.F. Taboada, L.V. Neto, F.R. van Haute, L.L. Corrêa, G.A. Balarini, Y. Shrank, M. Goulart, M.R. Gadelha, Prevalence of discordant GH and IGF-I levels in acromegalics at diagnosis, after surgical treatment and during treatment with octreotide LAR. Growth. Horm. IGF Res. 18, 389–393 (2008)
I.M. Holdaway, M.J. Bolland, G.D. Gamble, A meta-analysis of the effect of lowering serum levels of GH and IGF-I on mortality in acromegaly. Eur. J. Endocrinol 159, 89–95 (2008)
M.R. Farnoud, F. Farhadian, J.L. Samuel, P. Derome, F. Peillon, J.Y. Li, Fibronectin isoforms are differentially expressed in normal and adenomatous human anterior pituitaries. Int. J. Cancer 61, 27–34 (1995)
K. Thapar, K. Kovacs, B.W. Scheithauer, L. Stefaneanu, E. Horvath, P.J. Pernicone, D. Murray, E.R. Laws Jr., Proliferative activity and invasiveness among pituitary adenomas and carcinomas: an analysis using the MIB-1 antibody. Neurosurgery 38, 99–106 (1996)
A. Page-McCaw, A.J. Ewald, Z. Werb, Matrix metalloproteinases and the regulation of tissue remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8, 221–233 (2007)
A. Nagase, R. Visse, G. Murphy, Structure and function of matrix metalloproteinases and TIMPs. Cardiovasc. Res. 69, 562–573 (2006)
M.J. Duff, The role of proteolytic enzymes in cancer invasion and metastasis. Clin. Exp. Metastasis. 10, 145–155 (1992)
H. Kawamoto, T. Uozomi, K. Kawamoto, K. Arita, Y. Yano, T. Hirohata, Type IV collagenase activity and cavernous sinus invasion in human pituitary adenomas. Acta Neurochir. (Wien). 138, 390–395 (1996)
W. Liu, Y. Matsumoto, M. Okada, K. Miyake, K. Kunishio, N. Kawai, T. Tamiya, S. Nagao, Matrix metalloproteinase 2 and 9 expression correlated with cavernous sinus invasion of pituitary adenomas. J. Med. Invest. 52, 151–158 (2005)
E. Beaulieu, Z. Kachra, N. Mousseau, L. Delbecchi, J. Hardy, R. Béliveau, Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in human pituitary tumors. Neurosurgery 45, 1432–1440 (1999)
S. Yokoyama, H. Hirano, K. Moraki, M. Goto, S. Imamura, J.I. Kuratsu, Are nonfunctioning pituitary adenomas extending into the cavernous sinus aggressive and/or invasive? Neurosurgery 49, 857–862 (2001)
U.J. Knappe, C. Hagel, B.W. Lisboa, W. Wilczak, D.K. Lüdecke, W. Saeger, Expression of serine proteases and metalloproteinases in human pituitary adenomas and anterior pituitary lobe tissue. Acta Neuropathol. 106, 471–478 (2003)
M. Páez Pereda, M.F. Ledda, V. Goldberg, A. Chervín, G. Carrizo, H. Molina, A. Müller, U. Renner, O. Podhajcer, E. Arzt, G.K. Stalla, High levels of matrix metalloproteinases regulate proliferation and hormone secretion in pituitary cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 85, 263–269 (2000)
J. Daroszewski, M. Bolanowski, M. Kaluzny, M. Siewinski, The imbalance of cathepsin B-like activity in acromegalic patients-preliminary report. Neuro. Endocrinol. Lett. 31, 256–260 (2010)
A. Giustina, P. Chanson, M.D. Bronstein, A. Klibanski, S. Lamberts, F.F. Casanueva, P. Trainer, E. Ghigo, K. Ho, S. Melmed; Acromegaly Consensus Group., A consensus on criteria for cure of acromegaly. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 95, 3141–3148 (2010)
K. Yoshimura, T. Tsuchida, K. Kawamoto, Expression of cathepsin B and cystatin C in the human adenohypophysis and in pituitary adenomas. Oncol. Rep. 7, 27–31 (2000)
I. Berdowska, Cysteine proteases as disease markers. Clin. Chim. Acta 342, 41–69 (2004)
A.N. Paisley, C.J. O’Callaghan, K.C. Lewandowski, C. Parkinson, M.E. Roberts, W.M. Drake, J.P. Monson, P.J. Trainer, H.S. Randeva, Reductions of circulating matrix metalloproteinase 2 and vascular endothelial growth factor levels after treatment with pegvisomant in subjects with acromegaly. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 91, 4635–4640 (2006)
G.A. Kanakis, A. Chrisoulidou, A. Bargiota, L. Efstathiadou, A. Papanastasiou, A. Theodoropoulou, S.K. Tigas, D.A. Vassiliadi, S. Tsagarakis, M. Alevizaki, The ongoing challenge of discrepant growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor I results in the evaluation of treated acromegalic patients: a systematic review and meta analysis. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf). 85, 681–688 (2016)
E.T. Cerit, K. Ağbaht, Ö. Demir, M. Şahin, V.T. Gedik, C. Özcan, D. Çorapçıoğlu, Discordance between GH and IGF-1 levels in Turkish acromegalic patients. Endocr. Pract. 22, 1422–1428 (2016)
P.U. Freda, Monitoring of acromegaly: what should be performed when GH and IGF-1 levels are discrepant? Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf). 71, 166–170 (2009)
H.J. Kim, S.H. Kwon, S.W. Kim, D.J. Park, C.S. Shin, K.S. Park, S.Y. Kim, B.Y. Cho, H.K. Lee, Diagnostic value of serum IGF-I and IGFBP-3 in growth hormone disorders in adults. Horm. Res. 56, 117–123 (2001)
M. Arosio, S. Garrone, P. Bruzzi, G. Faglia, F. Minuto, A. Barreca, Diagnostic value of the acid-labile subunit in acromegaly: evaluation in comparison with insulin-like growth factor (IGF) I, and IGF-binding protein 1, -2, -3. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86, 1091–1098 (2001)
Acknowledgements
We thank Biochemistry Department for laboratory measurements of research assays. The research was funded by Research Fund of Kocaeli University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Ethics Committee of Medical Faculty of Kocaeli University and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karci, A.C., Canturk, Z., Tarkun, I. et al. Matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2) levels are increased in active acromegaly patients. Endocrine 57, 148–155 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-017-1283-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-017-1283-8