Abstract
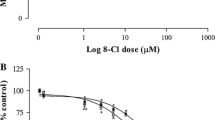
The main purpose of our work was to evaluate the effects of different cyclic adenosine monophosphate analogs on thyroid cancer-derived cell lines. In particular we studied 8-chloroadenosine-3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate, the most powerful cyclic adenosine monophosphate analog, and the protein kinase A I-selective combination of 8-hexylaminoadenosine-3′,5′cyclic monophosphate and 8-piperidinoadenosine-3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate. The cyclic adenosine monophosphate/protein kinase A pathway plays a fundamental role in the regulation of thyroid cells growth. Site-selective cyclic adenosine monophosphate analogs are a class of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-derivate molecules that has been synthesized to modulate protein kinase A activity. Although the cyclic adenosine monophosphate/protein kinase A pathway plays a fundamental role in the regulation of thyroid cells proliferation, there are currently no studies exploring the role of cyclic adenosine monophosphate analogs in thyroid cancer. We evaluated the effects on cell proliferation, apoptosis activation and alterations of different intracellular pathways using 3-(4,5-dimetylthiazole-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay, flow cytofluorimetry, western blotting, and kinase inhibitors. Our results show that both compounds have antiproliferative potential. Both treatments were able to modify protein kinase A RI/RII ratio, thus negatively influencing cancer cells growth. Moreover, the two treatments differentially modulated various signaling pathways that regulate cell proliferation and apoptosis. Both treatments demonstrated interesting characteristics that prompt further studies aiming to understand the intimate interaction between different intracellular pathways and possibly develop novel anticancer therapies for undifferentiated thyroid cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Pellegriti, F. Frasca, C. Regalbuto, S. Squatrito, R. Vigneri, Worldwide increasing incidence of thyroid cancer: update on epidemiology and risk factors. J. Cancer Epidemiol. (2013). doi: 10.1155/2013/965212
Y.E. Nikiforov, Thyroid carcinoma: molecular pathways and therapeutic targets. Mod. Pathol. 21(Suppl 2), S37–S43 (2008). doi:10.1038/modpathol.2008.10
J. Ferlay, E. Steliarova-Foucher, J. Lortet-Tieulent, S. Rosso, J.W. Coebergh, H. Comber, D. Forman, F. Bray, Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: estimates for 40 countries in 2012. Eur. J. Cancer 49, 1374–1403 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2012.12.027
N. Smith, C. Nucera, Personalized therapy in patients with anaplastic thyroid cancer: targeting genetic and epigenetic alterations. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 100, 35–42 (2015). doi:10.1210/jc.2014-2803
A.L. Boynton, J.F. Whitfield, The role of cAMP in cell proliferation: a critical assessment of the evidence. Adv. Cyclic Nucl. Res. 15, 201 (1983)
B.S. Skalhegg, K. Tasken, Specificity in the cAMP/PKA signaling pathway. Differential expression, regulation, and subcellular localization of subunits of PKA. Front. Biosci. 5, D678–D693 (2000)
P.J. Stork, J.M. Schmitt, Crosstalk between cAMP and MAP kinase signaling in the regulation of cell proliferation. Trends Cell Biol. 12, 258–266 (2002)
E. Vitali, E. Peverelli, E. Giardino, M. Locatelli, G.B. Lasio, P. Beck-Peccoz, A. Spada, A.G. Lania, G. Mantovani, Cyclic adenosine 3′-5′-monophosphate (cAMP) exerts proliferative and anti-proliferative effects in pituitary cells of different types by activating both cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA) and exchange proteins directly activated by cAMP (Epac). Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 383, 193–202 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.mce.2013.12.006
L.S. Weinstein, A. Shenker, P.V. Gejman, M.J. Merino, E. Friedman, A.M. Spiegel, Activating mutations of the stimulatory G protein in the McCune-Albright syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 325, 1688–1695 (1991)
L.S. Kirschner, J.A. Carney, S.D. Pack, S.E. Taymans, C. Giatzakis, Y.S. Cho, Y.S. Cho-Chung, C.A. Stratakis, Mutations of the gene encoding the protein kinase A type I-alpha regulatory subunit in patients with the Carney complex. Nat. Genet. 26, 89–92 (2000)
L. Persani, A. Lania, L. Alberti, R. Romoli, G. Mantovani, S. Filetti, A. Spada, M. Conti, Induction of specific phosphodiesterase isoforms by constitutive activation of the cAMP pathway in autonomous thyroid adenomas. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 85, 2872–2878 (2000)
A. Horvath, S. Boikos, C. Giatzakis, A. Robinson-White, L. Groussin, K.J. Griffin, E. Stein, E. Levine, G. Delimpasi, H.P. Hsiao, M. Keil, S. Heyerdahl, L. Matyakhina, R. Libè, A. Fratticci, L.S. Kirschner, K. Cramer, R.C. Gaillard, X. Bertagna, J.A. Carney, J. Bertherat, I. Bossis, C.A. Stratakis, A genome-wide scan identifies mutations in the gene encoding phosphodiesterase 11A4 (PDE11A) in individuals with adrenocortical hyperplasia. Nat. Genet. 38, 794–800 (2006)
A. Horvath, V. Mericq, C.A. Stratakis, Mutation in PDE8B, a cyclic AMP-specific phosphodiesterase in adrenal hyperplasia. N. Engl. J. Med. 358, 750–752 (2008). doi:10.1056/NEJMc0706182
A. Horvath, L. Korde, M.H. Greene, R. Libe, P. Osorio, F.R. Faucz, M.L. Raffin-Sanson, K.M. Tsang, L. Drori-Herishanu, Y. Patronas, E.F. Remmers, M.E. Nikita, J. Moran, J. Greene, M. Nesterova, M. Merino, J. Bertherat, C.A. Stratakis, Functional phosphodiesterase 11A mutations may modify the risk of familial and bilateral testicular germ cell tumors. Cancer Res. 69, 5301–5306 (2009)
Y.S. Cho-Chung, S. Pepe, T. Clair, A. Budillon, M. Nesterova, cAMP-dependent protein kinase: role in normal and malignant growth. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 21, 33–61 (1995)
C. Cheadle, M. Nesterova, T. Watkins, K.C. Barnes, J.C. Hall, A. Rosen, K.G. Becker, Y.S. Cho-Chung, Regulatory subunits of PKA define an axis of cellular proliferation/differentiation in ovarian cancer cells. BMC Med. Genomics 1, 43 (2008). doi:10.1186/1755-8794-1-43
G. Tortora, S. Pepe, C. Bianco, V. Damiano, A. Ruggiero, G. Baldassarre, C. Corbo, Y.S. Cho-Chung, A.R. Bianco, F. Ciardiello, Differential effects of protein kinase A sub-units on Chinese-hamster-ovary cell cycle and proliferation. Int. J. Cancer 59, 712–716 (1994)
G. Tortora, T. Clair, Y.S. Cho-Chung, An antisense oligodeoxynucleotide targeted against the type II beta regulatory subunit mRNA of protein kinase inhibits cAMP-induced differentiation in HL-60 leukemia cells without affecting phorbol ester effects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 87, 705–708 (1990)
C.L. Neary, M. Nesterova, Y.S. Cho, C. Cheadle, K.G. Becker, Y.S. Cho-Chung, Protein kinase A isozyme switching: eliciting differential cAMP signaling and tumor reversion. Oncogene 23, 8847–8856 (2004)
Y.S. Cho-Chung, Role of cyclic AMP receptor proteins in growth, differentiation, and suppression of malignancy: new approaches to therapy. Cancer Res. 50, 7093–7100 (1990)
S. Naviglio, M. Caraglia, A. Abbruzzese, E. Chiosi, D. Di Gesto, M. Marra, M. Romano, A. Sorrentino, L. Sorvillo, A. Spina, G. Illiano, Protein kinase A as a biological target in cancer therapy. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 13, 83–92 (2009). doi:10.1517/14728220802602349
S. Ferrero, V. Vaira, A. Del Gobbo, L. Vicentini, S. Bosari, P. Beck-Peccoz, G. Mantovani, A. Spada, A.G. Lania, Different expression of protein kinase A (PKA) regulatory subunits in normal and neoplastic thyroid tissues. Histol. Histopathol. 30, 473–478 (2015)
F. Sandrini, L. Matyakhina, N.J. Sarlis, L.S. Kirschner, C. Farmakidis, O. Gimm, C.A. Stratakis, Regulatory subunit type I-alpha of protein kinase A (PRKAR1A): a tumor-suppressor gene for sporadic thyroid cancer. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 35, 182–192 (2002)
D.J. Propper, M.P. Saunders, A.J. Salisbury, L. Long, K.J. O’Byrne, J.P. Braybrooke, M. Dowsett, M. Taylor, D.C. Talbot, T.S. Ganesan, A.L. Harris, Phase I study of the novel cyclic AMP (cAMP) analogue 8-chloro-cAMP in patients with cancer: toxicity, hormonal, and immunological effects. Clin. Cancer Res. 5, 1682–1689 (1999)
G. Tortora, F. Ciardiello, Protein kinase A as target for novel integrated strategies of cancer therapy. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 968, 139–147 (2002)
M. Unoki, Current and potential anticancer drugs targeting members of the UHRF1 complex including epigenetic modifiers. Recent Pat. Anticancer Drug Discov. 6, 116–130 (2011)
A. Traynor, Tocladesine in treating patients withPlease provide URL and accessed date in reference no. [27], if applicable. recurrent or refractory multiple myeloma. (2000).
L.S. Rosen, Tocladesine in treating patients with recurrent or progressive metastatic colorectal cancer (2001), https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/results/NCT00004902. Accessed 10 June 2016
E.M. Weissinger, K. Oettrich, C. Evans, H.G. Genieser, F. Schwede, M. Dangers, E. Dammann, H.J. Kolb, H. Mischak, A. Ganser, W. Kolch, Activation of protein kinase A (PKA) by 8-Cl-cAMP as a novel approach for antileukaemic therapy. Br. J. Cancer 91, 186–192 (2004)
S. Ally, G. Tortora, T. Clair, D. Grieco, G. Merlo, D. Katsaros, D. Ogreid, S.O. Døskeland, T. Jahnsen, Y.S. Cho-Chung, Selective modulation of protein kinase isozymes by the site-selective analog 8-chloroadenosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate provides a biological means for control of human colon cancer cell growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 85, 6319–6322 (1988)
C. Rohlff, T. Clair, Y.S. Cho-Chung, 8-Cl-cAMP induces truncation and down-regulation of the RI alpha subunit and up-regulation of the RII beta subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase leading to type II holoenzyme-dependent growth inhibition and differentiation of HL-60 leukemia cells. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 5774–5782 (1993)
V. Gandhi, M. Ayres, R.G. Halgren, N.L. Krett, R.A. Newman, S.T. Rosen, 8-chloro-cAMP and 8-chloro-adenosine act by the same mechanism in multiple myeloma cells. Cancer Res. 61, 5474–5479 (2001)
C.H. Langeveld, C.A. Jongenelen, J.W. Theeuwes, J.P. Baak, J.J. Heimans, J.C. Stoof, G.J. Peters, The antiproliferative effect of 8-chloro-adenosine, an active metabolite of 8-chloro-cyclic adenosine monophosphate, and disturbances in nucleic acid synthesis and cell cycle kinetics. Biochem. Pharmacol. 53, 141–148 (1997)
A.J. Robinson-White, H.P. Hsiao, W.W. Leitner, E. Greene, A. Bauer, N.L. Krett, M. Nesterova, C.A. Stratakis, Protein kinase A-independent inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis in human thyroid cancer cells by 8-Cl-adenosine. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 93, 1020–1029 (2008)
S.N. Kim, Y.H. Ahn, S.G. Kim, S.D. Park, Y.S. Cho-Chung, S.H. Hong, 8-Cl-cAMP induces cell cycle-specific apoptosis in human cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 93, 33–41 (2001)
J.H. Han, Y.H. Ahn, K.Y. Choi, S.H. Hong, Involvement of AMP-activated protein kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in 8-Cl-cAMP-induced growth inhibition. J. Cell. Physiol. 218, 104–112 (2009). doi:10.1002/jcp.21573
S. Lucchi, D. Calebiro, T. de Filippis, E.S. Grassi, M.O. Borghi, L. Persani, 8-Chloro-cyclic AMP and protein kinase A I-selective cyclic AMP analogs inhibit cancer cell growth through different mechanisms. PLoS One 6, e20785 (2011). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0020785
R.E. Schweppe, J.P. Klopper, C. Korch, U. Pugazhenthi, M. Benezra, J.A. Knauf, J.A. Fagin, L.A. Marlow, J.A. Copland, R.C. Smallridge, B.R. Haugen, Deoxyribonucleic acid profiling analysis of 40 human thyroid cancer cell lines reveals cross-contamination resulting in cell line redundancy and misidentification. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 93, 4331–4341 (2008). doi:10.1210/jc.2008-1102
D. Ogreid, R. Ekanger, R.H. Suva, J.P. Miller, P. Sturm, J.D. Corbin, S.O. Døskeland, Activation of protein kinase isozymes by cyclic nucleotide analogs used singly or in combination. Principles for optimizing the isozyme specificity of analog combinations. Eur. J. Biochem. 150, 219–227 (1985)
D. Calebiro, T. de Filippis, S. Lucchi, F. Martinez, P. Porazzi, R. Trivellato, M. Locati, P. Beck-Peccoz, L. Persani, Selective modulation of protein kinase A I and II reveals distinct roles in thyroid cell gene expression and growth. Mol. Endocrinol. 20, 3196–3211 (2006)
A. Dicitore, E.S. Grassi, M. Caraglia, M.O. Borghi, G. Gaudenzi, L.J. Hofland, L. Persani, G. Vitale, The cAMP analogs have potent anti-proliferative effects on medullary thyroid cancer cell lines. Endocrine 51, 101–112 (2016). doi:10.1007/s12020-015-0597-7.
E.S. Grassi, V. Vezzoli, I. Negri, Á. Lábadi, L. Fugazzola, G. Vitale, L. Persani, SP600125 has a remarkable anticancer potential against undifferentiated thyroid cancer through selective action on ROCK and p53 pathways. Oncotarget 6, 36383–36399 (2015). doi:10.18632/oncotarget.5799
G. Vitale, A. Dicitore, D. Mari, F. Cavagnini, A new therapeutic strategy against cancer: cAMP elevating drugs and leptin. Cancer Biol. Ther. 8, 1191–1193 (2009)
Y.S. Cho-Chung, T. Clair, P. Tagliaferri, S. Ally, D. Katsaros, G. Tortora, L. Neckers, T.L. Avery, G.W. Crabtree, R.K. Robins, Site-selective cyclic AMP analogs as new biological tools in growth control, differentiation, and proto-oncogene regulation. Cancer Invest. 7, 161–177 (1989)
A. Feliciello, A. Gallo, E. Mele, A. Porcellini, G. Troncone, C. Garbi, M.E. Gottesman, E.V. Avvedimento, The localization and activity of cAMP-dependent protein kinase affect cell cycle progression in thyroid cells. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 303–311 (2000)
S. Elmore, Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol. 35, 495–516 (2007)
A. Sharma, K. Singh, A. Almasan, Histone H2AX phosphorylation: a marker for DNA damage. Methods Mol. Biol. 920, 613–626 (2012). doi:10.1007/978-1-61779-998-3_40
A. Cuenda, S. Rousseau, p38 MAP-kinases pathway regulation, function and role in human diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1773, 1358–1375 (2007)
J. Liu, A. Lin, Role of JNK activation in apoptosis: a double-edged sword. Cell Res. 15, 36–42 (2005)
E.D. Chan, B.W. Winston, M.B. Jarpe, M.W. Wynes, D.W. Riches, Preferential activation of the p46 isoform of JNK/SAPK in mouse macrophages by TNF alpha. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 94, 13169–13174 (1997)
T. Kato, H. Noma, M. Kitagawa, T. Takahashi, N. Oshitani, S. Kitagawa, Distinct role of c-Jun N-terminal kinase isoforms in human neutrophil apoptosis regulated by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J. Interf. Cytok. Res. 28, 235–243 (2008). doi:10.1089/jir.2007.0075
K.Y. Choi, Y.H. Ahn, H.W. Ahn, Y.J. Cho, S.H. Hong, Involvement of Akt2/protein kinase B beta (PKBbeta) in the 8-Cl-cAMP-induced cancer cell growth inhibition. J. Cell. Physiol. 228, 890–902 (2013). doi:10.1002/jcp.24240
I.B. Weinstein, A. Joe, Oncogene addiction. Cancer Res. 68, 3077–3080 (2008). discussion 3080
R. Bansal, M.A. Nikiforov, Pathways of oncogene-induced senescence in human melanocytic cells. Cell Cycle 9, 2782–2788 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Negri’s present address: IRIBHM, Institute of Interdisciplinary Research in Molecular Human Biology, Université Libre de Bruxelles, Brussels, Belgium
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grassi, E.S., Dicitore, A., Negri, I. et al. 8-Cl-cAMP and PKA I-selective cAMP analogs effectively inhibit undifferentiated thyroid cancer cell growth. Endocrine 56, 388–398 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-016-1057-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-016-1057-8