Abstract
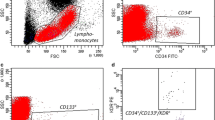
We investigated the effects of sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP)-4 inhibitor, on the number of circulating CD34+CXCR4+cells, a candidate for endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs), plasma levels of stromal cell-derived factor (SDF)-1α, a ligand for CXCR4 receptor and a substrate for DPP-4, and plasma levels of interferon-inducible protein (IP)-10, for a substrate for DPP-4, in patients with type 2 diabetes. We studied 30 consecutive patients with type 2 diabetes who had poor glycemic control despite treatment with metformin and/or sulfonylurea. Thirty diabetic patients were randomized in a 2:1 ratio into a sitagliptin (50 mg/day) treatment group or an active placebo group (glimepiride 1 mg/day) for 12 weeks. Both groups showed similar improvements in glycemic control. The number of circulating CD34+CXCR4+ cells was increased from 30.5 (20.0, 47.0)/106 cells at baseline to 55.5 (31.5, 80.5)/106 cells at 12 weeks of treatment with 50 mg/day sitagliptin (P = 0.0014), while showing no significant changes in patients treated with glimepiride. Plasma levels of SDF-1α and IP-10, both physiological substrates of endogenous DPP-4 and chemokines, were significantly decreased at 12 weeks of sitagliptin treatment. In conclusion, treatment with sitagliptin increased the number of circulating CD34+CXCR4+ cells by approximately 2-fold in patients with type 2 diabetes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Asahara, T. Murohara, A. Sullivan, M. Silver, R. van der Zee, T. Li, B. Witzenbichler, G. Schatteman, J.M. Isner, Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science 275, 964–967 (1997)
T. Takahashi, C. Kalka, H. Masuda, D. Chen, M. Silver, M. Kearney, M. Magner, J.M. Isner, T. Asahara, Ischemia- and cytokine-induced mobilization of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells for neovascularization. Nat. Med. 5, 434–438 (1999)
O.M. Tepper, R.D. Galiano, J.M. Capla, C. Kalka, P.J. Gagne, G.R. Jacobowitz, J.P. Levine, G.C. Gurtner, Human endothelial progenitor cells from type II diabetics exhibit impaired proliferation, adhesion, and incorporation into vascular structures. Circulation 106, 2781–2786 (2002)
G.P. Fadini, M. Miorin, M. Facco, S. Bonamico, I. Baesso, F. Grego, M. Menegolo, S.V. de Kreutzenberg, A. Tiengo, C. Agostini, A. Avogaro, Circulating endothelial progenitor cells are reduced in peripheral vascular complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 45, 1449–1457 (2005)
S.K. Ghadge, S. Mühlstedt, C. Ozcelik, M. Bader, SDF-1α as a therapeutic stem cell homing factor in myocardial infarction. Pharmacol. Ther. 129, 97–108 (2011)
A.M. Lambeir, C. Durinx, S. Scharpé, I. De Meester, Dipeptidyl-peptidase IV from bench to bedside: an update on structural properties, functions, and clinical aspects of the enzyme DPP IV. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 40, 209–294 (2003)
G.P. Fadini, E. Boscaro, M. Albiero, L. Menegazzo, V. Frison, S. de Kreutzenberg, C. Agostini, A. Tiengo, A. Avogaro, The oral dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin increases circulating endothelial progenitor cells in patients with type 2 diabetes: possible role of stromal-derived factor-1alpha. Diabetes Care 33, 1607–1609 (2010)
W. Wojakowski, M. Tendera, A. Michałowska, M. Majka, M. Kucia, K. Maślankiewicz, R. Wyderka, A. Ochała, M.Z. Ratajczak, Mobilization of CD34/CXCR4+, CD34/CD117+, c-met+ stem cells, and mononuclear cells expressing early cardiac, muscle, and endothelial markers into peripheral blood in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 110, 3213–3220 (2004)
G.P. Fadini, D. Losordo, S. Dimmeler, Critical reevaluation of endothelial progenitor cell phenotypes for therapeutic and diagnostic use. Circ. Res. 110, 624–637 (2012)
A. Antonelli, S.M. Ferrari, D. Giuggioli, E. Ferrannini, C. Ferri, P. Fallahi, Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand (CXCL)10 in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 13, 272–280 (2014)
Y. Aso, N. Ozeki, T. Terasawa, R. Naruse, K. Hara, M. Suetsugu, K. Takebayashi, M. Shibazaki, K. Haruki, K. Morita, T. Inukai, Serum level of soluble CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) predicts the response to sitagliptin, a DPP-4 inhibitor, in patients with type 2 diabetes controlled inadequately by metformin and/or sulfonylurea. Transl. Res. 159, 25–31 (2012)
C.G. Egan, R. Lavery, F. Caporali, C. Fondelli, F. Laghi-Pasini, F. Dotta, V. Sorrentino, Generalised reduction of putative endothelial progenitors and CXCR4-positive peripheral blood cells in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 51, 1296–1305 (2008)
R. Wyderka, W. Wojakowski, T. Jadczyk, K. Maślankiewicz, Z. Parma, T. Pawłowski, P. Musiałek, M. Majka, M. Król, W. Kuczmik, S. Dworowy, B. Korzeniowska, M.Z. Ratajczak, M. Tendera, Mobilization of CD34+CXCR4+ stem/progenitor cells and the parameters of left ventricular function and remodeling in 1-year follow-up of patients with acute myocardial infarction. Mediat Inflamm. 2012, 56402 (2012)
R. Möhle, F. Bautz, S. Rafii, M.A. Moore, W. Brugger, L. Kanz, The chemokine receptor CXCR-4 is expressed on CD34+ hematopoietic progenitors and leukemic cells and mediates transendothelial migration induced by stromal cell-derived factor-1. Blood 91, 4523–4530 (1998)
R&D Systems, Inc., Datasheet. Quantikine. Human CXCL12/SDF-1α immunoassay. (R&D Systems, Inc., Minneapolis, 2014), pp. 1–10
M. Dettin, A. Pasquato, C. Scarinci, M. Zanchetta, A. De Rossi, C. Di Bello, Anti-HIV activity and conformational studies of peptides derived from the C-terminal sequence of SDF-1. J. Med. Chem. 47, 3058–3064 (2004)
T. Kusuyama, T. Omura, D. Nishiya, S. Enomoto, R. Matsumoto, K. Takeuchi, J. Yoshikawa, M. Yoshiyama, Effects of treatment for diabetes mellitus on circulating vascular progenitor cells. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 102, 96–102 (2006)
G.P. Fadini, A. Avogaro, Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition and vascular repair by mobilization of endogenous stem cells in diabetes and beyond. Atherosclerosis 229, 23–97 (2013)
Acknowledgments
All authors have read the journal’s authorship agreement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have read the journal’s policy on conflicts of interest and have none to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aso, Y., Jojima, T., Iijima, T. et al. Sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, increases the number of circulating CD34+CXCR4+ cells in patients with type 2 diabetes. Endocrine 50, 659–664 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-015-0688-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-015-0688-5