Abstract
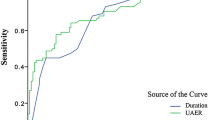
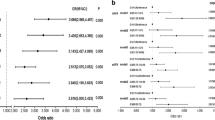
The aim of this study is to investigate the association between serum albumin concentrations and nerve conduction (NC) parameters in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM). A total of 409 T2DM patients were enrolled between October 2010 and April 2014. All participants underwent nerve conduction studies. The composite Z scores for NC parameters including conduction velocity (CV), amplitude, and latency were calculated as well. Serum albumin was measured by Bromcresol Green dye-binding method. The composite Z scores of CV and amplitude increased with the increasing albumin tertiles (test for trend, both P < 0.001), while the composite Z score of latency decreased with increasing albumin tertiles (test for trend, P < 0.001). After adjusting for age, sex, duration, and HbA1c, higher serum albumin concentrations were associated with higher composite Z scores of CV (β = 0.314, P < 0.001), amplitude (β = 0.279, P < 0.001), and lower composite Z score of latency (β = −0.279, P < 0.001). When participants were stratified into albuminuria and normoalbuminuria group, we found the associations of serum albumin with composite Z scores of NC parameters remained significant only in the albuminuria group (CV Z score: β = 0.253, P = 0.002; amplitude Z score: β = 0.233, P = 0.006; latency Z score: β = −0.217 P = 0.013) after further adjustment for urinary albumin to creatinine ratio. The optimal cutoff point of serum albumin to indicate abnormal peripheral nerve function was 36.75 g/L in T2DM patients with albuminuria, with a sensitivity of 65.6 % and a specificity of 78.0 %. Serum albumin was independently associated with peripheral nerve function in T2DM patients, especially in those with albuminuria. Serum albumin could be a potential biomarker for diabetic peripheral neuropathy.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- T2DM:
-
Type 2 diabetes
- DPN:
-
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- NCSs:
-
Nerve conduction studies
- NC:
-
Nerve conduction
- CV:
-
Conduction velocity
- ACR:
-
Urinary albumin to creatinine ratio
- HbA1c:
-
Glycated hemoglobin
References
S. Wild, G. Roglic, A. Green, R. Sicree, H. King, Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 27(5), 1047–1053 (2004)
S. Tesfaye, A.J. Boulton, P.J. Dyck, R. Freeman, M. Horowitz, P. Kempler, G. Lauria, R.A. Malik, V. Spallone, A. Vinik, L. Bernardi, P. Valensi, Diabetic neuropathies: update on definitions, diagnostic criteria, estimation of severity, and treatments. Diabetes Care 33(10), 2285–2293 (2010). doi:10.2337/dc10-1303
A.J. Boulton, L. Vileikyte, G. Ragnarson-Tennvall, J. Apelqvist, The global burden of diabetic foot disease. Lancet 366(9498), 1719–1724 (2005). doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(05)67698-2
R.A. Malik, Which test for diagnosing early human diabetic neuropathy? Diabetes 63(7), 2206–2208 (2014). doi:10.2337/db14-0492
Writing Team for the Diabetes, C., Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes, I., and Complications Research, G, Effect of intensive therapy on the microvascular complications of type 1 diabetes mellitus. JAMA 287(19), 2563–2569 (2002)
N. Singh, D.G. Armstrong, B.A. Lipsky, Preventing foot ulcers in patients with diabetes. JAMA 293(2), 217–228 (2005). doi:10.1001/jama.293.2.217
N. Papanas, D. Ziegler, New vistas in the diagnosis of diabetic polyneuropathy. Endocrine 47(3), 690–698 (2014). doi:10.1007/s12020-014-0285-z
P.J. Dyck, J.W. Albers, H. Andersen, J.C. Arezzo, G.J. Biessels, V. Bril, E.L. Feldman, W.J. Litchy, P.C. O’Brien, J.W. Russell, Diabetic polyneuropathies: update on research definition, diagnostic criteria and estimation of severity. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 27(7), 620–628 (2011). doi:10.1002/dmrr.1226
B.A. Perkins, V. Bril, Diabetic neuropathy: a review emphasizing diagnostic methods. Clin. Neurophysiol. 114(7), 1167–1175 (2003)
J.D. England, G.S. Gronseth, G. Franklin, R.G. Miller, A.K. Asbury, G.T. Carter, J.A. Cohen, M.A. Fisher, J.F. Howard, L.J. Kinsella, N. Latov, R.A. Lewis, P.A. Low, A.J. Sumner, Distal symmetrical polyneuropathy: definition for clinical research. Muscle Nerve 31(1), 113–123 (2005). doi:10.1002/mus.20233
A. Weisman, V. Bril, M. Ngo, L.E. Lovblom, E.M. Halpern, A. Orszag, B.A. Perkins, Identification and prediction of diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy using individual and simple combinations of nerve conduction study parameters. PLoS ONE 8(3), e58783 (2013). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0058783
P. Caraceni, M. Domenicali, A. Tovoli, L. Napoli, C.S. Ricci, M. Tufoni, M. Bernardi, Clinical indications for the albumin use: still a controversial issue. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 24(8), 721–728 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2013.05.015
W.J. Zhang, B. Frei, Albumin selectively inhibits TNF alpha-induced expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in human aortic endothelial cells. Cardiovasc. Res. 55(4), 820–829 (2002)
K. Oettl, R.E. Stauber, Physiological and pathological changes in the redox state of human serum albumin critically influence its binding properties. Br. J. Pharmacol. 151(5), 580–590 (2007). doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0707251
N. Ishizaka, Y. Ishizaka, R. Nagai, E. Toda, H. Hashimoto, M. Yamakado, Association between serum albumin, carotid atherosclerosis, and metabolic syndrome in Japanese individuals. Atherosclerosis 193(2), 373–379 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2006.06.031
F. Barutta, G. Bruno, S. Grimaldi, G. Gruden, Inflammation in diabetic nephropathy: moving toward clinical biomarkers and targets for treatment. Endocrine (2014). doi:10.1007/s12020-014-0437-1
A.M. Vincent, J.W. Russell, P. Low, E.L. Feldman, Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy. Endocr. Rev. 25(4), 612–628 (2004). doi:10.1210/er.2003-0019
H.Y. Jin, K.A. Lee, J.Z. Wu, H.S. Baek, T.S. Park, The neuroprotective benefit from pioglitazone (PIO) addition on the alpha lipoic acid (ALA)-based treatment in experimental diabetic rats. Endocrine 47(3), 772–782 (2014). doi:10.1007/s12020-014-0198-x
A.M. Joussen, V. Poulaki, M.L. Le, K. Koizumi, C. Esser, H. Janicki, U. Schraermeyer, N. Kociok, S. Fauser, B. Kirchhof, T.S. Kern, A.P. Adamis, A central role for inflammation in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. FASEB J. 18(12), 1450–1452 (2004). doi:10.1096/fj.03-1476fje
Dalla Vestra, M. Mussap, M. Gallina, P. Bruseghin, A.M. Cernigoi, A. Saller, M. Plebani, P. Fioretto, Acute-phase markers of inflammation and glomerular structure in patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 16(Suppl 1), S78–S82 (2005)
J.F. Navarro, C. Mora, Role of inflammation in diabetic complications. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 20(12), 2601–2604 (2005). doi:10.1093/ndt/gfi155
R. Pazdro, J.R. Burgess, The role of vitamin E and oxidative stress in diabetes complications. Mech. Ageing Dev. 131(4), 276–286 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.mad.2010.03.005
R. Sayin, M. Aslan, M.E. Kucukoglu, A. Luleci, M. Atmaca, R. Esen, H. Demir, Serum prolidase enzyme activity and oxidative stress levels in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Endocrine 47(1), 146–151 (2014). doi:10.1007/s12020-013-0136-3
R. Sandireddy, V.G. Yerra, A. Areti, P. Komirishetty, A. Kumar, Neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in diabetic neuropathy: futuristic strategies based on these targets. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 674987 (2014). doi:10.1155/2014/674987
R. Stavniichuk, H. Shevalye, S. Lupachyk, A. Obrosov, J.T. Groves, I.G. Obrosova, M.A. Yorek, Peroxynitrite and protein nitration in the pathogenesis of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 30(8), 669–678 (2014). doi:10.1002/dmrr.2549
R.D. Hoeldtke, K.D. Bryner, G.R. Hobbs, G.G. Horvath, J.E. Riggs, I. Christie, G. Ganser, S.M. Marcovina, A. Lernmark, Antibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase and peripheral nerve function in type 1 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 85(9), 3297–3308 (2000). doi:10.1210/jcem.85.9.6830
M.E. Molitch, R.A. DeFronzo, M.J. Franz, W.F. Keane, C.E. Mogensen, H.H. Parving, M.W. Steffes, Nephropathy in diabetes. Diabetes care 27(Suppl 1), S79–S83 (2004)
C.P. Wilkinson, F.L. Ferris 3rd, R.E. Klein, P.P. Lee, C.D. Agardh, M. Davis, D. Dills, A. Kampik, R. Pararajasegaram, J.T. Verdaguer, Proposed international clinical diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema disease severity scales. Ophthalmology 110(9), 1677–1682 (2003). doi:10.1016/s0161-6420(03)00475-5
L. Rodriguez-Rodriguez, C. Gonzalez-Juanatey, R. Palomino-Morales, T.R. Vazquez-Rodriguez, J.A. Miranda-Filloy, B. Fernandez-Gutierrez, J. Llorca, J. Martin, M.A. Gonzalez-Gay, TNFA -308 (rs1800629) polymorphism is associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Atherosclerosis 216(1), 125–130 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.10.052
P.J. Dyck, R.E. Carter, W.J. Litchy, Modeling nerve conduction criteria for diagnosis of diabetic polyneuropathy. Muscle Nerve 44(3), 340–345 (2011). doi:10.1002/mus.22074
N.H. Kim, K.B. Kim, D.L. Kim, S.G. Kim, K.M. Choi, S.H. Baik, D.S. Choi, Y.S. Kang, S.Y. Han, K.H. Han, Y.H. Ji, D.R. Cha, Plasma and urinary vascular endothelial growth factor and diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetic Med. 21(6), 545–551 (2004). doi:10.1111/j.1464-5491.2004.01200.x
Z. Wang, W.E. Hoy, Z. Wang, The correlates of urinary albumin to creatinine ratio (ACR) in a high risk Australian aboriginal community. BMC Nephrol. 14, 176 (2013). doi:10.1186/1471-2369-14-176
H. Taskapan, M.C. Taskapan, I. Orman, O. Ulutas, A. Yigit, F. Ozyalin, S. Yologlu, NGAL and NT-proBNP levels in diabetic patients with macroproteinuria. Ren. Fail. 35(9), 1273–1277 (2013). doi:10.3109/0886022x.2013.824336
L. Djousse, K.J. Rothman, L.A. Cupples, D. Levy, R.C. Ellison, Serum albumin and risk of myocardial infarction and all-cause mortality in the Framingham Offspring Study. Circulation 106(23), 2919–2924 (2002)
J.D. Lang Jr, M. Figueroa, P. Chumley, M. Aslan, J. Hurt, M.M. Tarpey, B. Alvarez, R. Radi, B.A. Freeman, Albumin and hydroxyethyl starch modulate oxidative inflammatory injury to vascular endothelium. Anesthesiology 100(1), 51–58 (2004)
G.J. Quinlan, S. Mumby, G.S. Martin, G.R. Bernard, J.M. Gutteridge, T.W. Evans, Albumin influences total plasma antioxidant capacity favorably in patients with acute lung injury. Crit. Care Med. 32(3), 755–759 (2004)
M. Roche, P. Rondeau, N.R. Singh, E. Tarnus, E. Bourdon, The antioxidant properties of serum albumin. FEBS Lett. 582(13), 1783–1787 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2008.04.057
M. Taverna, A.L. Marie, J.P. Mira, B. Guidet, Specific antioxidant properties of human serum albumin. Ann. Intensive Care 3(1), 4 (2013). doi:10.1186/2110-5820-3-4
S.S. Awad, S. Sawada, O.S. Soldes, P.B. Rich, R. Klein, W.H. Alarcon, S.C. Wang, R.H. Bartlett, Can the clearance of tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 6 be enhanced using an albumin dialysate hemodiafiltration system? ASAIO J. 45(1), 47–49 (1999)
K.R. Walley, T.E. McDonald, Y. Wang, S. Dai, J.A. Russell, Albumin resuscitation increases cardiomyocyte contractility and decreases nitric oxide synthase II expression in rat endotoxemia. Crit. Care Med. 31(1), 187–194 (2003). doi:10.1097/01.ccm.0000037157.55600.7f
D.J. Leehey, H.J. Kramer, T.M. Daoud, M.P. Chatha, M.A. Isreb, Progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes—beyond blood pressure control: an observational study. BMC Nephrol. 6, 8 (2005). doi:10.1186/1471-2369-6-8
T. Iwasaki, Y. Togashi, Y. Terauchi, Significant association of serum albumin with severity of retinopathy and neuropathy, in addition to that of nephropathy, in Japanese type 2 diabetic patients. Endocr. J. 55(2), 311–316 (2008)
P.J. Dyck, W.J. Litchy, J.R. Daube, C.M. Harper, P.J. Dyck, J. Davies, P.C. O’Brien, Individual attributes versus composite scores of nerve conduction abnormality: sensitivity, reproducibility, and concordance with impairment. Muscle Nerve 27(2), 202–210 (2003). doi:10.1002/mus.10320
A. Festa, R. D’Agostino, G. Howard, L. Mykkanen, R.P. Tracy, S.M. Haffner, Inflammation and microalbuminuria in nondiabetic and type 2 diabetic subjects: the Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study. Kidney Int. 58(4), 1703–1710 (2000). doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2000.00331.x
M. Aslan, T. Sabuncu, A. Kocyigit, H. Celik, S. Selek, Relationship between total oxidant status and severity of diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetic patients. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 17(10), 734–740 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.numecd.2006.08.005
J.F. Navarro, C. Mora, M. Maca, J. Garca, Inflammatory parameters are independently associated with urinary albumin in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 42(1), 53–61 (2003)
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all of the involved clinicians, nurses, and technicians for dedicating their time and skill to the completion of this study. This work was supported by the Science and Technology Innovation Fund of Shanghai Jinshan district, China (2011-3-16) and the Programs of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81170760; 81300666).
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Lu Li and Bo Liu have contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Liu, B., Lu, J. et al. Serum albumin is associated with peripheral nerve function in patients with type 2 diabetes. Endocrine 50, 397–404 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-015-0588-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-015-0588-8