Abstract
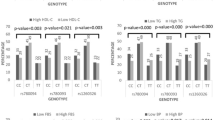
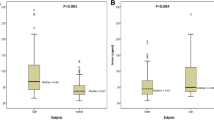
Polymorphisms of the NR3C1 (glucocorticoid receptor) gene have been reported to be associated with altered glucocorticoids sensitivity and changes in body composition and metabolic parameters. This study explored the relationship between single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of the NR3C1 gene and metabolic syndrome (MetS) in a Chinese population. Fourteen tag-SNPs and five functionally important SNPs in the NR3C1 gene were genotyped in MetS patients (n = 431) and normal controls (n = 461) using the high-throughput Sequenom genotyping platform. Genotype, allelic and haplotype associations were examined using logistic regression and Haploview. There are four SNPs significantly associated with MetS. The T allele of rs2963156 was associated with an increased risk effect for MetS (adjusted OR = 1.66, 95 % CI 1.25–2.22, P = 0.001). By contrast, rs10052957 A allele carriers were significantly associated with a decreased risk of MetS (adjusted OR = 0.58, 95 % CI 0.42–0.80, P = 0.001). Rs41423247 GG genotype (adjusted OR = 2.01, 95 % CI 1.25–3.22, P = 0.004), and rs7701443 AA genotype (adjusted OR = 1.88, 95 % CI 1.24–2.83, P = 0.003) were significantly associated with an increased risk of MetS. Haplotype CGGA is risk conferring (adjusted OR = 1.53, 95 % CI 1.06–2.20, P = 0.023), whereas haplotype CCAG was protective (adjusted OR = 0.30, 95 % CI 0.20–0.47, P < 0.001). Polymorphism of NR3C1 gene is associated with MetS and may contribute to the susceptibility of MetS.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.E. Moller, K.D. Kaufman, Metabolic syndrome: a clinical and molecular perspective. Annu. Rev. Med. 56, 45–62 (2005)
K.L. Tamashiro, R.R. Sakai, C.A. Shively, I.N. Karatsoreos, L.P. Reagan, Chronic stress, metabolism, and metabolic syndrome. Stress 14(5), 468–474 (2011)
G.P. Chrousos, T. Kino, Glucocorticoid action networks and complex psychiatric and/or somatic disorders. Stress 10, 213–219 (2007)
J. Zhou, J.A. Cidlowski, The human glucocorticoid receptor: one gene, multiple proteins and diverse responses. Steroids 70, 407–417 (2005)
D. Duma, C.M. Jewell, J.A. Cidlowski, Multiple glucocorticoid receptor isoforms and mechanisms of post-translational modification. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 102, 11–21 (2006)
N.C. Nicolaides, Z. Galata, T. Kino, G.P. Chrousos, E. Charmandari, The human glucocorticoid receptor: molecular basis of biologic function. Steroids 75, 1–12 (2010)
S.W. Lamberts, A.T. Huizenga, P. de Lange, F.H. de Jong, J.W. Koper, Clinical aspects of glucocorticoid sensitivity. Steroids 61, 157–160 (1996)
P. Smit, H. Russcher, F.H. de Jong, A.O. Brinkmann, S.W. Lamberts, J.W. Koper, Differential regulation of synthetic glucocorticoids on gene expression levels of glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper and interleukin-2. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 90, 2994–3000 (2005)
E.F. van Rossum, S.W. Lamberts, Polymorphisms in the glucocorticoid receptor gene and their associations with metabolic parameters and body composition. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 59, 333–357 (2004)
R.C. Lin, X.L. Wang, B. Dalziel, I.D. Caterson, B.J. Morris, Association of obesity, but not diabetes or hypertension, with glucocorticoid receptor N363S variant. Obes. Res. 11, 802–808 (2003)
R. Rosmond, Y.C. Chagnon, G. Holm, M. Chagnon, L. Pérusse, K. Lindell et al., A glucocorticoid receptor gene marker is associated with abdominal obesity, leptin, and dysregulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Obes. Res. 8, 211–218 (2000)
E.F. Van Rossum, J.W. Koper, N.A. Huizenga, A.G. Uitterlinden, J.A. Janssen, A.O. Brinkmann et al., A polymorphism in the glucocorticoid receptor gene, which decreases sensitivity to glucocorticoids in vivo, is associated with low insulin and cholesterol levels. Diabetes 51, 3128–3134 (2002)
E.F. Van Rossum, P.H. Roks, F.H. De Jong, A.O. Brinkmann, H.A. Pols, J.W. Koper et al., Characterization of a promoter polymorphism in the glucocorticoid receptor gene and its relationship to three other polymorphisms. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf) 61, 573–581 (2004)
E. Charmandari, T. Ichijo, W. Jubiz, S. Baid, K. Zachman, G.P. Chrousos et al., A novel point mutation in the amino terminal domain of the human glucocorticoid receptor (hGR) gene enhancing hGR-mediated gene expression. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 93, 4963–4968 (2008)
A.A. Syed, J.A. Irving, C.P. Redfern, A.G. Hall, N.C. Unwin, M. White et al., Association of glucocorticoid receptor polymorphism A3669G in exon 9beta with reduced central adiposity in women. Obesity (Silver Spring) 14, 759–764 (2006)
Porzezińska-Furtak J, Krzyżanowska-Świniarska B, Miazgowski T, Safranow K, Kamiński R. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity, personality traits, and BCL1 and N363S polymorphisms of the glucocorticoid receptor gene in metabolically obese normal-weight women. Endocrine. 45. doi:10.1007/s12020-014-0187-0 (2014)
Y.X. Yan, J. Dong, L.J. Wu, S. Shao, J. Zhang, L. Zhang et al., Associations between polymorphisms in the glucocorticoid-receptor gene and cardiovascular risk factors in a Chinese population. J. Epidemiol. 23, 389–395 (2013)
K.G. Alberti, R.H. Eckel, S.M. Grundy, P.Z. Zimmet, J.I. Cleeman, K.A. Donato et al., Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 120, 1640–1645 (2009)
J. Galon, D. Franchimont, N. Hiroi, G. Frey, A. Boettner, M. Ehrhart-Bornstein et al., Gene profiling reveals unknown enhancing and suppressive actions of glucocorticoids on immune cells. FASEB. J. 16, 61–71 (2002)
G.P. Chrousos, T. Kino, Intracellular glucocorticoid signaling: a formerly simple system turns stochastic. Sci. STKE. 2005, pe48 (2005)
P.J. Bray, R.G. Cotton, Variations of the human glucocorticoid receptor gene (NR3C1): pathological and in vitro mutations and polymorphisms. Hum. Mutat. 21, 557–568 (2003)
M. Panarelli, C.D. Holloway, R. Fraser, J.M. Connell, M.C. Ingram, N.H. Anderson et al., Glucocorticoid receptor polymorphism, skin vasoconstriction, and other metabolic intermediate phenotypes in normal human subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 83, 1846–1852 (1998)
M. Panek, T. Pietras, A. Fabijan, M. Milanowski, L. Wieteska, P. Górski, P. Kuna, J. Szemraj, Effect of glucocorticoid receptor gene polymorphisms on asthma phenotypes. Exp. Ther. Med. 5, 572–580 (2013)
S.D. Detera-Wadleigh, I.J. Encio, D.Y. Rollins, D. Coffman, D. Wiesch, A Tth111I polymorphism on the 5′ flanking region of the glucocorticoid receptor gene (GRL). Nucleic Acids Res. 19, 1960 (1991)
E.F. Van Rossum, P.G. Voorhoeve, S.J. Te Velde, J.W. Koper, H.A.D. van de Waal, H.C. Kemper et al., The ER22, 23EK polymorphism in the glucocorticoid receptor gene is associated with a beneficial body composition and muscle strength in young adults. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89, 4004–4009 (2004)
A. Krupoves, D. Mack, C. Deslandres, E. Seidman, D.K. Amre, Variation in the glucocorticoid receptor gene (NR3C1) may be associated with corticosteroid dependency and resistance in children with Crohn’s disease. Pharmacogenet. Genomics 21, 454–460 (2011)
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (81102208), the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (7133229), the National Science and Technology Support Program (2012BAI37B03), and the Importation and Development of High-Caliber Talents Project of Beijing Municipal Institutions (CIT&TCD201304181).
Conflict of interest
There was no conflict of interest in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, YX., Dong, J., Zhang, J. et al. Polymorphisms in NR3C1 gene associated with risk of metabolic syndrome in a Chinese population. Endocrine 47, 740–748 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0324-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0324-9