Abstract
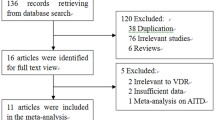
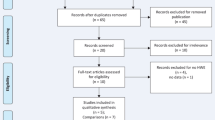
Environmental and genetic factors are thought to be involved in the pathogenesis of autoimmune thyroid diseases (AITD), which include Graves’ disease, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Polymorphisms of vitamin D receptor (VDR) were implicated in AITDs risk. To date, many studies have evaluated the association between a functional polymorphism in the VDR gene and AITDs risk; however, the result is still ambiguous and inconclusive. To address the association of VDR gene FokI (rs10735810), TaqI (rs731236), BsmI (rs1544410), and ApaI (rs7975232) polymorphisms with AITD risk by meta-analysis. By searching the relevant literature, a total of eight studies were identified and meta-analyzed. HWE for each study are checked. Crude odds ratios (OR) with 95 % confidence intervals (CIs) were used to assess the strength of association in the allele polymorphism, codominant model, dominant model, and recessive model. The result indicates that the BsmI or TaqI polymorphisms is significantly associated with AITD risk (OR = 0.801 95 % CI 0.705, 0.910, Pz = 0.001 for B vs. b; OR = 0.854, 95 % CI 0.757, 0.963, Pz = 0.010 for t vs. T), while the ApaI or FokI polymorphism do not. In the subgroup analysis in Europeans, the decreased risk of AITD remained for the B or t variant. This gene-based analysis indicates that, based on current evidence from published studies, the cumulative effect of BsmI or TaqI polymorphisms in VDR is significantly associated with AITD.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.J. DeGroot, J. Quintans, The causes of autoimmune thyroid disease. Endocr. Rev. 10(4), 537–562 (1989)
Y. Tomer, T.F. Davies, Infection, thyroid disease, and autoimmunity. Endocr. Rev. 14(1), 107–120 (1993)
F. Guarneri, S. Benvenga, Environmental factors and genetic background that interact to cause autoimmune thyroid disease. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 14(5), 398–409 (2007)
J.M. Valdivielso, E. Fernandez, Vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and diseases. Clin. Chim. Acta 371(1), 1–12 (2006)
J.D. Simmons, C. Mullighan, K.I. Welsh, D.P. Jewell, Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism: association with Crohn’s disease susceptibility. Gut 47(2), 211–214 (2000)
A. Vogel, C.P. Strassburg, M.P. Manns, Genetic association of vitamin D receptor polymorphisms with primary biliary cirrhosis and autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology 35(1), 126–131 (2002)
Y.H. Lee, S.C. Bae, S.J. Choi, J.D. Ji, G.G. Song, Associations between vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus: a meta-analysis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 38(6), 3643–3651 (2011)
C.A. Hitchon, Y. Sun, D.B. Robinson, C.A. Peschken, C.N. Bernstein, K.A. Siminovitch, H.S. El-Gabalawy, Vitamin D receptor polymorphism rs2228570 (Fok1) is associated with rheumatoid arthritis in North American natives. J. Rheumatol. 39(9), 1792–1797 (2012)
A.G. Uitterlinden, Y. Fang, J.B.J. van Meurs, H.A.P. Pols, J.P.T.M. van Leeuwen, Genetics and biology of vitamin D receptor polymorphisms. Gene 338(2), 143–156 (2004)
M. Stefanic, I. Karner, L. Glavas-Obrovac, S. Papic, D. Vrdoljak, G. Levak, B. Krstonosic, Association of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism with susceptibility to Graves’ disease in Eastern Croatian population: case–control study. Croat. Med. J. 46(4), 639–646 (2005)
E. Ramos-Lopez, A. Kurylowicz, T. Bednarczuk, J. Paunkovic, C. Seidl, K. Badenhoop, Vitamin D receptor polymorphisms are associated with Graves’ disease in German and Polish but not in Serbian patients. Thyroid 15(10), 1125–1130 (2005)
W. Horst-Sikorska, M. Ignaszak-Szczepaniak, M. Marcinkowska, M. Kaczmarek, M. Stajgis, R. Slomski, Association analysis of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms with bone mineral density in young women with Graves’ disease. Acta Biochim. Pol. 55(2), 371–380 (2008)
X.J. Huo, F. Wei, J.X. Huo, R.N. Su, Y.X. Xue, J.H. Wei, Association of vitamin D receptor gene BsmI polymorphism with autoimmune thyroid disease in Innermongolia People of the Han Nationality. J. Radioimmunol. 23(1), 72–74 (2010)
A. Maalej, E. Petit-Teixeira, G. Chabchoub, M.B. Hamad, A. Rebai, N.R. Farid, F. Cornelis, H. Ayadi, Lack of association of VDR gene polymorphisms with thyroid autoimmune disorders: familial and case/control studies. J. Clin. Immunol. 28(1), 21–25 (2008)
M. Stefanic, S. Papic, M. Suver, L. Glavas-Obrovac, I. Karner, Association of vitamin D receptor gene 3′-variants with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis in the Croatian population. Int. J. Immunogenet. 35(2), 125–131 (2008)
Y. Ban, Y. Ban, M. Taniyama, T. Katagiri, Vitamin D receptor initiation codon polymorphism in Japanese patients with Graves’ disease. Thyroid 10(6), 475–480 (2000)
W.Y. Lin, L. Wan, C.H. Tsai, R.H. Chen, C.C. Lee, F.J. Tsai, Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms are associated with risk of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis in Chinese patients in Taiwan. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 20(3), 109–112 (2006)
D.M. Provvedini, C.D. Tsoukas, L.J. Deftos, S.C. Manolagas, 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptors in human leukocytes. Science 221(4616), 1181–1183 (1983)
J. Smolders, E. Peelen, M. Thewissen, P. Menheere, J.W. Tervaert, R. Hupperts, J. Damoiseaux, The relevance of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms for vitamin D research in multiple sclerosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 8(7), 621–626 (2009)
T. Yasuda, Y. Okamoto, N. Hamada, K. Miyashita, M. Takahara, F. Sakamoto, T. Miyatsuka, T. Kitamura, N. Katakami, D. Kawamori, M. Otsuki, T.A. Matsuoka, H. Kaneto, I. Shimomura, Serum vitamin D levels are decreased and associated with thyroid volume in female patients with newly onset Graves’ disease. Endocrine (2012). doi:10.1007/s12020-012-9679-y
M. Rotondi, L. Chiovato, Vitamin D deficiency in patients with Graves’ disease: probably something more than a casual association. Endocrine (2012). doi:10.1007/s12020-012-9776-y
T. Yasuda, Y. Okamoto, N. Hamada, K. Miyashita, M. Takahara, F. Sakamoto, T. Miyatsuka, T. Kitamura, N. Katakami, D. Kawamori, M. Otsuki, T.A. Matsuoka, H. Kaneto, I. Shimomura, Serum vitamin D levels are decreased in patients without remission of Graves’ disease. Endocrine (2012). doi:10.1007/s12020-012-9789-6
C.M. Huang, M.C. Wu, J.Y. Wu, F.J. Tsai, Association of vitamin D receptor gene BsmI polymorphisms in Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 11(1), 31–34 (2002)
V. Skrabic, T. Zemunik, M. Situm, J. Terzic, Vitamin D receptor polymorphism and susceptibility to type 1 diabetes in the Dalmatian population. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 59(1), 31–35 (2003)
G.K. Whitfield, L.S. Remus, P.W. Jurutka, H. Zitzer, A.K. Oza, H.T. Dang, C.A. Haussler, M.A. Galligan, M.L. Thatcher, C. Encinas Dominguez, M.R. Haussler, Functionally relevant polymorphisms in the human nuclear vitamin D receptor gene. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 177(1–2), 145–159 (2001)
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in the submission of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, M., Li, H., Chen, SF. et al. Polymorphisms in the vitamin D receptor gene and risk of autoimmune thyroid diseases: a meta-analysis. Endocrine 43, 318–326 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-012-9812-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-012-9812-y