Abstract
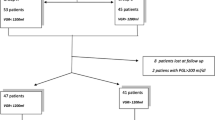
Anorexia is a problem of paramount importance in patients with advanced liver failure. Ghrelin has important actions on feeding and weight homeostasis. Concentrations of ghrelin are controversial in liver cirrhosis. Our aim was to study fasting ghrelin and their response to an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) in liver failure patients and normal subjects. Methods We included 16 patients with severe liver failure prior to liver transplantation. As a control group we included 10 age- and BMI-matched healthy subjects. After an overnight fast, 75 g of oral glucose were administered; glucose, insulin, and ghrelin were obtained at baseline and at times 30, 60, 90, and 120 min, respectively. Results Fasting ghrelin (median and range) were statistically significantly lower for patients compared to the controls, 527 (377–971) pg/ml vs. 643 (523–2163) pg/ml, P = 0.045, for patients and controls, respectively. The area under the curve for total ghrelin post-OGTT were lower in end-stage liver failure patients than in the control group, 58815 (44730–87420) pg/ml min vs. 76560 (56160–206385) pg/ml min, for patients and controls, respectively, P = 0.027. Conclusions Ghrelin levels are significantly decreased both fasting and post-OGTT in patients with liver failure candidates for transplantation. Decreased ghrelin levels could contribute to anorexia in patients with cirrhosis.





Similar content being viewed by others

References
O. Selberg, J. Böttcher, G. Tusch, R. Pichlmayr, E. Henkel, M.J. Muller, Identification of high- and low-risk patients before liver transplantation: a prospective cohort study of nutritional and metabolic parameters in 150 patients. Hepatology 25, 652–657 (1997)
C. Matos, M.K. Porayko, N. Francisco-Ziller, S. DiCecco, Nutrition and chronic liver disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 35, 391–397 (2002)
H.I.M. Davidson, R. Richardson, D. Sutherland, O.J. Garden, Macronutrient preference, dietary intake, and substrate oxidation among stable cirrhotic patients. Hepatology 29, 1380–1386 (1999)
G. Marchesini, G. Bianchi, P. Lucidi, N. Villanova, M. Zoli, P. De Feo, Plasma ghrelin concentrations, food intake, and anorexia in liver failure. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89, 2136–2141 (2004)
J. Ockenga, S.C. Bischoff, H.L. Tillmann, K. Rifai, A. Widjaja, K.H. Böker, M.P. Manns, G. Brabant, Elevated bound leptin correlates with energy expenditure in cirrhotics. Gastroenterology 119, 1656–1662 (2001)
A.M. Madden, M.Y. Morgan, Resting energy expenditure should be measured in patients with cirrhosis, not predicted. Hepatology 30, 655–664 (1999)
A. Laviano, C. Cangiano, I. Preziosa, O. Riggio, L. Conversano, A. Cascino, S. Ariemma, F. Rossi Fanelli, Plasma tryptophan levels and anorexia in liver cirrhosis. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 21, 181–186 (1997)
H.U. Lautz, O. Selberg, J. Korber, M. Burger, M.J. Muller, Forms of malnutrition in patients with liver cirrhosis. Clin. Invest. 70, 178–186 (1992)
M. Merli, O. Riggio, L. Dally, Does malnutrition affect survival in cirrhosis? Policentrica Italiana Nutrizione Cirrosi (PINC). Hepatology 23, 1041–1046 (1996)
M. Kojima, H. Hosoda, Y. Date, M. Nakazato, H. Matsuo, K. Kangawa, Ghrelin is a growth hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 402, 656–658 (1999)
F. Cordido, A. Peñalva, C. Dieguez, F. Casanueva, Massive growth hormone (GH) discharge in obese subjects after the combined administration of Growth Hormone releasing hormone and GHRP-6: evidence for a marked somatotroph secretory capability in obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 76, 819–823 (1993)
P. Alvarez, L. Isidro, J. Garcia-Buela, J. Leal-Cerro, F. Broglio, F. Tassone, E. Ghigo, C. Dieguez, F.F. Casanueva, F. Cordido, Marked GH secretion after ghrelin alone or combined with GH-releasing hormone (GHRH) in obese patients. Clin. Endocrinol. 61, 250–255 (2004)
A.J. van der Lely, M. Tschop, M.L. Heiman, E. Ghigo, Biological, physiological, pathophysiological, and pharmacological aspects of ghrelin. Endocr. Rev. 25, 426–457 (2004)
M. Tschop, D.L. Smiley, M.L. Heiman, Ghrelin induces adiposity in rodents. Nature 407, 908–909 (2000)
M. Nakazato, N. Murakami, Y. Date, M. Kojima, H. Matsuo, K. Kangawa, S. Matsukura, A role for ghrelin in the central regulation of feeding. Nature 409, 194–198 (2001)
Y. Shuto, T. Shibasaki, A. Otagiri, H. Kuriyama, H. Ohata, H. Tamura, J. Kamegai, H. Sugihara, S. Oikawa, I. Wakabayashi, Hypothalamic growth hormone secretagogue receptor regulates growth hormone secretion, feeding and adiposity. J. Clin. Invest. 109, 1429–1436 (2002)
A.M. Wren, L.J. Seal, M.A. Cohen, A.E. Brynes, G.S. Frost, K.G. Murphy, Ghrelin enhances appetite and increases food intake in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86, 5992–5998 (2001)
D.E. Cummings, K. Clement, J.Q. Purnell, C. Vaisse, K.E. Foster, R.S. Frayo, M.W. Schwartz, A. Basdevant, D.S. Weigle, Elevated plasma ghrelin levels in Prader-Willi syndrome. Nat. Med. 8, 643–644 (2002)
D.E. Cummings, D.S. Weigle, R.S. Frayo, P.A. Breen, M.K. Ma, E.P. Dellinger, J.Q. Purnell, Plasma ghrelin levels after diet-induced weight loss or gastric bypass surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 346, 1623–1630 (2002)
M. Tschop, C. Weyer, P.A. Tataranni, V. Devanarayan, E. Ravussin, M.L. Heiman, Circulating ghrelin are decreased in human obesity. Diabetes 50, 707–709 (2001)
A.M. Haqq, I.S. O′Farooqi, S. Rahilly, D.D. Stadler, R.G. Rosenfeld, K.L. Prat, S.H. LaFranchi, J.Q. Purnell, Serum ghrelin levels are inversely correlated with body mass index, age, and insulin concentrations in normal children and are markedly increased in Prader-Willi syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 88, 174–178 (2003)
G. Muccioli, M. Tschop, M. Papotti, R. Deghenghi, M. Heiman, E. Ghigo, Neuroendocrine and peripheral activities of ghrelin: implications in metabolism and obesity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 440, 235–254 (2002)
B. Otto, U. Cuntz, E. Fruehauf, R. Wawarta, C. Folwaczny, R.L. Riepl, M.L. Heiman, P. Lehnert, M. Fichter, M. Tschöp, Weight gain decreases elevated plasma ghrelin concentrations of patients with anorexia nervosa. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 145, 669–673 (2001)
O. Ukkola, Ghrelin and insulin metabolism. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 33, 183–185 (2003)
A. Asakawa, A. Inui, T. Kaga, G. Katsuura, M. Fujimiya, M.A. Fujino, M. Kasuga, Antagonism of ghrelin receptor reduces food intake and body weight gain in mice. Gut 52, 947–952 (2003)
T. McLaughlin, F. Abbasi, C. Lamendola, R.S. Frayo, D.E. Cummings, Plasma ghrelin concentrations are decreased in insulin-resistant obese adults relative to equally obese insulin-sensitive controls. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89, 1630–1635 (2004)
T. Shiiya, M. Nakazato, M. Mizuta, Y. Date, M.S. Mondal, M. Tanaka, S. Nozoe, H. Hosoda, K. Kangawa, S. Matsukura, Plasma ghrelin levels in lean and obese humans and the effect of glucose on ghrelin secretion. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 87, 240–244 (2002)
D.E. Cummings, J.Q. Purnell, R.S. Frayo, K. Schmidova, B.E. Wisse, D.S. Weigle, A preprandial rise in plasma ghrelin levels suggests a role in meal initiation in humans. Diabetes 50, 1714–1719 (2001)
M. Kojima, K. Kangawa, Ghrelin: structure and function. Physiol. Rev. 85, 495–522 (2005)
M. Hotta, R. Ohwada, H. Katakami, T. Shibasaki, N. Hizuka, K. Takano, Plasma levels of intact and degraded ghrelin and their responses to glucose infusion in anorexia nervosa. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89, 571–5707 (2004)
E. Kalaitzakis, I. Bosaeus, L. Ohman, E. Björnsson, Altered postprandial glucose, insulin, leptin, and ghrelin in liver cirrhosis: correlations with energy intake and resting energy expenditure. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 85, 808–815 (2007)
H. Ataseven, I.H. Bahcecioglu, N. Kuzu, M. Yalniz, S. Celebi, A. Erensoy, B. Ustundag, The levels of ghrelin, leptin, TNF-alpha, and IL-6 in liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma due to HBV and HDV infection. Mediators Inflamm. 2006, 78380–78385 (2006)
H. Takahashi, A. Kato, K. Onodera, K. Suzuki, Fasting plasma ghrelin levels reflect malnutrition state in patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatol. Res. 34, 117–123 (2006)
M. Breidert, T.F. Zimmermann, R. Schneider, G. Ehninger, G. Brabant, Ghrelin/Leptin-imbalance in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 112, 123–126 (2004)
F. Tacke, G. Brabant, E. Kruck, R. Horn, P. Schöffski, H. Hecker, M.P. Manns, C. Trautwein, Ghrelin in chronic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 38, 447–454 (2003)
M. Granado, A.I. Martín, M. López-Menduiña, A. López-Calderón, M.A. Villanúa, GH-releasing peptide-2 administration prevents liver inflammatory response in endotoxemia. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 294, E131–E141 (2008)
S.O. Işeri, G. Sener, B. Saglam, F. Ercan, N. Gedik, B.C. Yeğen, Ghrelin alleviates biliary obstruction-induced chronic hepatic injury in rats. Regul. Pept. 146, 73–79 (2008)
O. Kasımay, S.O. Işeri, A. Barlas, D. Bangir, C. Yeğen, S. Arbak, B.C. Yeğen, Ghrelin ameliorates pancreaticobiliary inflammation and associated remote organ injury in rats. Hepatol. Res. 36, 11–19 (2006)
H. Hosoda, M. Kojima, T. Mizushima, S. Shimizu, K. Kangawa, Structural divergence of human ghrelin. Identification of multiple ghrelin-derived molecules produced by post-translational processing. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 64–70 (2003)
X. Zhu, Y. Cao, K. Voodg, D.F. Steiner, On the processing of proghrelin to ghrelin. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 38867–38870 (2006)
M.A. Bednarek, S.D. Feighner, S.S. Pong, K.K. McKee, D.L. Hreniuk, M.V. Silva, V.A. Warren, A.D. Howard, L.H. Van Der Ploeg, J.V. Heck, Structure-function studies on the new growth hormone-releasing peptide, ghrelin: minimal sequence of ghrelin necessary for activation of growth hormone secretagogue receptor 1a. J. Med. Chem. 43, 4370–4376 (2000)
P. Cassoni, M. Papotti, C. Ghe, F. Catapano, A. Sapino, A. Graziani, R. Deghenghi, T. Reissmann, E. Ghigo, G. Muccioli, Identification, characterization, and biological activity of specific receptors for natural (ghrelin) and synthetic growth hormone secretagogues and analogs in human breast carcinomas and cell lines. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86, 1738–1745 (2001)
I. Bedendi, G. Alloatti, A. Marcantoni, D. Malan, F. Catapano, C. Ghe, R. Deghenghi, E. Ghigo, G. Muccioli, Cardiac effects of ghrelin and its endogenous derivatives des-octanoyl ghrelin and des-Gln14-ghrelin. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 476, 87–95 (2003)
N.M. Thompson, D.A. Gill, R. Davies, N. Loveridge, P.A. Houston, I.C. Robinson, T. Wells, Ghrelin and des-octanoyl ghrelin promote adipogenesis directly in vivo by a mechanism independent of the type 1a growth hormone secretagogue receptor. Endocrinology 145, 234–242 (2004)
K. Toshinai, H. Yamaguchi, Y.X. Sun, R.G. Smith, A. Yamanaka, T. Sakurai, Y. Date, M.S. Mondal, T. Shimbara, T. Kawagoe, N. Murakami, M. Miyazato, K. Kangawa, M. Nakazato, Des-acyl ghrelin induces food intake by a mechanism independent of the growth hormone secretagogue receptor. Endocrinology 147, 2306–2314 (2006)
C. Gauna, P.J. Delhanty, M.O. van Aken, J.A. Janssen, A.P. Themmen, L.J. Hofland, M. Culler, F. Broglio, E. Ghigo, A.J. van der Lely, Unacylated ghrelin is active on the INS-1E rat insulinoma cell line independently of the growth hormone secretagogue receptor type 1a and the corticotropin releasing factor 2 receptor. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 251, 103–111 (2006)
C. Gauna, F.M. Meyler, J.A. Janssen, P.J.D. Delhanty, T. Abribat, P. van Koetsveld, L.J. Hofland, F. Broglio, E. Ghigo, A.J. van der Lely, Administration of acylated ghrelin reduces insulin sensitivity, whereas the combination of acylated plus unacylated ghrelin strongly improves insulin sensitivity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89, 5035–5042 (2004)
M. Tschöp, R. Wawarta, R.L. Riepl, S. Friedrich, M. Bidlingmaier, R. Landgraf, C. Folwaczny, Post-prandial decrease of circulating human ghrelin levels. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 24, RC19–RC21 (2001)
K.E. Foster-Schubert, J. Overduin, C.E. Prudom, J. Liu, H.S. Callahan, B.D. Gaylinn, M.O. Thorner, D.E. Cummings, Acyl and total ghrelin are suppressed strongly by ingested proteins, weakly by lipids, and biphasically by carbohydrates. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 93, 1971–1979 (2008)
J. Liu, C.E. Prudom, R. Nass, S.S. Pezzoli, M.C. Oliveri, M.L. Johnson, P. Veldhuis, D.A. Gordon, A.D. Howard, D.R. Witcher, H.M. Geysen, B.D. Gaylinn, M.O. Thorner, Novel ghrelin assays provide evidence for independent regulation of ghrelin acylation and secretion in healthy young men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 93, 1980–1987 (2008)
G. Marchesini, U. Pagotto, E. Bugianesi, R. De Iasio, R. Manini, E. Vanni, R. Pasquali, N. Melchionda, M. Rizzetto, Low ghrelin concentrations in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease are related to insulin resistance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 88, 5674–5679 (2003)
G. Murdolo, P. Lucidi, C. Di Loreto, N. Parlanti, A. De Cicco, C. Fatone, C.G. Fanelli, G.B. Bolli, F. Santeusanio, P. De Feo, Insulin is required for prandial ghrelin suppression in humans. Diabetes 52, 2923–2927 (2003)
D.E. Flanagan, M.L. Evans, T.P. Monsod, F. Rife, R.A. Heptulla, W.V. Tamborlane, R.S. Sherwin, The influence of insulin on circulating ghrelin. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 284, E313–E316 (2003)
W.A.M. Blom, A. Stafleu, C. de Graaf, F.J. Kok, G. Schaafsma, H.F. Hendriks, Ghrelin response to carbohydrate-enriched breakfast is related to insulin. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 81, 367–375 (2005)
A. Caixas, C. Bashore, W. Nash, X. Pi-Sunyer, B. Laferrere, Insulin, unlike food intake, does not suppress ghrelin in human subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 87, 1902–1905 (2002)
G. Schaller, A. Schmidt, J. Pleiner, W. Woloszczuk, M. Woltz, A. Luger, Plasma ghrelin concentrations are not regulated by glucose or insulin: a double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover clamp study. Diabetes 5, 16–20 (2003)
R. Nass, L.S. Farhy, J. Liu, C.E. Prudom, M.L. Johnson, P. Veldhuis, S.S. Pezzoli, M.C. Oliveri, B.D. Gaylinn, H.M. Geysen, M.O. Thorner, Evidence for acyl-ghrelin modulation of growth hormone release in the fed state. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 93, 1988–1994 (2008)
F.M. Van der Toorn, J.A. Janssen, W.W. de Herder, F. Broglio, E. Ghigo, A.J. van der Lely, Central ghrelin production does not substantially contribute to systemic ghrelin concentration: a study inn two subjects with active acromegaly. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 147, 195–199 (2002)
A.L. Barkan, E.V. Dimaraki, S.K. Jessup, K.V. Symons, M. Ermolenko, C.A. Jaffe, Ghrelin secretion in humans is sexually dimorphic, suppressed by somatostatin, and not affected by the ambient growth hormone levels. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 88, 2180–2184 (2003)
Z. Jarkovska, M. Rosicka, J. Marek, V. Hana, V. Weiss, V. Justova, Z. Lacinová, M. Haluzík, M. Krsek, Plasma levels of total and active ghrelin in acromegaly and growth hormone deficiency. Physiol. Res. 55, 175–181 (2006)
M.L. Isidro, R. Nemiña, J. Garcia-Buela, S. Sangiao-Alvarellos, F. Cordido, Effect of oral glucose on acylated and total ghrelin secretion in acromegalic patients. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 28, 596–603 (2007)
V. Cappiello, C. Ronchi, P.S. Mospurgo, P. Epaminonda, P. Beck-Peccoz, A. Spada, Circulating ghrelin levels in basal conditions and during glucose tolerance test in acromegalic patients. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 147, 189–194 (2002)
P.U. Freda, C.M. Reyes, I.M. Conwell, R.E. Sundeen, S.L. Wardlaw, Serum ghrelin levels in acromegaly: effects of surgical and long-acting octreotide therapy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 88, 2037–2044 (2003)
J. Kozakowski, M. Rabijewski, W. Zgliczynski, Decreased in serum ghrelin levels in patients with acromegaly normalize after successful surgical treatment. Endokrynol. Pol. 56, 862–870 (2005)
E.T. Vestergaard, R. Dall, K.H. Lange, M. Kjaer, J.S. Christiansen, J.O. Jorgensen, The ghrelin response to exercise before and after growth hormone administration. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 92, 297–303 (2007)
H.J. Kim, L. Sangyeoup, T.W. Kim, H.H. Kim, T.Y. Jeon, Y.S. Yoon, S.W. Oh, H. Kwak, J.G. Lee, Effects of exercise-induced weight loss on acylated and unacylated ghrelin in overweight children. Clin. Endocrinol. 68, 416–422 (2008)
M. Perez-Fontán, F. Cordido, A. Rodriguez-Carmona, J. Peteiro, R. Garcia-Naveiro, J. Garcia-Buela, Plasma ghrelin levels in patients undergoing haemodialysis and peritoneal diálysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 19, 2095–2100 (2004)
M. Perez-Fontán, F. Cordido, A. Rodriguez-Carmona, R. Garcia-Naveiro, M.L. Isidro, P. Villaverde, J. Garcia-Buela, Acute plasma ghrelin and leptin responses to oral feeding or intraperitoneal hypertonic glucose-based dialysate in patients with chronic renal failure. Kidney Int. 2005(68), 2877–2885 (2005)
M. Pérez-Fontán, F. Cordido, A. Rodríguez-Carmona, M. Penín, H. Díaz-Cambre, A. López-Muñiz, S. Sangiao-Alvarellos, J. García-Buela, Short-term regulation of peptide YY secretion by a mixed meal or peritoneal glucose-based dialysate in patients with chronic renal failure. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 23, 3696–3703 (2008)
D.R. Matthews, J.P. Hosker, A.S. Rudenski, D.B. Naylor, D.F. Treacher, R.C. Turner, Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetología 28, 412–419 (1985)
Acknowledgements
We thank Rosa Nemiña, Ramón Pensado, Iria Brandón, and Sonia Pertega for his technical assistance. Supported in part by: FIS del Instituto de Salud Carlos III PI051024, PI070413 and Red de Grupos RGTO (G03/028, PI050983) and Xunta de Galicia PS07/12, PGIDT05PXIC91605PN, INCITE08ENA916110ES and Redes 2006/27, Spain.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diz-Lois, M.T., Garcia-Buela, J., Suarez, F. et al. Fasting and postprandial plasma ghrelin levels are decreased in patients with liver failure previous to liver transplantation. Endocr 35, 467–476 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-009-9170-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-009-9170-6