Abstract
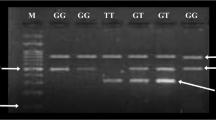
Background TRB3, a human homolog of Drosophila Tribbles, has been shown as a critical negative regulator of Akt (also known as protein kinase B), which is a key component in insulin signaling. In addition, TRB3 is another PPAR-target gene and functions as an important link between glucose and lipid metabolism. The Q84R polymorphic variant of TRB3 has been linked to insulin resistance and related clinical outcomes. However, it is unclear whether this polymorphism is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in the Chinese population. Methods In this study, we genotyped Q84R polymorphism in 177 patients with T2DM and 245 control subjects in Chinese population by using the polymerase chain reaction/ligase detection reaction (PCR/LDR) assay. Results No significant difference in the Q84R genotype frequency was observed between T2DM patients and controls (P = 0.642). In T2DM group, the Q84R variant in cases was associated with higher FINS, higher HOMA-IR, and lower LnISI (P = 0.003, 0.001, and 0.001, respectively). However, the changes in HOMA-IR and LnISI were not significant in controls (the P value is 0.098 and 0.203, respectively). In addition, FINS levels were also significantly increased from Q84Q to R84 in controls (P = 0.036). Conclusion Our data indicate that the TRB3 Q84R polymorphism is not associated with T2DM in Chinese population. However, the Q84R variant is associated with insulin resistance among T2DM patients in Chinese population.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
N.D. Wong, Metabolic syndrome: cardiovascular risk assessment and management. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 7(4), 259–272 (2007)
C.M. Taniguchi, B. Emanuelli, C.R. Kahn, Critical nodes in signalling pathways: insights into insulin action. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 7, 85–96 (2006)
S. Ghosh, R.M. Watanabe, T.T. Valle, E.R. Hauser, V.L. Magnuson, C.D. Langefeld, D.S. Ally, K.L. Mohlke, K. Silander, K. Kohtamaki, P. Chines, J. Balow Jr, G. Birznieks, J. Chang, W. Eldridge, M.R. Erdos, Z.E. Karanjawala, J.I. Knapp, K. Kudelko, C. Martin, A. Morales-Mena, A. Musick, T. Musick, C. Pfahl, R. Porter, J.B. Rayman, The Finland-United States investigation of non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus genetics (FUSION) study I: an autosomal genome scan for genes that predispose to type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 67, 1174–1185 (2000)
M.A. Permutt, J.C. Wasson, B.K. Suarez, J. Lin, J. Thomas, J. Meyer, S. Lewitzky, J.S. Rennich, A. Parker, L. DuPrat, S. Maruti, S. Chayen, B. Glaser, A genome scan for type 2 diabetes susceptibility loci in a genetically isolated population. Diabetes 50, 681–685 (2001)
K. Du, S. Herzig, R.N. Kulkarni, M. Montminy, TRB3: a Tribbles homolog that inhibits Akt/PKB activation by insulin in liver. Science 6, 1574–1577 (2003)
S.H. Koo, H. Satoh, S. Herzig et al., PGC-1 promotes insulin resistance in liver through PPAR-alpha-dependent induction of TRB-3. Nat. Med. 10, 530–534 (2004)
X.-P. Bi, H.-W. Tan, S.-S. Xing, Z.-H. Wang, M.-X. Tang, Y. Zhang, W. Zhang, Overexpression of TRB3 gene in adipose tissue of rats with high fructose-induced metabolic syndrome. Endocr. J. 55(4), 747–752 (2008)
S. Prudente, M.L. Hribal, E. FIex et al., The functional Q84R polymorphism of mammalian Tribbles homolog TRB3 is associated with insulin resistance and related cardiovascular risk in Caucasians from Italy. Diabetes 54, 2807–2811 (2005)
World Health Organization Definition, Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications: report of a WHO consultation. Part 1. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus (World Health Organization, Geneva, 1999)
S.G. Wannamethee, A.G. Shaper, I.J. Perry, K.G.M.M. Alberti, Alcohol consumption and the incidence of type II diabetes. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 56, 542–548 (2002)
Y. Onishi, M. Honda, T. Ogihara et al., Ethanol feeding induces insulin resistance with enhanced PI3-kinase activation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 303, 788–794 (2003)
L. He, F.A. Simmen, H.M. Mehendale et al., Chronic ethanol intake impairs insulin signaling in rats by disrupting Akt association with the cell membrane. Role of TRB3 in inhibition of Akt/protein kinase B activation. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 11126–11134 (2006)
S.M. Haffner, E. Kennedy, C. Gonzalez et al., A prospective analysis of the HOMA model. The Mexico City Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care 19, 1138–1141 (1996)
G.-w. Li, X.-r. Pan, A new insulin-sensitivity index for the population. Chin. J. Intern. Med. 32, 656–660 (1993)
R. Matsushima, N. Harada, N.J.G. Webster, Y.M. Tsutsumi, Y. Nakaya, Effect of TRB3 on insulin and nutrient-stimulated hepatic p70 S6 kinase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 29719–29729 (2006)
K.S. Walker, M. Deak, A. Paterson, K. Hudson, P. Cohen, D.R. Alessi, Activation of protein kinase B beta and gamma isoforms by insulin in vivo and by 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 in vitro: comparison with protein kinase B alpha. Biochem. J. 331, 299–308 (1998)
H. Cho, J. Mu, J.K. Kim, J.L. Thorvaldsen, Q. Chu, E.B. Crenshaw III, K.H. Kaestner, M.S. Bartolomei, G.I. Shulman, M.J. Birnbaum, Insulin resistance and a diabetes mellitus-like syndrome in mice lacking the protein kinase Akt2 (PKB beta). Science 292, 1728–1731 (2001)
D.R. Alessi, Discovery of PDK1, one of the missing links in insulin signal transduction. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 29, 1–14 (2001)
J. Großhans, E. Wieschaus, A genetic link between morphogenesis and cell division during formation of the ventral furrow in drosophila. Cell 101, 523–531 (2000)
J. Ding, S. Kato, K. Du, PI3K activates negative and positive signals to regulate TRB3 expression in hepatic cells. Exp. Cell Res. 314, 1566–1574 (2008)
P.B. Iynedjian, Lack of evidence for a role of TRB3/NIPK as an inhibitor of PKB-mediated insulin signalling in primary hepatocytes. Biochem. J. 386(Pt1), 113–118 (2005)
H. Okamoto, E. Latres, R. Liu, K. Thabet, A. Murphy, D. Valenzeula, G.D. Yancopoulos, T.N. Stitt, D.J. Glass, M.W. Sleeman, Genetic deletion of Trb3, the mammalian Drosophila tribbles homolog, displays normal hepatic insulin signaling and glucose homeostasis. Diabetes 56, 1350–1356 (2007)
A. Oku, M. Nawano, K. Ueta et al., Inhibitory effect of hyperglycemia on insulin-induced Akt/protein kinase B activation in skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 280, E816–E824 (2001)
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the excellent technical assistance of staff members working in Endocrine Disease Department of Gansu Provincial People’s Hospital and those working in MEC of Gansu Provincial People’s Hospital. This study was supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province (No. 0803RJZA067).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Z., Liu, J., Guo, Q. et al. Association of TRB3 gene Q84R polymorphism with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Chinese population. Endocr 35, 414–419 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-009-9162-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-009-9162-6