Abstract
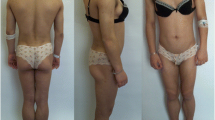
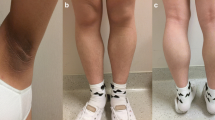
Dunnigan-type familial partial lipodystrophy (FPLD) is a rare monogenic adipose tissue disorder in which the affected subjects have increased predisposition to insulin resistance and related metabolic complications, such as glucose intolerance, diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hepatic steatosis. Our patient was a 35-year-old female who had been receiving insulin injection therapy for diabetes mellitus and was transferred to our hospital. She was diagnosed with FPLD on the basis of the following symptoms: increase in subcutaneous fat in the face, neck, and upper trunk; loss of subcutaneous fat in the lower limbs and the gluteal region. We found a heterozygous CGG to CAG transition in codon 482 of exon 8 in the gene encoding lamin A/C (LMNA), which leads to an arginine to glutamine substitution (R482Q). At the time of admission, her serum creatinine level was 8.4 mg/dl, and her blood urea nitrogen (BUN) level was 81 mg/dl. Her serum creatinine level was elevated and hemodialysis was performed twice every week. However, she died of cerebral hemorrhage 9 months after hemodialysis. Although it is uncommon for patients with FPLD to exhibit renal dysfunction and require hemodialysis, this case suggests the need for careful analysis of renal function in a patient with FPLD.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.G. Dunnigan, M.A. Cochrane, A. Kelly, J.W. Scott, Familial lipoatrophic diabetes with dominant transmission: a new syndrome. Q. J. Med. 43, 33–48 (1974)
S.N. Jackson, T.A. Howlett, P.G. McNally, S. O’Rahilly, R.C. Trembath, Dunnigan-Kobberling syndrome: an autosomal dominant form of partial lipodystrophy. Q. J. Med. 90, 27–36 (1997)
D.C. Robbins, E.S. Horton, O. Tulp, E.A. Sims, Familial partial lipodystrophy: complications of obesity in the non-obese? Metab. Clin. Exp. 31, 445–452 (1982)
W.A. Haque, F. Vuitch, A. Garg, Postmortem findings in patients with familial partial lipodystrophy, Dunnigan variety. Diabet. Med. 19, 1022–1025 (2002)
R.A. Hegele, Monogenic forms of insulin resistance: apertures that expose the common metabolic syndrome. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 14, 371–377 (2003)
H. Cao, R.A. Hegele, Nuclear lamin A/C R482Q mutation in Canadian kindreds with Dunnigan-type familial partial lipodystrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 9, 109–112 (2000)
R.A. Speckman, A. Garg, F. Du, L. Bennett, R. Veile, E. Arioglu, S.I. Taylor, M. Lovett, A.M. Bowcock, Mutational and haplotype analyses of families with familial partial lipodystrophy (Dunnigan variety) reveal recurrent missense mutations in the globular C-terminal domain of lamin A/C. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 66, 1192–1198 (2000)
S. Shackleton, D.J. Lloyd, S.N. Jackson, R. Evans, M.F. Niermeijer, B.M. Singh, H. Schmidt, G. Brabant, S. Kumar, P.N. Durrington, S. Gregory, S. O’Rahilly, R.C. Trembath, LMNA, encoding lamin A/C, is mutated in partial lipodystrophy. Nat. Genet. 24, 153–156 (2000)
J.M. Peters, R. Barnes, L. Bennett, W.M. Gitomer, A.M. Bowcock, A. Garg, Localization of the gene for familial partial lipodystrophy (Dunnigan variety) to chromosome 1q21–22. Nat. Genet. 18, 292–295 (1998)
A. Garg, Gender differences in the prevalence of metabolic complications in familial partial lipodystrophy (Dunnigan variety). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 85, 1776–1782 (2001)
R.A. Hegele, Premature atherosclerosis associated with monogenic insulin resistance. Circulation 103, 2225–2229 (2001)
W.A. Haque, E.A. Oral, K. Dietz, A.M. Bowcock, A.K. Agarwal, A. Garg, Risk factors for diabetes in familial partial lipodystrophy, Dunnigan variety. Diabetes Care 26, 1350–1355 (2003)
K. Iseki, K. Kinjo, Y. Kimura, A. Osawa, K. Fukiyama, Evidence for high risk of cerebral hemorrhage in chronic dialysis patients. Kidney Int. 44, 1086–1090 (1993)
F. Lin, H.J. Worman, Structural organization of the human gene encoding nuclear lamin A and nuclear lamin C. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 16321–16326 (1993)
H.J. Worman, J.C. Courvalin, The inner nuclear membrane. J. Membr. Biol. 177, 1–11 (2000)
N. Stuurman, S. Heins, U. Aebi, Nuclear lamins: their structure, assembly, and interactions. J. Struct. Biol. 122, 42–66 (1998)
G. Bonne, M.R. Di Barletta, S. Varnous, H.M. Becane, E.H. Hammouda, L. Merlini, F. Muntoni, C.R. Greenberg, F. Gary, J.A. Urtizberea, D. Duboc, M. Fardeau, D. Toniolo, K. Schwartz, Mutations in the gene encoding lamin A/C cause autosomal dominant Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Nat. Genet. 21, 285–288 (1999)
M. RaffaeleDiBarletta, E. Ricci, G. Galluzzi, P. Tonali, M. Mora, L. Morandi, A. Romorini, T. Voit, K.H. Orstavik, L. Merlini, C. Trevisan, V. Biancalana, I. Housmanowa-Petrusewicz, S. Bione, R. Ricotti, K. Schwartz, G. Bonne, D. Toniolo, Different mutations in the LMNA gene cause autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 66, 1407–1412 (2000)
A. Muchir, G. Bonne, A.J. van der Kooi, M. van Meegen, F. Baas, P.A. Bolhuis, M. de Visser, K. Schwartz, Identification of mutations in the gene encoding lamins A/C in autosomal dominant limb girdle muscular dystrophy with atrioventricular conduction disturbances (LGMD1B). Hum. Mol. Genet. 9, 1453–1459 (2000)
D. Fatkin, C. MacRae, T. Sasaki, M.R. Wolff, M. Porcu, M. Frenneaux, J. Atherton, H.J. Vidaillet Jr, S. Spudich, U. De Girolami, J.G. Seidman, C. Seidman, F. Muntoni, G. Muehle, W. Johnson, B. McDonough, Missense mutations in the rod domain of the lamin A/C gene as causes of dilated cardiomyopathy and conduction-system disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 341, 1715–1724 (1999)
A. De Sandre-Giovannoli, M. Chaouch, S. Kozlov, J.M. Vallat, M. Tazir, N. Kassouri, P. Szepetowski, T. Hammadouche, A. Vandenberghe, C.L. Stewart, D. Grid, N. Levy, Homozygous defects in LMNA, encoding lamin A/C nuclear-envelope proteins, cause autosomal recessive axonal neuropathy in human (Charcot-Marie-Tooth disorder type 2) and mouse. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 70, 726–736 (2002)
C. Vigouroux, J. Magré, M.C. Vantyghem, C. Bourut, O. Lascols, S. Shackleton, D.J. Lloyd, B. Guerci, G. Padova, P. Valensi, A. Grimaldi, R. Piquemal, P. Touraine, R.C. Trembath, J. Capeau, Lamin A/C gene: sex-determined expression of mutations in Dunnigan-type familial partial lipodystrophy and absence of coding mutations in congenital and acquired generalized lipoatrophy. Diabetes 49, 1958–1962 (2000)
G. Novelli, A. Muchir, F. Sangiuolo, A. Helbling-Leclerc, M.R. D’Apice, C. Massart, F. Capon, P. Sbraccia, M. Federici, R. Lauro, C. Tudisco, R. Pallotta, G. Scarano, B. Dallapiccola, L. Merlini, G. Bonne, Mandibuloacral dysplasia is caused by a mutation in LMNA-encoding lamin A/C. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 71, 426–431 (2002)
C. Musso, E. Javor, E. Cochran, J.E. Balow, P. Gorden, Spectrum of renal diseases associated with extreme forms of insulin resistance. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1, 616–622 (2006)
K.R. Owen, M. Donohoe, S. Ellard, T.J. Clarke, A.J. Nicholls, A.T. Hattersley, C. Bingham, Mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis type 2 associated with familial partial lipodystrophy (Dunnigan-Kobberling syndrome). Nephron. Clin. Pract. 96, c35–c38 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Imachi, H., Murao, K., Ohtsuka, S. et al. A case of Dunnigan-type familial partial lipodystrophy (FPLD) due to lamin A/C (LMNA) mutations complicated by end-stage renal disease. Endocr 35, 18–21 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-008-9127-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-008-9127-1