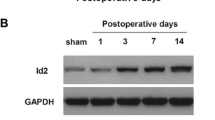
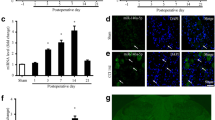
Abstract
The role of circular RNAs (circRNAs) in neuropathic pain is linked to the fundamental physiological mechanisms involved. However, the exact function of circRNAs in the context of neuropathic pain is still not fully understood. The functional impact of circGRIN2B on the excitability of dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons was investigated using siRNA or overexpression technology in conjunction with fluorescence in situ hybridization and whole-cell patch-clamp technology. The therapeutic efficacy of circGRIN2B in treating neuropathic pain was confirmed by assessing the pain threshold in a chronic constrictive injury (CCI) model. The interaction between circGRIN2B and NF-κB was examined through RNA pulldown, RIP, and mass spectrometry assays. CircGRIN2B knockdown significantly affected the action potential discharge frequency and the sodium-dependent potassium current flux (SLICK) in DRG neurons. Furthermore, knockdown of circGRIN2B dramatically reduced the SLICK channel protein and mRNA expression in vivo and in vitro. Our research confirmed the interaction between circGRIN2B and NF-κB. These findings demonstrated that circGRIN2B promotes the transcription of the SLICK gene by binding to NF-κB. In CCI rat models, the overexpression of circGRIN2B has been shown to hinder the progression of neuropathic pain, particularly by reducing mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia. Additionally, this upregulation significantly diminished the levels of the inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in the DRG. Upon reviewing these findings, it was determined that circGRIN2B may mitigate the onset of neuropathic pain by modulating the NF-κB/SLICK pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets produced and examined throughout the study can be obtained from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Bennett, G. J., & Xie, Y.-K. (1988). A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain, 33, 87–107.
Cao, S., Deng, W., Li, Y., Qin, B., Zhang, L., Yu, S., Xie, P., Xiao, Z., & Yu, T. (2017). Chronic constriction injury of sciatic nerve changes circular RNA expression in rat spinal dorsal horn. Journal of Pain Research, 10, 1687–1696.
Finnerup, N. B., Kuner, R., & Jensen, T. S. (2020). Neuropathic pain: From mechanisms to treatment. Physiological Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00045.2019
Floris, G., Gillespie, A., Zanda, M. T., Dabrowski, K. R., & Sillivan, S. E. (2022). Heroin regulates orbitofrontal circular RNAs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23, 1453.
Gilron, I., Baron, R., & Jensen, T. (2015). Neuropathic pain: Principles of diagnosis and treatment. Mayo clinic proceedings (pp. 532–545). Elsevier.
Ji, L. J., Shi, J., Lu, J. M., & Qm, H. (2018). MiR-150 alleviates neuropathic pain via inhibiting toll-like receptor 5. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 119, 1017–1026.
Kim, G. E., & Kaczmarek, L. K. (2014). Emerging role of the KCNT1 Slack channel in intellectual disability. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 8, 209.
Ma, X., Hao, C., Zhang, Z., Jiang, H., Zhang, W., Huang, J., Chen, X., & Yang, W. (2021). Shenjinhuoxue mixture attenuates inflammation, pain, and cartilage degeneration by inhibiting TLR-4 and NF-κB activation in rats with osteoarthritis: A synergistic combination of multitarget active phytochemicals. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2021, 1–21.
Miao, J., Zhou, X., Ji, T., & Chen, G. (2020). NF-κB p65-dependent transcriptional regulation of histone deacetylase 2 contributes to the chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain via the microRNA-183/TXNIP/NLRP3 axis. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 17, 1–13.
Misir, S., Wu, N., & Yang, B. B. (2022). Specific expression and functions of circular RNAs. Cell Death & Differentiation, 29, 481–491.
Patop, I. L., Wüst, S., & Kadener, S. (2019). Past, present, and future of circ RNA s. The EMBO Journal, 38, e100836.
Rybak-Wolf, A., Stottmeister, C., Glažar, P., Jens, M., Pino, N., Giusti, S., Hanan, M., Behm, M., Bartok, O., & Ashwal-Fluss, R. (2015). Circular RNAs in the mammalian brain are highly abundant, conserved, and dynamically expressed. Molecular Cell, 58, 870–885.
Sa, T., Nie, X., Ruan, J., Cao, Y., Kang, J., & Ding, C. (2022). Circular RNA circNFKB1 promotes osteoarthritis progression through interacting with ENO1 and sustaining NF-κB signaling. Cell Death & Disease, 13, 695.
Sabo, S. L., Lahr, J. M., Offer, M., Weekes, A. L., & Sceniak, M. P. (2023). GRIN2B-related neurodevelopmental disorder: Current understanding of pathophysiological mechanisms. Frontiers in Synaptic Neuroscience, 14, 1090865.
Sun, J., Zhou, Y.-q, Xu, B.-y, Li, J.-y, Zhang, L.-q, Li, D.-y, Zhang, S., Wu, J.-y, Gao, S.-j, & Ye, D.-W. (2021). STING/NF-κB/IL-6-mediated inflammation in microglia contributes to spared nerve injury (SNI)-induced pain initiation. Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26269
Tomasello, D. L., Gancarz-Kausch, A. M., Dietz, D. M., & Bhattacharjee, A. (2015). Transcriptional regulation of the sodium-activated potassium channel SLICK (KCNT2) promoter by nuclear factor-κB. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 290, 18575–18583.
Tomasello, D. L., Hurley, E., Wrabetz, L., & Bhattacharjee, A. (2017). Slick (Kcnt2) sodium-activated potassium channels limit peptidergic nociceptor excitability and hyperalgesia. Journal of Experimental Neuroscience, 11, 1179069517726996.
Wang, K., Bao, J.-P., Zhou, Z.-M., Mao, L., & Wu, X.-T. (2022). CircRNA-associated ceRNA network reveals focal adhesion and metabolism pathways in neuropathic pain. Journal of Oncology. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7246904
Wang, K., Wang, F., Bao, J.-P., Xie, Z.-Y., Chen, L., Zhou, B.-Y., Xie, X.-H., & Wu, X.-T. (2017). Tumor necrosis factor α modulates sodium-activated potassium channel SLICK in rat dorsal horn neurons via p38 MAPK activation pathway. Journal of Pain Research, 10, 1265–1271.
Xia, L. X., Ke, C., & Lu, J. M. (2018). NEAT1 contributes to neuropathic pain development through targeting miR-381/HMGB1 axis in CCI rat models. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 233, 7103–7111.
Zhang, R.-X., Yan, X.-B., Gu, Y.-H., Huang, D., Gan, L., Han, R., & Huang, L.-H. (2013). Gene silencing of NR2B-containing NMDA receptor by intrathecal injection of short hairpin RNA reduces formalin-induced nociception in C57BL/6 mouse. International Journal of Neuroscience, 123, 650–656.
Zhou, J., Xiong, Q., Chen, H., Yang, C., & Fan, Y. (2017). Identification of the spinal expression profile of non-coding RNAs involved in neuropathic pain following spared nerve injury by sequence analysis. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience, 10, 91.
Acknowledgements
The authors express their gratitude to the editorial staff of American Journal Experts (AJE) for their valuable contribution in refining and enhancing the quality of the article.
Funding
This research was funded by a Grant (No. 81902252) from the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by KW, ZS, and XP. Financial support and supervision were completed by XW, KW, and LM. The first draft of the manuscript was written by KW, and all the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that there are no commercial or financial affiliations that could pose a latent conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All surgical procedures and experiments conducted in this study received approval from the Southeast University Ethical Committee (No. 20190218002). These procedures were carried out in strict compliance with the US National Institutes of Health’s Guidelines for the Care and Treatment of Laboratory Animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, K., Shen, Z., Peng, X. et al. Circular RNA-GRIN2B Suppresses Neuropathic Pain by Targeting the NF-κB/SLICK Pathway. Neuromol Med 26, 12 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-024-08774-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-024-08774-5