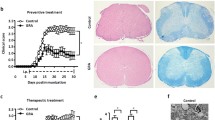
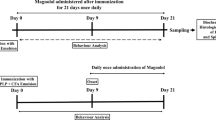
Abstract
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune inflammatory disease of the central nervous system (CNS). Sinomenine (SIN), a bioactive alkaloid extracted from the Chinese medicinal plant Sinomenium acutum, has powerful anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive therapeutic benefits. In our previous research, we found that SIN increased resistance to oxidative stress via the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) signaling pathway in PC12 neuronal cells. However, whether SIN can improve the symptoms and pathological features of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), a murine model of MS, via the Nrf2 signaling pathway remains unclear. EAE was immunized followed by SIN treatment. Then we evaluated the effects of SIN in EAE. Subsequently, primary microglia were cultured to explore the effect of SIN on microglia activation. Further, the levels of Nrf2 and its downstream molecules were detected to assess the molecular mechanisms of SIN. We demonstrated that SIN effectively ameliorated the severity of EAE, accompanied by a reduction in the demyelination, axonal damage and inhibition of inflammatory cell infiltration. Mechanistically, SIN decreased the inflammatory cytokines expression, and suppressed microglia and astrocytes activation in EAE mice. Furthermore, SIN suppressed lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced microglial activation and the production of pro-inflammatory factors in vitro. Moreover, SIN inhibited oxidative stress via the activation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Our work proves that SIN exerts its neuroprotective effects by the Nrf2-dependent anti-oxidative stress and diminishing neuroinflammation, suggesting that the “antioxiflammation” effect of SIN is expected to be an ideal treatment strategy for MS/EAE.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and analyzed in the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- AOPP:
-
Advanced oxidation protein products
- ARE:
-
Antioxidant-responsive elements
- BBB:
-
Blood-brain barrier
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- cDNA:
-
Complementary DNA
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- COX-2:
-
Cyclooxygenase-2
- DAPI:
-
4′, 6-diamidino‐2‐phenylindole
- dHEt:
-
Dihydroethidium
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- DNA:
-
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- EAE:
-
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- Et:
-
Ethidium
- FITC:
-
Fluorescein isothiocyanate
- GFAP:
-
Glial fibrillary acidic protein
- GM-CSF:
-
Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor
- H&E:
-
Hematoxylin and eosin
- HO-1:
-
Heme oxygenase-1
- i.p.:
-
Intraperitoneal injection
- Iba1:
-
Ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule 1
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- iNOS:
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
- LFB:
-
Luxol fast blue
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- MBP:
-
Myelin basic protein
- MCP-1:
-
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- MOG:
-
Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein
- MS:
-
Multiple sclerosis
- NF:
-
Neurofilaments
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- NQO1:
-
NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1
- Nrf2:
-
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2
- NADPH:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- PFA:
-
Paraformaldehyde
- qPCR:
-
Quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- RNA:
-
Ribonucleic acid
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SD:
-
Standard deviation of the mean
- SIN:
-
Sinomenine
- TBST:
-
Tris-buffered saline/0.1% Tween-20
- Th:
-
T helper
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
References
AbdulSalam, S. F., Thowfeik, F. S., & Merino, E. J. (2016). Excessive reactive oxygen species and exotic DNA lesions as an exploitable liability. Biochemistry, 55(38), 5341–5352. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00703.
Adamczyk, B., & Adamczyk-Sowa, M. (2016). New Insights into the Role of Oxidative Stress Mechanisms in the Pathophysiology and Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2016, 1973834, https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/1973834.
Adamczyk-Sowa, M., Sowa, P., Adamczyk, J., Niedziela, N., Misiolek, H., Owczarek, M., et al. (2016). Effect of melatonin supplementation on plasma lipid hydroperoxides, homocysteine concentration and chronic fatigue syndrome in multiple sclerosis patients treated with interferons-beta and mitoxantrone. Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology, 67(2), 235–242.
Blaser, H., Dostert, C., Mak, T. W., & Brenner, D. (2016). TNF and ROS crosstalk in inflammation. Trends in Cell Biology, 26(4), 249–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2015.12.002.
Brambilla, R. (2019). The contribution of astrocytes to the neuroinflammatory response in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Acta Neuropathologica, 137(5), 757–783. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-019-01980-7.
Brieger, K., Schiavone, S., Miller, F. J. Jr., & Krause, K. H. (2012). Reactive oxygen species: From health to disease. Swiss Medical Weekly, 142, w13659. https://doi.org/10.4414/smw.2012.13659.
Buendia, I., Michalska, P., Navarro, E., Gameiro, I., Egea, J., & Leon, R. (2016). Nrf2-ARE pathway: An emerging target against oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 157, 84–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2015.11.003.
Choi, B. Y., Kim, J. H., Kho, A. R., Kim, I. Y., Lee, S. H., Lee, B. E., et al. (2015). Inhibition of NADPH oxidase activation reduces EAE-induced white matter damage in mice. J Neuroinflammation, 12, 104. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-015-0325-5.
Choi, J. H., Oh, J., Lee, M. J., Bae, H., Ko, S. G., Nah, S. Y., et al. (2021). Inhibition of lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1–3 deteriorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by inducing oxidative stress. J Neuroinflammation, 18(1), 240. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-021-02278-w.
Chu, F., Shi, M., Zheng, C., Shen, D., Zhu, J., Zheng, X., et al. (2018). The roles of macrophages and microglia in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Journal of Neuroimmunology, 318, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2018.02.015.
Constantinescu, C. S., Farooqi, N., O’Brien, K., & Gran, B. (2011). Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) as a model for multiple sclerosis (MS). British Journal of Pharmacology, 164(4), 1079–1106. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01302.x.
Di Meo, S., Reed, T. T., Venditti, P., & Victor, V. M. (2016). Role of ROS and RNS Sources in Physiological and Pathological Conditions. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2016, 1245049, https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/1245049.
Ding, C., Li, Y., Sun, Y., Wu, Y., Wang, F., Liu, C., et al. (2022). Sinomenium acutum: A Comprehensive Review of its Botany, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology and clinical application. American Journal of Chinese Medicine, 50(5), 1219–1253. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0192415X22500501.
Fan, H., Shu, Q., Guan, X., Zhao, J., Yan, J., Li, X., et al. (2017). Sinomenine protects PC12 neuronal cells against H2O2-induced cytotoxicity and oxidative stress via a ROS-dependent Up-regulation of endogenous antioxidant system. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology, 37(8), 1387–1398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-017-0469-1.
Gao, W. J., Liu, J. X., Xie, Y., Luo, P., Liu, Z. Q., Liu, L., et al. (2021). Suppression of macrophage migration by down-regulating Src/FAK/P130Cas activation contributed to the anti-inflammatory activity of sinomenine. Pharmacological Research, 167, 105513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105513.
Gu, B., Zeng, Y., Yin, C., Wang, H., Yang, X., Wang, S., et al. (2012). Sinomenine reduces iNOS expression via inhibiting the T-bet IFN-gamma pathway in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in rats. J Biomed Res, 26(6), 448–455. https://doi.org/10.7555/JBR.26.20110114.
Huppert, J., Closhen, D., Croxford, A., White, R., Kulig, P., Pietrowski, E., et al. (2010). Cellular mechanisms of IL-17-induced blood-brain barrier disruption. The Faseb Journal, 24(4), 1023–1034. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.09-141978.
Jiang, X. M., Hu, J. H., Wang, L. L., Ma, C., Wang, X., & Liu, X. L. (2018). Ulinastatin alleviates neurological deficiencies evoked by transient cerebral ischemia via improving autophagy, Nrf-2-ARE and apoptosis signals in hippocampus. Physiological Research, 67(4), 637–646. https://doi.org/10.33549/physiolres.933780.
Jiménez-Villegas, J., Kirby, J., Mata, A., Cadenas, S., Turner, M. R., Malaspina, A., et al. (2022). Dipeptide repeat Pathology in C9orf72-ALS is Associated with Redox, mitochondrial and NRF2 pathway imbalance. Antioxidants (Basel), 11(10), https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11101897.
Kim, R. Y., Hoffman, A. S., Itoh, N., Ao, Y., Spence, R., Sofroniew, M. V., et al. (2014). Astrocyte CCL2 sustains immune cell infiltration in chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Journal of Neuroimmunology, 274(1–2), 53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2014.06.009.
Kim, T. W., Kim, Y., Jung, W., Kim, D. E., Keum, H., Son, Y., et al. (2021). Bilirubin nanomedicine ameliorates the progression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by modulating dendritic cells. Journal of Controlled Release : Official Journal of the Controlled Release Society, 331, 74–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.01.019.
Kong, W., Hooper, K. M., & Ganea, D. (2016). The natural dual cyclooxygenase and 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor flavocoxid is protective in EAE through effects on Th1/Th17 differentiation and macrophage/microglia activation. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, 53, 59–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2015.11.002.
Kuo, P. C., Weng, W. T., Scofield, B. A., Paraiso, H. C., Brown, D. A., Wang, P. Y., et al. (2020). Dimethyl itaconate, an itaconate derivative, exhibits immunomodulatory effects on neuroinflammation in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroinflammation, 17(1), 138. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-020-01768-7.
Lassmann, H., van Horssen, J., & Mahad, D. (2012). Progressive multiple sclerosis: Pathology and pathogenesis. Nat Rev Neurol, 8(11), 647–656. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2012.168.
Li, Q., Zhou, W., Wang, Y., Kou, F., Lyu, C., & Wei, H. (2020). Metabolic mechanism and anti-inflammation effects of sinomenine and its major metabolites N-demethylsinomenine and sinomenine-N-oxide. Life Sciences, 261, 118433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118433.
Liang, L., Gao, C., Luo, M., Wang, W., Zhao, C., Zu, Y., et al. (2013). Dihydroquercetin (DHQ) induced HO-1 and NQO1 expression against oxidative stress through the Nrf2-dependent antioxidant pathway. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 61(11), 2755–2761. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf304768p.
Liddell, J. R. (2017). Are astrocytes the predominant cell type for activation of Nrf2 in aging and neurodegeneration? Antioxidants (Basel), 6(3), https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox6030065.
Lin, M. T., & Beal, M. F. (2006). Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature, 443(7113), 787–795. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05292.
Mayo, L., Trauger, S. A., Blain, M., Nadeau, M., Patel, B., Alvarez, J. I., et al. (2014). Regulation of astrocyte activation by glycolipids drives chronic CNS inflammation. Nature Medicine, 20(10), 1147–1156. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3681.
McGinley, A. M., Edwards, S. C., Raverdeau, M., & Mills, K. H. G. (2018). Th17cells, gammadelta T cells and their interplay in EAE and multiple sclerosis. Journal of Autoimmunity. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2018.01.001.
Mendiola, A. S., Ryu, J. K., Bardehle, S., Meyer-Franke, A., Ang, K. K., Wilson, C., et al. (2020). Transcriptional profiling and therapeutic targeting of oxidative stress in neuroinflammation. Nature Immunology, 21(5), 513–524. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-020-0654-0.
Michalickova, D., Kotur-Stevuljevic, J., Miljkovic, M., Dikic, N., Kostic-Vucicevic, M., Andjelkovic, M., et al. (2018). Effects of Probiotic supplementation on selected parameters of blood prooxidant-antioxidant balance in Elite athletes: A double-blind randomized placebo-controlled study. J Hum Kinet, 64, 111–122. https://doi.org/10.1515/hukin-2017-0203.
Michalickova, D., Sima, M., & Slanar, O. (2020). New insights in the mechanisms of impaired redox signaling and its interplay with inflammation and immunity in multiple sclerosis. Physiological Research, 69(1), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.33549/physiolres.934276.
Mills, K. H. (2011). TLR-dependent T cell activation in autoimmunity. Nature Reviews Immunology, 11(12), 807–822. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3095.
Morgan, M. J., & Liu, Z. G. (2011). Crosstalk of reactive oxygen species and NF-kappaB signaling. Cell Research, 21(1), 103–115. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2010.178.
Mossakowski, A. A., Pohlan, J., Bremer, D., Lindquist, R., Millward, J. M., Bock, M., et al. (2015). Tracking CNS and systemic sources of oxidative stress during the course of chronic neuroinflammation. Acta Neuropathologica, 130(6), 799–814. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-015-1497-x.
Niedzielska, E., Smaga, I., Gawlik, M., Moniczewski, A., Stankowicz, P., Pera, J., et al. (2016). Oxidative stress in neurodegenerative Diseases. Molecular Neurobiology, 53(6), 4094–4125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9337-5.
Ramaglia, V., Rojas, O., Naouar, I., & Gommerman, J. L. (2021). The ins and outs of Central Nervous System Inflammation-Lessons learned from multiple sclerosis. Annual Review of Immunology, 39, 199–226. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-immunol-093019-124155.
Rojo, A. I., McBean, G., Cindric, M., Egea, J., Lopez, M. G., Rada, P., et al. (2014). Redox control of microglial function: Molecular mechanisms and functional significance. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 21(12), 1766–1801. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2013.5745.
Rothhammer, V., Borucki, D. M., Tjon, E. C., Takenaka, M. C., Chao, C. C., Ardura-Fabregat, A., et al. (2018). Microglial control of astrocytes in response to microbial metabolites. Nature, 557(7707), 724–728. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0119-x.
Schattling, B., Steinbach, K., Thies, E., Kruse, M., Menigoz, A., Ufer, F., et al. (2012). TRPM4 cation channel mediates axonal and neuronal degeneration in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis. Nature Medicine, 18(12), 1805–1811. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3015.
Sies, H., & Jones, D. P. (2020). Reactive oxygen species (ROS) as pleiotropic physiological signalling agents. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 21(7), 363–383. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-020-0230-3.
Sies, H., Berndt, C., & Jones, D. P. (2017). Oxidative stress. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 86, 715–748. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-061516-045037.
Silva-Islas, C. A., & Maldonado, P. D. (2018). Canonical and non-canonical mechanisms of Nrf2 activation. Pharmacological Research, 134, 92–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2018.06.013.
Simpson, D. S. A., & Oliver, P. L. (2020). ROS Generation in Microglia: Understanding oxidative stress and inflammation in neurodegenerative disease. Antioxidants (Basel), 9(8), https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9080743.
Sykiotis, G. P. (2021). Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Antioxidants (Basel), 10(6), https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10060828.
Tanabe, S., Saitoh, S., Miyajima, H., Itokazu, T., & Yamashita, T. (2019). Microglia suppress the secondary progression of autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Glia, 67(9), 1694–1704. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.23640.
Thompson, A. J., Banwell, B. L., Barkhof, F., Carroll, W. M., Coetzee, T., Comi, G., et al. (2018a). Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: 2017 revisions of the McDonald criteria. The Lancet Neurology, 17(2), 162–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(17)30470-2.
Thompson, A. J., Baranzini, S. E., Geurts, J., Hemmer, B., & Ciccarelli, O. (2018b). Multiple sclerosis. The Lancet, 391(10130), 1622–1636. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(18)30481-1.
Valacchi, G., Virgili, F., Cervellati, C., & Pecorelli, A. (2018). OxInflammation: From Subclinical Condition to Pathological Biomarker. Frontiers in Physiology, 9, 858. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.00858.
van den Hoogen, W. J., Laman, J. D., & t Hart, B. A. (2017). Modulation of multiple sclerosis and its animal Model Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis by Food and Gut Microbiota. Frontiers in Immunology, 8, 1081. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.01081.
Wang, Y., Cao, L., Xu, L. M., Cao, F. F., Peng, B., Zhang, X., et al. (2015). Celastrol ameliorates EAE induction by suppressing pathogenic T cell responses in the Peripheral and Central Nervous Systems. Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology : The Official Journal of the Society on Neuroimmune Pharmacology, 10(3), 506–516. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-015-9598-9.
Weng, W. T., Kuo, P. C., Brown, D. A., Scofield, B. A., Furnas, D., Paraiso, H. C., et al. (2021). 4-Ethylguaiacol modulates neuroinflammation and Th1/Th17 differentiation to ameliorate disease severity in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroinflammation, 18(1), 110. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-021-02143-w.
Witte, M. E., Mahad, D. J., Lassmann, H., & van Horssen, J. (2014). Mitochondrial dysfunction contributes to neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis. Trends in Molecular Medicine, 20(3), 179–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2013.11.007.
Xie, L., Saimaier, K., Wang, C., Yang, J., Han, M., Lv, J., et al. (2021). Methyl acetate arrests Th1 in peripheral immune system and alleviates CNS inflammation in EAE. International Immunopharmacology, 101(Pt B), 108291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108291.
Yang, T., Zha, Z., Yang, X., Kang, Y., Wang, X., Tong, Y., et al. (2021). Neuroprotective Effects of Fingolimod supplement on the retina and Optic nerve in the mouse model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Front Neurosci, 15, 663541. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2021.663541.
Zhang, Y., Zou, B., Tan, Y., Su, J., Wang, Y., Xu, J., et al. (2019). Sinomenine inhibits osteolysis in breast cancer by reducing IL-8/CXCR1 and c-Fos/NFATc1 signaling. Pharmacological Research, 142, 140–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2019.02.015.
Zhao, Z., Xiao, J., Wang, J., Dong, W., Peng, Z., & An, D. (2015). Anti-inflammatory effects of novel sinomenine derivatives. International Immunopharmacology, 29(2), 354–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2015.10.030.
Zheng, X., Li, W., Xu, H., Liu, J., Ren, L., Yang, Y., et al. (2021). Sinomenine ester derivative inhibits glioblastoma by inducing mitochondria-dependent apoptosis and autophagy by PI3K/AKT/mTOR and AMPK/mTOR pathway. Acta Pharm Sin B, 11(11), 3465–3480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2021.05.027.
Zhong, S. S., Xiang, Y. J., Liu, P. J., He, Y., Yang, T. T., Wang, Y. Y., et al. (2017). Effect of Cordyceps sinensis on the treatment of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: A pilot study on mice Model. Chin Med J (Engl), 130(19), 2296–2301. https://doi.org/10.4103/0366-6999.215335.
Zhou, J., Cai, W., Jin, M., Xu, J., Wang, Y., Xiao, Y., et al. (2015). 18beta-glycyrrhetinic acid suppresses experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis through inhibition of microglia activation and promotion of remyelination. Scientific Reports, 5, 13713. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep13713.
Zilkha-Falb, R., Rachutin-Zalogin, T., Cleaver, L., Gurevich, M., & Achiron, A. (2020). RAM-589.555 favors neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory profile of CNS-resident glial cells in acute relapse EAE affected mice. J Neuroinflammation, 17(1), 313. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-020-01983-2.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant nos. U1504808 and 81801201), the Henan Provincial Key R&D and Promotion Project (Grant no. 212102311042) and the Henan Provincial Science and Technology R&D Project (Grant no. 222103810048).
Funding
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant nos. U1504808 and 81801201), the Henan Provincial Key R&D and Promotion Project (Grant no. 212102311042) and the Henan Provincial Science and Technology R&D Project (Grant no. 222103810048).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hua Fan, Yanhui Yang, and Dongmei Wang conceived and designed the experiments; Yang Yang, Qianqian Bai, Xiaofei Shi, and Lele Zhang performed the experiments; Yang Yang and Qianqian Bai analyzed the data; Hua Fan, Yang Yang, and Qianqian Bai wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, H., Yang, Y., Bai, Q. et al. Neuroprotective Effects of Sinomenine on Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis via Anti-Inflammatory and Nrf2-Dependent Anti-Oxidative Stress Activity. Neuromol Med 25, 545–562 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-023-08756-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-023-08756-z