Abstract
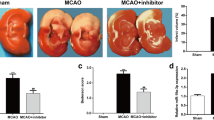
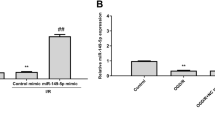
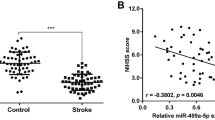
MicroRNA (miRNA) miR-143-3p has been reported to participate in the progression of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury, but its function in cerebral I/R injury remains unclear. Mice were subjected to 60 min of cerebral ischemia followed by different times of reperfusion to construct an I/R injury model in vivo. Human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells were treated with oxygen–glucose deprivation (OGD) for 2 h followed by different times of re-oxygenation to establish I/R injury model in vitro. Neurological deficit was assessed by a five-point score. Infarct volume was detected using 2, 3, 5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining. The expression of miR-143-3p was evaluated by qRT-PCR. The expression levels of FSTL1, Bcl-2, Bax and cleaved caspase-3 proteins were detected by western blot. The relationship between miR-143-3p and FSTL1 was explored by luciferase reporter assay. Cell viability was measured by CCK-8 assay. Cell apoptosis was evaluated by TUNEL staining and flow cytometry. MiR-143-3p was significantly upregulated during cerebral I/R injury both in vivo and in vitro. Inhibition of miR-143-3p effectively reduced I/R-induced neurological deficit score and infarct volume in vivo, and enhanced cell viability, while decreased cell apoptosis and LDH release of OGD/R-treated SH-SY5Y cells in vitro. Meanwhile, inhibition of miR-143-3p obviously decreased the expression levels of Bax and cleaved caspase-3, while increased the expression levels of Bcl-2. In addition, these changes induced by miR-143-3p inhibition in vitro was effectively reversed by silencing of FSTL1. Our results demonstrated that inhibition of miR-143-3p protected against cerebral I/R injury through targeting FSTL1.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author: * Zhenguo Liu, Intensive Care Unit, Shaanxi Provincial People’s Hospital, No. 256 Friendship (Youyi) West Road, Xi’an City, Shaanxi Province, 710068, PR. China. The data are not publicly available due to their containing information that could compromise the privacy of research participants.
References
Barthels, D., & Das, H. (2020). Current advances in ischemic stroke research and therapies. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 1866(4), 165260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.09.012
Bredesen, D. E., Rao, R. V., & Mehlen, P. (2006). Cell death in the nervous system. Nature, 443(7113), 796–802. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05293
Chang, L., Shi, R., Wang, X., & Bao, Y (2020) Gypenoside A protects ischemia/reperfusion injuries by suppressing miR-143–3p level via the activation of AMPK/Foxo1 pathway. 46(3): 432–440, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.1601.
Cheng, J., Uchida, M., Zhang, W., Grafe, M. R., Herson, P. S., & Hurn, P. D. (2011). Role of salt-induced kinase 1 in androgen neuroprotection against cerebral ischemia. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 31(1), 339–350. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2010.98
Ghafouri-Fard, S., Shoorei, H., & Taheri, M. (2020). Non-coding RNAs participate in the ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy, 129, 110419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110419
Hassan, M., Watari, H., AbuAlmaaty, A., Ohba, Y., & Sakuragi, N. (2014). Apoptosis and molecular targeting therapy in cancer. BioMed Research International, 2014, 150845. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/150845
Hu, Z., Zhao, P., Zhang, K., Zang, L., Liao, H., & Ma, W. (2020). Hsa_circ_0011290 regulates proliferation, apoptosis and glycolytic phenotype in papillary thyroid cancer via miR-1252/ FSTL1 signal pathway. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 685, 108353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2020.108353
Huang, L., Ma, Q., Li, Y., Li, B., & Zhang, L. (2018). Inhibition of microRNA-210 suppresses pro-inflammatory response and reduces acute brain injury of ischemic stroke in mice. Experimental Neurology, 300, 41–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2017.10.024
Kalogeris, T., Baines, C. P., Krenz, M., & Korthuis, R. J. (2016). Ischemia/Reperfusion. Compr Physiol, 7(1), 113–170. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphy.c160006
Li, D., Zhang, M., Zhang, Q., Wang, Y., Song, X., & Zhang, Q. (2015). Functional recovery after acute intravenous administration of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Intractable Rare Dis Res, 4(2), 98–104. https://doi.org/10.5582/irdr.2015.01010
Li, K. S., Jiang, W. P., Li, Q. C., Zhang, H. W., Bai, Y., Zhang, X., et al. (2020). MiR-29a in mesenchymal stem cells inhibits FSTL1 secretion and promotes cardiac myocyte apoptosis in hypoxia-reoxygenation injury. Cardiovasc Pathol, 46, 107180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carpath.2019.107180
Li, W., Dong, M., Chu, L., Feng, L., & Sun, X. (2019). MicroRNA-451 relieves inflammation in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion via the Toll-like receptor 4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep, 20(4), 3043–3054. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.10587
Liang, X., Hu, Q., Li, B., McBride, D., Bian, H., Spagnoli, P., et al. (2014). Follistatin-like 1 attenuates apoptosis via disco-interacting protein 2 homolog A/Akt pathway after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Stroke, 45(10), 3048–3054. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.114.006092
Lok, J., & Martin, L. J. (2002). Rapid subcellular redistribution of Bax precedes caspase-3 and endonuclease activation during excitotoxic neuronal apoptosis in rat brain. Journal of Neurotrauma, 19(7), 815–828. https://doi.org/10.1089/08977150260190410
Longa, E. Z., Weinstein, P. R., Carlson, S., & Cummins, R. (1989). Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke, 20(1), 84–91. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.20.1.84
Lu, T. X., & Rothenberg, M. E. (2018). MicroRNA. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 141(4), 1202–1207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2017.08.034
Mohr, A. M., & Mott, J. L. (2015). Overview of microRNA biology. Seminars in Liver Disease, 35(1), 3–11. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1397344
Murakami, K., Tanaka, M., Usui, T., Kawabata, D., Shiomi, A., Iguchi-Hashimoto, M., et al. (2012). Follistatin-related protein/follistatin-like 1 evokes an innate immune response via CD14 and toll-like receptor 4. FEBS Letters, 586(4), 319–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2012.01.010
O’Brien, J., Hayder, H., Zayed, Y., & Peng, C. (2018). Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 9, 402. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00402
Oshima, Y., Ouchi, N., Sato, K., Izumiya, Y., Pimentel, D. R., & Walsh, K. (2008). Follistatin-like 1 is an Akt-regulated cardioprotective factor that is secreted by the heart. Circulation, 117(24), 3099–3108. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.108.767673
Powers, W. J. (2020). Acute Ischemic Stroke. The New England journal of medicine, 383(3), 252–260. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMcp1917030
Qian, Y., Teng, Y., Li, Y., Lin, X., Guan, M., Li, Y., et al. (2019). MiR-143-3p suppresses the progression of nasal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting Bcl-2 and IGF1R. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 518(3), 492–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.08.075
Rink, C., & Khanna, S. (2011). MicroRNA in ischemic stroke etiology and pathology. Physiological Genomics, 43(10), 521–528. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00158.2010
Shi, H., Shen, H., Xu, J., Zhao, S., Yao, S., & Jiang, N. (2018). MiR-143-3p suppresses the progression of ovarian cancer. Am J Transl Res, 10(3), 866–874.
Shibanuma, M., Mashimo, J., Mita, A., Kuroki, T., & Nose, K. (1993). Cloning from a mouse osteoblastic cell line of a set of transforming-growth-factor-beta 1-regulated genes, one of which seems to encode a follistatin-related polypeptide. European journal of biochemistry, 217(1), 13–19. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18212.x
Sun, C., Jia, N., Li, R., Zhang, Z., Zhong, Y., & Han, K. (2020). miR-143-3p inhibition promotes neuronal survival in an Alzheimer’s disease cell model by targeting neuregulin-1. Folia Neuropathologica, 58(1), 10–21. https://doi.org/10.5114/fn.2020.94002
Sun, X., Dai, G., Yu, L., Hu, Q., Chen, J., & Guo, W. (2018). miR-143-3p inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion in osteosarcoma by targeting FOSL2. Sci Rep, 8(1), 606. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-18739-3
Tay, Y., Rinn, J., & Pandolfi, P. P. (2014). The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature, 505(7483), 344–352. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12986
Xia, C., Yang, Y., Kong, F., Kong, Q., & Shan, C. (2018). MiR-143-3p inhibits the proliferation, cell migration and invasion of human breast cancer cells by modulating the expression of MAPK7. Biochimie, 147, 98–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2018.01.003
Xiao, Y., Zhang, Y., Chen, Y., Li, J., Zhang, Z., Sun, Y., et al. (2019). Inhibition of MicroRNA-9-5p Protects Against Cardiac Remodeling Following Myocardial Infarction in Mice. Human Gene Therapy, 30(3), 286–301. https://doi.org/10.1089/hum.2018.059
Xie, F., Li, C., Zhang, X., Peng, W., & Wen, T. (2019). MiR-143-3p suppresses tumorigenesis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by targeting KRAS. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 119, 109424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109424
Yu, B., Yu, M., Zhang, H., Xie, D., Nie, W., & Shi, K. (2020). Suppression of miR-143-3p contributes to the anti-fibrosis effect of atorvastatin on myocardial tissues via the modulation of Smad2 activity. Experimental and Molecular Pathology, 112, 104346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexmp.2019.104346
Zhang, M., Wu, X., Xu, Y., He, M., Yang, J., Li, J., et al. (2017). The cystathionine β-synthase/hydrogen sulfide pathway contributes to microglia-mediated neuroinflammation following cerebral ischemia. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, 66, 332–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2017.07.156
Zhang, Z. M., Zhang, A. R., Xu, M., Lou, J., & Qiu, W. Q. (2017). TLR-4/miRNA-32-5p/FSTL1 signaling regulates mycobacterial survival and inflammatory responses in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected macrophages. Experimental Cell Research, 352(2), 313–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.02.025
Zhong, Y., Yu, C., & Qin, W. (2019). LncRNA SNHG14 promotes inflammatory response induced by cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through regulating miR-136-5p /ROCK1. Cancer Gene Therapy, 26(7–8), 234–247. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-018-0067-5
Zuo, X., Lu, J., Manaenko, A., Qi, X., Tang, J., Mei, Q., et al. (2019). MicroRNA-132 attenuates cerebral injury by protecting blood-brain-barrier in MCAO mice. Experimental Neurology, 316, 12–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.03.017
Funding
Not Applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shunda Wang, Zhenguo Liu: study concepts, literature research, clinical studies, data analysis, experimental studies, manuscript writing and review, study design, literature research, experimental studies and manuscript editing, definition of intellectual content, clinical studies, data acquisition and statistical analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All other authors have no conflicts of interest. We declare that we do not have any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
Ethical Approval
All producers were approved by Institutional Animal Care and Use committee of Shaanxi Provincial People’ s Hospital.
Consent to Participate
Procedures operated in this research were completed in keeping with the standards set out in the principles on ethical animal research outlined in the Basel Declaration.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Liu, Z. Inhibition of microRNA-143-3p Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Targeting FSTL1. Neuromol Med 23, 500–510 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-021-08650-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-021-08650-6