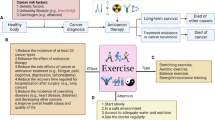
Abstract
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) and strength exercise are known to improve health markers, such as cardiovascular health, metabolic health, and cognitive function, as well as to reduce all-cause mortality. High-Intensity Functional Training (HIFT) is a training paradigm derived from both HIIT and strength exercise to elicit greater muscle recruitment than repetitive aerobic exercises, thereby improving both cardiovascular fitness and strength parameters. Herein, we provide a focused review of the known molecular mechanisms that underlie the beneficial effects of HIFT on cardiovascular, metabolic, and cognitive functions.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barak, B., Feldman, N., & Okun, E. (2015). Cardiovascular fitness and cognitive spatial learning in rodents and in humans. Journals of Gerontology. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, 70(9), 1059–1066. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glu162.
Ben-Zeev, T., Hirsh, T., Weiss, I., Gornstein, M., & Okun, E. (2020). The effects of high-intensity functional training (HIFT) on spatial learning, visual pattern separation and attention span in adolescents. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 14(165), 577390. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2020.577390.
Calverley, T. A., Ogoh, S., Marley, C. J., Steggall, M., Marchi, N., Brassard, P., et al. (2020). HIITing the brain with exercise: Mechanisms, consequences and practical recommendations. Journal of Physiology, 598(13), 2513–2530. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP275021.
Feito, Y., Heinrich, K. M., Butcher, S. J., & Poston, W. S. C. (2018). High-intensity functional training (HIFT): Definition and research implications for improved fitness. Sports (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/sports6030076.
Finkbeiner, S., Tavazoie, S. F., Maloratsky, A., Jacobs, K. M., Harris, K. M., & Greenberg, M. E. (1997). CREB: A major mediator of neuronal neurotrophin responses. Neuron, 19(5), 1031–1047. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80395-5.
Gehlert, S., Suhr, F., Gutsche, K., Willkomm, L., Kern, J., Jacko, D., et al. (2015). High force development augments skeletal muscle signalling in resistance exercise modes equalized for time under tension. Pflugers Archiv. European Journal of Physiology, 467(6), 1343–1356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-014-1579-y.
Hansen, C. G., Ng, Y. L., Lam, W. L., Plouffe, S. W., & Guan, K. L. (2015). The Hippo pathway effectors YAP and TAZ promote cell growth by modulating amino acid signaling to mTORC1. Cell Research, 25(12), 1299–1313. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2015.140.
Impey, S., McCorkle, S. R., Cha-Molstad, H., Dwyer, J. M., Yochum, G. S., Boss, J. M., et al. (2004). Defining the CREB regulon: A genome-wide analysis of transcription factor regulatory regions. Cell, 119(7), 1041–1054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2004.10.032.
Klossner, S., Durieux, A. C., Freyssenet, D., & Flueck, M. (2009). Mechano-transduction to muscle protein synthesis is modulated by FAK. European Journal of Applied Physiology, 106(3), 389–398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-009-1032-7.
Lee, M. C., Okamoto, M., Liu, Y. F., Inoue, K., Matsui, T., Nogami, H., et al. (2012). Voluntary resistance running with short distance enhances spatial memory related to hippocampal BDNF signaling. Journal of Applied Physiology (1985), 113(8), 1260–1266. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00869.2012.
McLeod, M., Breen, L., Hamilton, D. L., & Philp, A. (2016). Live strong and prosper: The importance of skeletal muscle strength for healthy ageing. Biogerontology, 17(3), 497–510. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-015-9631-7.
Morland, C., Andersson, K. A., Haugen, Ø., Hadzic, A., Kleppa, L., Gille, A., et al. (2017). Exercise induces cerebral VEGF and angiogenesis via the lactate receptor HCAR1. Nature Communication, 8, 15557. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15557.
Pedersen, B. K., & Febbraio, M. A. (2012). Muscles, exercise and obesity: Skeletal muscle as a secretory organ. Nature Reviews Endocrinology, 8(8), 457–465. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2012.49.
Stary, C. M., & Hogan, M. C. (2016). Cytosolic calcium transients are a determinant of contraction-induced HSP72 transcription in single skeletal muscle fibers. Journal of Applied Physiology (1985), 120(10), 1260–1266. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.01060.2015.
Tari, A. R., Norevik, C. S., Scrimgeour, N. R., Kobro-Flatmoen, A., Storm-Mathisen, J., Bergersen, L. H., et al. (2019). Are the neuroprotective effects of exercise training systemically mediated? Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases, 62(2), 94–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcad.2019.02.003.
Vaynman, S., Ying, Z., & Gomez-Pinilla, F. (2003). Interplay between brain-derived neurotrophic factor and signal transduction modulators in the regulation of the effects of exercise on synaptic-plasticity. Neuroscience, 122(3), 647–657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2003.08.001.
Wackerhage, H., Schoenfeld, B. J., Hamilton, D. L., Lehti, M., & Hulmi, J. J. (2019). Stimuli and sensors that initiate skeletal muscle hypertrophy following resistance exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology (1985), 126(1), 30–43. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00685.2018.
Wilke, J. (2020). Functional high-intensity exercise is more effective in acutely increasing working memory than aerobic walking: An exploratory randomized, controlled trial. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 12335. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-69139-z.
Wu, J., Weisshaar, N., Hotz-Wagenblatt, A., Madi, A., Ma, S., Mieg, A., et al. (2020). Skeletal muscle antagonizes antiviral CD8. Science Advances, 6(24), eaba3458. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aba3458.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Paul Feder fund for Alzheimer’s disease research. We would like to thank Yael Laure for editing this manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the Paul Feder fund for Alzheimer’s disease research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TBZ and EO wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben-Zeev, T., Okun, E. High-Intensity Functional Training: Molecular Mechanisms and Benefits. Neuromol Med 23, 335–338 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-020-08638-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-020-08638-8