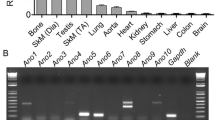
Abstract
GNE myopathy is a recessive adult onset, slowly progressive distal and proximal myopathy, caused by mutations in the GNE gene. The most frequent mutation in GNE myopathy patients is the Middle Eastern founder mutation M712T. We have generated Gne M712T/M712T knockin mice. A high mortality rate in the first generation due to renal failure was recorded (as previously described). However, the following Gne M712T/M712T offspring generations could be classified into 3 phenotypic categories: severe, mild and without apparent phenotype. By further crossing between mice with no apparent phenotype, we were able to establish a colony of Gne M712T/M712T knockin mice with a high- and long-term survival rate, lacking any renal phenotype. These mice did not present any muscle phenotype (clinical or pathological) for up to 18 months. No correlation was found between the expression of any of the two mRNA Gne isoforms in muscle and the mouse genotype or phenotype. However, the expression of isoform 2 mRNA was significantly higher in the kidney of Gne M712T/M712T kidney affected mice compared with control. In contrast, the expression of UPR markers Bip, Chop and of the spliced form of XBP1, was upregulated in muscle of Gne M712T/M712T mice compared with controls, but was unchanged in the affected kidney. Thus, Gne defects can affect both muscle and kidney in mouse, but probably through different mechanisms.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Argov, Z., Eisenberg, I., & Mitrani-Rosenbaum, S. (1998). Genetics of inclusion body myopathies. Current Opinion in Rheumatology, 10, 543–547.
Argov, Z., & Mitrani-Rosenbaum, S. (2008). The hereditary inclusion body myopathy enigma and its future therapy. Neurotherapeutics, 5, 633–637.
Argov, Z., & Yarom, R. (1984). ‘Rimmed vacuole myopathy’ sparing the quadriceps: A unique disorder in Iranian Jews. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 64, 33–43.
Broccolini, A., Gidaro, T., Morosetti, R., Sancricca, C., & Mirabella, M. (2011). Hereditary inclusion-body myopathy with sparing of the quadriceps: The many tiles of an incomplete puzzle. Acta Myologica, 30, 91–95.
Broccolini, A., Gliubizzi, C., Pavoni, E., et al. (2005). Alpha-Dystroglycan does not play a major pathogenic role in autosomal recessive hereditary inclusion-body myopathy. Neuromuscular Disorders, 15, 177–184.
Eisenberg, I., Avidan, N., Potikha, T., Hochner, H., Chen, M., Olender, T., et al. (2001). The UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase gene is mutated in recessive hereditary inclusion body myopathy. Nature Genetics, 29, 83–87.
Eisenberg, I., Grabov-Nardini, G., Hochner, H., Korner, M., Sadeh, M., Bertorini, T., et al. (2003). Mutations spectrum of GNE in hereditary inclusion body myopathy sparing the quadriceps. Human Mutation, 21, 99–105.
Galeano, B., Klootwijk, R., Manoli, I., Sun, M., Ciccone, C., Darvish, D., et al. (2007). Mutation in the key enzyme of sialic acid biosynthesis causes severe glomerular proteinuria and is rescued by N-acetylmannosamine. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 117, 1585–1594.
Hinderlich, S., Salama, I., Eisenberg, I., Potikha, T., Mantey, L. R., Yarema, K. J., et al. (2004). The homozygous M712T mutation of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase results in reduced enzyme activities but not in altered overall cellular sialylation in hereditary inclusion body myopathy. FEBS Letters, 566, 105–109.
Huizing, M., & Krasnewich, D. M. (2009). Hereditary inclusion body myopathy: A decade of progress. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1792, 881–887.
Huizing, M., Rakocevic, G., Sparks, S. E., et al. (2004). Hypoglycosylation of alpha-dystroglycan in patients with hereditary IBM due to GNE mutations. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism, 2004(81), 196–202.
Ii, K., Hizawa, K., Nonaka, I., Sugita, H., Kominami, E., & Katunuma, N. (1986). Abnormal increases of lysosomal cysteinine proteinases in rimmed vacuoles in the skeletal muscle. American Journal of Pathology, 122, 193–198.
Ito, M., Sugihara, K., Asaka, T., Toyama, T., Yoshihara, T., Furuichi, K., et al. (2012). Glycoprotein hyposialylation gives rise to a nephrotic-like syndrome that is prevented by sialic acid administration in GNE V572L point-mutant mice. PLoS ONE, 7, e29873.
Keppler, O. T., Hinderlich, S., Langner, J., Schwartz-Albiez, R., Reutter, W., & Pawlita, M. (1999). UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase: A regulator of cell surface sialylation. Science, 284, 1372–1376.
Lowe, J. B. (2003). Glycan-dependent leukocyte adhesion and recruitment in inflammation. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 15, 531–538.
Malicdan, M. C., Noguchi, S., Hayashi, Y. K., Nonaka, I., & Nishino, I. (2009). Prophylactic treatment with sialic acid metabolites precludes the development of the myopathic phenotype in DMRV hIBM mouse model. Nature Medicine, 15, 690–695.
Malicdan, M. C., Noguchi, S., & Nishino, I. (2007a). Autophagy in a mouse model of distal myopathy with rimmed vacuoles or hereditary inclusion body myopathy. Autophagy, 3, 396–398.
Malicdan, M. C., Noguchi, S., Nonaka, I., Hayashi, W. K., & Nishino, I. (2007b). A Gne knockout mouse expressing human GNE D176V mutation develops features similar to distal myopathy with rimmed vacuoles or hereditary inclusion body myopathy. Human Molecular Genetics, 16, 2669–2682.
Nagy, A., Rossant, J., Nagy, R., Abramow-Newerly, W., & Roder, J. C. (1993). Derivation of completely cell culture-derived mice from early-passage embryonic stem cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 90, 8424–8428.
Nonaka, I., Sunohara, N., Ishiura, S., & Satoyoshi, E. (1981). Familial distal myopathy with rimmed vacuole and lamellar (myeloid) body formation. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 51, 141–155.
Reinke, S. O., Eidenschink, C., Jay, C. M., & Hinderlich, S. (2009). Biochemical characterization of human and murine isoforms of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase (GNE). Glycoconjugate Journal, 26, 415–422.
Ricci, E., Broccolini, A., Gidaro, T., et al. (2006). NCAM is hyposialylated in hereditary inclusion body myopathy due to GNE mutations. Neurology, 66, 755–758.
Saito, F., Tomimitsu, H., Arai, K., et al. (2004). A Japanese patient with distal myopathy with rimmed vacuoles: Missense mutations in the epimerase domain of the UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase (GNE) gene accompanied by hyposialylation of skeletal muscle glycoproteins. Neuromuscular Disorders, 14, 158–161.
Salama, I., Hinderlich, S., Shlomai, Z., Eisenberg, I., Krause, S., Yarema, K., et al. (2005). No overall hyposialylation in hereditary inclusion body myopathy myoblasts carrying the homozygous M712T GNE mutation. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 328, 221–226.
Sela, I., Milman Krentsis, I., Shlomai, Z., Sadeh, M., Dabby, R., Argov, Z., et al. (2011). The proteomic profile of hereditary inclusion body myopathy. PLoS ONE, 6, e16334.
Seppala, R., Lehto, V. P., & Gahl, W. A. (1999). Mutations in the human UDP-N- acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase gene define the disease sialuria and the allosteric site of the enzyme. American Journal of Human Genetics, 64, 1563–1569.
The ENCODE Project Consortium. (2012). An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature, 489(5), 7–74.
Tsuruta, Y., Furuta, A., Furuta, K., Yamada, T., Kira, J., & Iwaki, T. (2001). Expression of the lysosome-associated membrane proteins in myopathies with rimmed vacuoles. Acta Neuropathologica, 101, 579–584.
Varki, A., & Angata, T. (2006). Siglecs—The major subfamily of I-type lectins. Glycobiology, 16, 1R–27R.
Weinhold, B., Sellmeier, M., Schaper, W., Blume, L., Philippens, B., Kats, E., et al. (2012). Deficits in sialylation impair podocyte maturation. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 23, 1319–1328.
Acknowledgments
We thank Rebecca Haffner, Weizmann Institute of Sciences, for her directions in the mouse generation process and for helpful discussions, and Ynon Ben-Neriah, The Hebrew University—Hadassah Medical School, Jerusalem, for kindly providing C57BL/6J-Tg-PGK-Cre mice. This project was supported in part by the Neuromuscular Disease Foundation (NDF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sela, I., Yakovlev, L., Becker Cohen, M. et al. Variable Phenotypes of Knockin Mice Carrying the M712T Gne Mutation. Neuromol Med 15, 180–191 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-012-8209-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-012-8209-7