Abstract
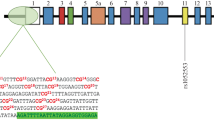
The α-synuclein gene (SNCA) plays a major role in the aetiology of Lewy body disease (LBD) including Parkinson’s disease (PD). Point mutations and genetic alterations causing elevated gene expression are causally linked to familial PD. To what extent epigenetic changes play a role in the regulation of α-synuclein expression and may contribute to the aetiology of sporadic LBD is a matter of debate. We analysed the methylation state of the promoter region and a CpG-rich region of intron 1 of α-synuclein in several brain regions in sporadic LBD and controls using 454 GS-FLX-based high-resolution bisulphite sequencing. Our results indicate that there are significant differences in the level of methylation between different brain areas. The overall methylation levels in the promoter and intron 1 of α-synuclein are rather low in controls and—in contrast to previously reported findings—are not significantly different from LBD. However, single CpG analysis revealed significant hyper- and hypomethylation at different positions in various brain regions and LBD stages. A slight overall increase in methylation related to LBD patients’ age was detected.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvira, D., Ferrer, I., Gutierrez-Cuesta, J., Garcia-Castro, B., Pallas, M., & Camins, A. (2008). Activation of the calpain/cdk5/p25 pathway in the girus cinguli in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Related Disorder, 14(4), 309–313. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2007.09.005.
Asikainen, S., Rudgalvyte, M., Heikkinen, L., Louhiranta, K., Lakso, M., Wong, G., et al. (2010). Global microRNA expression profiling of Caenorhabditis elegans Parkinson’s disease models. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 41(1), 210–218. doi:10.1007/s12031-009-9325-1.
Ball, M. P., Li, J. B., Gao, Y., Lee, J. H., LeProust, E. M., Park, I. H., et al. (2009). Targeted and genome-scale strategies reveal gene-body methylation signatures in human cells. Natural Biotechnology, 27(4), 361–368. doi:10.1038/nbt.1533.
Bock, C., Reither, S., Mikeska, T., Paulsen, M., Walter, J., & Lengauer, T. (2005). BiQ analyzer: Visualization and quality control for DNA methylation data from bisulfite sequencing. Bioinformatics, 21(21), 4067–4068. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bti652.
Braak, H., Del Tredici, K., Rub, U., de Vos, R. A., Jansen Steur, E. N., & Braak, E. (2003). Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 24(2), 197–211.
Briggs, M. R., Kadonaga, J. T., Bell, S. P., & Tjian, R. (1986). Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science, 234(4772), 47–52.
Chhibber, A., & Schroeder, B. G. (2008). Single-molecule polymerase chain reaction reduces bias: Application to DNA methylation analysis by bisulfite sequencing. Analytical Biochemistry, 377(1), 46–54. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2008.02.026.
Datta, P. K., Raychaudhuri, P., & Bagchi, S. (1995). Association of p107 with Sp1: Genetically separable regions of p107 are involved in regulation of E2F- and Sp1-dependent transcription. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 15(10), 5444–5452.
Desplats, P., Spencer, B., Coffee, E., Patel, P., Michael, S., Patrick, C., et al. (2011). Alpha-synuclein sequesters DNMT1 from the nucleus: A novel mechanism for epigenetic alterations in Lewy body diseases. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 286(11), 9031–9037. doi:10.1074/jbc.C110.212589.
Doxakis, E. (2010). Post-transcriptional regulation of alpha-synuclein expression by mir-7 and mir-153. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 285(17), 12726–12734. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.086827.
Du, G., Liu, X., Chen, X., Song, M., Yan, Y., Jiao, R., et al. (2010). Drosophila histone deacetylase 6 protects dopaminergic neurons against {alpha}-synuclein toxicity by promoting inclusion formation. Molecular Biology Cell, 21(13), 2128–2137. doi:10.1091/mbc.E10-03-0200.
Esteller, M. (2007). Cancer epigenomics: DNA methylomes and histone-modification maps. Natural Review of Genetics, 8(4), 286–298. doi:10.1038/nrg2005.
Ghosh, S., Yates, A. J., Fruhwald, M. C., Miecznikowski, J. C., Plass, C., & Smiraglia, D. (2010). Tissue specific DNA methylation of CpG islands in normal human adult somatic tissues distinguishes neural from non-neural tissues. Epigenetics, 5(6), 527–538.
Graff, J., Kim, D., Dobbin, M. M., & Tsai, L. H. (2011). Epigenetic regulation of gene expression in physiological and pathological brain processes. Physiological Reviews, 91(2), 603–649. doi:10.1152/physrev.00012.2010.
Hoglinger, G. U., Breunig, J. J., Depboylu, C., Rouaux, C., Michel, P. P., Alvarez-Fischer, D., et al. (2007). The pRb/E2F cell-cycle pathway mediates cell death in Parkinson’s disease. Proceedings of the Natural Academy of Science U S A, 104(9), 3585–3590. doi:10.1073/pnas.0611671104.
Ibanez, P., Bonnet, A. M., Debarges, B., Lohmann, E., Tison, F., Pollak, P., et al. (2004). Causal relation between alpha-synuclein gene duplication and familial Parkinson’s disease. Lancet, 364(9440), 1169–1171. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)17104-3.
Jenal, M., Trinh, E., Britschgi, C., Britschgi, A., Roh, V., Vorburger, S. A., et al. (2009). The tumor suppressor gene hypermethylated in cancer 1 is transcriptionally regulated by E2F1. Molecular Cancer Research, 7(6), 916–922. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.mcr-08-0359.
Jin, H., Kanthasamy, A., Ghosh, A., Yang, Y., Anantharam, V., & Kanthasamy, A. G. (2011). Alpha-synuclein negatively regulates protein kinase C delta expression to suppress apoptosis in dopaminergic neurons by reducing p300 histone acetyltransferase activity. Journal of Neuroscience, 31(6), 2035–2051. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5634-10.2011.
Jin, S. G., Wu, X., Li, A. X., & Pfeifer, G. P. (2011). Genomic mapping of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in the human brain. Nucleic Acids Research, 39(12), 5015–5024, doi:10.1093/nar/gkr120.
Jowaed, A., Schmitt, I., Kaut, O., & Wullner, U. (2010). Methylation regulates alpha-synuclein expression and is decreased in Parkinson’s disease patients’ brains. Journal of Neuroscience, 30(18), 6355–6359. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6119-09.2010.
Junn, E., Lee, K. W., Jeong, B. S., Chan, T. W., Im, J. Y., & Mouradian, M. M. (2009). Repression of alpha-synuclein expression and toxicity by microRNA-7. Proceedings of the Natural Academy of Science U S A, 106(31), 13052–13057. doi:10.1073/pnas.0906277106.
Kinney, S. M., Chin, H. G., Vaisvila, R., Bitinaite, J., Zheng, Y., Esteve, P. O., Feng, S., Stroud, H., Jacobsen, S. E., & Pradhan, S. (2011). Tissue-specific distribution and dynamic changes of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in mammalian genomes. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 286(28), 24685–24693. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.217083.
Kontopoulos, E., Parvin, J. D., & Feany, M. B. (2006). Alpha-synuclein acts in the nucleus to inhibit histone acetylation and promote neurotoxicity. Human Molecular Genetics, 15(20), 3012–3023. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddl243.
Ladd-Acosta, C., Pevsner, J., Sabunciyan, S., Yolken, R. H., Webster, M. J., Dinkins, T., et al. (2007). DNA methylation signatures within the human brain. American Journal of Human Genetics, 81(6), 1304–1315. doi:10.1086/524110.
Lutsik, P., Feuerbach, L., Arand, J., Lengauer, T., Walter, J., & Bock, C. (2011). BiQ analyzer HT: Locus-specific analysis of DNA methylation by high-throughput bisulfite sequencing. Nucleic Acids Research, 39(suppl 2), W551–W556. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr312.
Marques, S. C., Oliveira, C. R., Pereira, C. M., & Outeiro, T. F. (2011). Epigenetics in neurodegeneration: A new layer of complexity. Progress in Neuropsychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry, 35(2), 348–355. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2010.08.008.
Matsumoto, L., Takuma, H., Tamaoka, A., Kurisaki, H., Date, H., Tsuji, S., et al. (2010). CpG demethylation enhances alpha-synuclein expression and affects the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One, 5(11), e15522, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0015522.
McKeith, I. G., Dickson, D. W., Lowe, J., Emre, M., O’Brien, J. T., Feldman, et al. (2005). Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: Third report of the DLB Consortium. Neurology, 65(12), 1863–1872. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000187889.17253.b1.
Nevins, J. R. (1992). Transcriptional regulation. A closer look at E2F. Nature, 358(6385), 375–376. doi:10.1038/358375a0.
Polymeropoulos, M. H., Lavedan, C., Leroy, E., Ide, S. E., Dehejia, A., Dutra, A., et al. (1997). Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science, 276(5321), 2045–2047.
Portela, A., & Esteller, M. (2010). Epigenetic modifications and human disease. Natural Biotechnology, 28(10), 1057–1068. doi:10.1038/nbt.1685.
Robertson, J., Robertson, A. B., & Klungland, A. (2011). The presence of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine at the gene promoter and not in the gene body negatively regulates gene expression. Biochemistry and Biophysics Research Community, 411(1), 40–43. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.06.077.
Satake, W., Nakabayashi, Y., Mizuta, I., Hirota, Y., Ito, C., Kubo, M., et al. (2009). Genome-wide association study identifies common variants at four loci as genetic risk factors for Parkinson’s disease. Natural Genetics, 41(12), 1303–1307. doi:10.1038/ng.485.
Scherzer, C. R., Grass, J. A., Liao, Z., Pepivani, I., Zheng, B., Eklund, A. C., et al. (2008). GATA transcription factors directly regulate the Parkinson’s disease-linked gene alpha-synuclein. Proceedings of Natural Academy of Science U S A, 105(31), 10907–10912, doi:10.1073/pnas.0802437105.
Shen, L., Guo, Y., Chen, X., Ahmed, S., & Issa, J. P. (2007). Optimizing annealing temperature overcomes bias in bisulfite PCR methylation analysis. Biotechniques, 42(1), 48, 50, 52 passim.
Sherer, T. B., Betarbet, R., & Greenamyre, J. T. (2001). Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Current Opinion in Investigation Drugs, 2(5), 657–662.
Simon-Sanchez, J., Schulte, C., Bras, J. M., Sharma, M., Gibbs, J. R., Berg, D., et al. (2009). Genome-wide association study reveals genetic risk underlying Parkinson’s disease. Natural Genetics, 41(12), 1308–1312. doi:10.1038/ng.487.
Singleton, A. B., Farrer, M., Johnson, J., Singleton, A., Hague, S., Kachergus, J., et al. (2003). Alpha-synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson’s disease. Science, 302(5646), 841. doi:10.1126/science.1090278.
Taby, R., & Issa, J. P. (2010). Cancer epigenetics. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 60(6), 376–392. doi:10.3322/caac.20085.
Taylor, K. H., Kramer, R. S., Davis, J. W., Guo, J., Duff, D. J., Xu, D., et al. (2007). Ultradeep bisulfite sequencing analysis of DNA methylation patterns in multiple gene promoters by 454 sequencing. Cancer Research, 67(18), 8511–8518. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-07-1016.
Urdinguio, R. G., Sanchez-Mut, J. V., & Esteller, M. (2009). Epigenetic mechanisms in neurological diseases: Genes, syndromes, and therapies. The Lancet Neurology, 8(11), 1056–1072. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70262-5.
Warnecke, P. M., Stirzaker, C., Song, J., Grunau, C., Melki, J. R., & Clark, S. J. (2002). Identification and resolution of artifacts in bisulfite sequencing. Methods, 27(2), 101–107.
Wojdacz, T. K., Hansen, L. L., & Dobrovic, A. (2008). A new approach to primer design for the control of PCR bias in methylation studies. BMC Research Notes, 1, 54. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-1-54.
Xin, Y., Chanrion, B., Liu, M. M., Galfalvy, H., Costa, R., Ilievski, B., et al. (2010). Genome-wide divergence of DNA methylation marks in cerebral and cerebellar cortices. PLoS One, 5(6), e11357. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0011357.
Zarranz, J. J., Alegre, J., Gomez-Esteban, J. C., Lezcano, E., Ros, R., Ampuero, I., et al. (2004). The new mutation, E46K, of alpha-synuclein causes Parkinson and Lewy body dementia. Annals of Neurology, 55(2), 164–173, doi:10.1002/ana.10795.
Zhu, L., van den Heuvel, S., Helin, K., Fattaey, A., Ewen, M., Livingston, D., et al. (1993). Inhibition of cell proliferation by p107, a relative of the retinoblastoma protein. Genes & Development, 7(7A), 1111–1125.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Friedrich-Baur-Stiftung (Grant Number 13/10) and Brain Net.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Boni, L., Tierling, S., Roeber, S. et al. Next-Generation Sequencing Reveals Regional Differences of the α-Synuclein Methylation State Independent of Lewy Body Disease. Neuromol Med 13, 310–320 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-011-8163-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-011-8163-9