Abstract
Since 1943, cases of sensitization or allergy to soy-based formulas (SBFs) have been described without any consensus on their real prevalence. We identified the adjusted prevalence of IgE-mediated soy allergies in children and performed a secondary analysis of the impact of age (less than and more than 6 months). We performed a systematic review with meta-analysis of studies published from 1909 to 2013 in PubMed, Embase, LILACS, ARTEMISA, Cochrane, Bandolier, DARE and the GRADE system for grading quality. Results are presented in tables and graphs using a forest plot. The 40 studies identified established weighted prevalence of soy allergies of 0 to 0.5 % (0.27) for the general population, 0.4 to 3.1 % (1.9) for the referred population, and 0 to 12.9 % (2.7) for allergic children. Prevalence of sensitization after the use of SBFs is 8.7 and 8.8 %, depending on the method used. The prevalence of allergies to soy and IgE sensitization to the use of SBFs is less than reported. Not enough evidence exists to show a higher risk of allergy in infants younger than 6 months. The concern about soy allergy is no reason to postpone the use of SBFs in IgE-mediated cow's milk allergy infants until the age of 6 months.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Forsyth D (1991) The history of infant feeding from Elizabethan times. Proc Soc Med 4:110–141
Holt l E (1902) The diseases of infancy and childhood, 2nd edn. Appleton, New York
Howarth, W. J. (1905), The influence of feeding on the mortality of infants. Lancet ii, 210–213
Stevens E, Patrick T, Pickler R (2009) A history of infant feeding. J Perinat Educ 18(2):32–39
Cantani A (1987) The struggle for breastfeeding. Ann Allergy 59:84
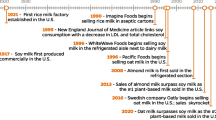
Ruhrah J (1909) The soybean in infant feeding. Prelim Rep Arch Pediatr 26:496–501
Shurtleff W, Aoyagl A (1984) Soymilk industry and market. The soy foods center, Lafayette
Hill l, Stuart H (1929) Soybean food preparation for feeding infants with milk idiosyncrasy. JAMA 93:985–987
Fomon SJ (1974) Infant nutrition, 2nd edn. WB Saunders, Philadelphia
The committee on nutrition of the American Academy of Pediatrics (1971) Vitamin K supplementation for infants receiving milk substitute infant formulas and for those with fat malabsorption. Pediatrics 48:483–487
United States Congress (1980) Infant Formula Act of 1980. United States Capitol Health Documents Room, Washington
Brooks JR, Morr CV (1985) Current aspects of soy protein fractionation and nomenclature. J Am Oil Chem Soc 62:1347–1350
Kay JL, Daeschner CW Jr, Desmond MM (1960) Evaluation of infants fed soybean and evaporated milk formulae from birth to 3 months. A comparison of weight, length, hemoglobin, hematocrit, plasma biochemical values. AJDC 100:264–276
The committee on nutrition of the American Academy of Pediatrics (1983) Soy-protein formulas: recommendations for use in infant feeding. Pediatrics 72:359–363
Cantani A, Ferrara M, Ragno W, Businco I (1990) Efficacy and safety of a soy-protein-formula for feeding babies with atopic dermatitis and cow milk hypersensitivity. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 12:311–318
European Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition. Committee on nutrition (1994) Comment on the composition of soy-protein based infant and follow-up formulas. Acta Paediatr Scand 79:1001–1045
Businco l, Rubaltelli F (1989) Management and prevention of cow's milk allergy in infants. Wyeth-Ayerst Nutr Semin Ser 1:41–64
Mimouni F, Campaigne B, Neylan M, Tsang RC (1993) Bone mineralization in the first year of life in infants fed human milk, cow-milk formula, or soy-based formula. J Pediatr 122:348–354
Eastham EJ (1989) Soy protein allergy. In: Hamburger RN (ed) Food intolerance in children. Raven Press, New York, pp 223–236
Eastham EJ, Lichauco T, Grady MI, Walker WA (1978) Antigenicity of infant formulas: role of immature intestine on protein permeability. J Pediatr 93(4):561–564
Kjellman NI, Johansson SGQ (1979) Soy versus cow milk in infants with biparental history of atopic disease: development of atopic disease and immunoglobulins from birth to 4 years of age. Clin Allergy 9:347–358
Chandra RK, Singh G, Shridhara B (1989) Effect of feeding whey hydrolysate, soy and conventional cow milk formulas on incidence of atopic disease in high risk infants. Ann Allergy 63:102–106
Gerrard JW, Lubos MC, Hardy LW, Holmlund BA, Webster D (1967) Milk allergy: clinical picture and familial incidence. Can Med Assoc J 97:780–785
Giampietro PG, Ragno V, Daniele S, Cantani A, Ferrara M, Businco L (1992) Soy hypersensitivity in children with food allergy. Ann Allergy 69:143–146
Bock SA, Sampson HA, Atkins FM et al (1988) Double-blind, placebo-controlled food challenge (DBPCFC) as an office procedure: a manual. J Allergy Clin Immunol 82:986–997
Bock SA (1996) Food challenges in the diagnosis of food hypersensitivity. Nestle Nutr Workshop Ser 34:105–117
Halken S, Host A, Hansen LG, Osterballe O (1993) Safety of a new, ultrafiltrated whey hydrolysate formula in children with cow's milk allergy: a clinical investigation. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 4:53–59
Gerrard JW, Mackenzie JWA, Goluboff N, Garson JZ, Maningis CS (1973) Cow's milk allergy: prevalence and manifestations in an unselected series of newborns. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl 234:1–21
Kuitunen P, Visakorpi JK, Savilahti E, Pelkonen P (1975) Malabsorption syndrome with cow milk intolerance. Clinical findings and course in 54 cases. Arch Dis Child 50:351–356
Jakobsson I, Lindberg T (1979) A prospective study of cow milk protein intolerance in Swedish infants. Acta Paediatr Scand 68:835–839
Hill DJ, Ford RPK, Shelton MJ, Hosking CS (1984) A study of 100 infants and young children with cow milk allergy. Clin Rev Allergy 2:125–142
Bishop JM, Hill DJ, Hosking CS (1990) Natural history of cow milk allergy: clinical outcome. J Pediatr 116:862–867
Perkkio M, Savilahti E, Kuitunen P (1981) Morphometric and immunohistochemical study of jejunal biopsies from children with intestinal soy allergy. Eur J Pediatr 137:63–69
Schwartz RH (1991) IgE-mediated allergic reactions to cow's milk. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am 11:717–741
Whitherly SA (1990) Soy formulas are not hypoallergenic. Am J Clin Nutr 51:705–706
Minford AMB, MacDonald A, Littlewood JM (1982) Food intolerance and food allergy in children: a review of 68 cases. Arch Dis Child 57:742–747
Hattevig G, Kjellman B, Johansson SGO, Bjorksten B (1984) Clinical symptoms and IgE responses to common food proteins in atopic and healthy children. Clin Allergy 14:551–559
Beningori N, Cantani A, Picarazzi A, Osmelli S, Busingo L (1985) Management of atopic dermatitis by elimination diet: a useful but difficult approach. Fisons SpA, Roma, pp 95–104
Host A, Halken S (1990) A prospective study of cow milk allergy in Danish infants during the first three years of life. Allergy 45:587–596
Bergmann R l, Bergmann KE, Lau-Schadensdorf S et al (1994) Atopic disease in infancy. The German multicenter atopy study (MAS-90). Pediatr Allergy Immunol 5(suppl 1):19–25
Kivity S, Dunner K, Marian Y (1994) The pattern of food hypersensitivity in patients with onset after 10 years of age. Clin Exp Allergy 24:19–22
Crespo JF, Pasgual C, Burks AW, Helm RM, Esteban MM (1995) Frequency of food allergy in a pediatric population from Spain. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 6:39–43
Noferi A, Fusghillo S, Iorio C (1995) Rilevanza epidemiológica e clinica deile arachidi quali causa di allergia. Osservazioni personali Notiz Allergol 14:113–117
Dean TP, Spurr M, Warner JO (1994) Soy sensitivity among cow's milk allergic children. Clin Exp Allergy 24:984A
Wilson NW, Hamburger RN (1988) Allergy to cow milk in the first year of life and its prevention. Ann Allergy 61:323–470
Magnolfi C, Zani G, Lacava L, Patria MF, Bardare M (1996) Soy allergy in atopic children. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 77:197–201
Branski D (1984) Specific etiologies of chronic diarrhea in infancy. Nestle Nutr Workshop Ser 6:107–145
The European Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology Working Group for the Diagnostic Criteria for Food Allergy (1992) Diagnostic criteria for food allergy with predominantly intestinal symptoms. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 14:108–112
Freier S, Eran M, Suranyi Y (1988) Antigen presentation. Nestle Nutr Workshop Ser 17:89–98
Kahn A, Mozin MJ, Rebuffat E et al (1988) Milk intolerance in children with persistent sleeplessness: a prospective double-blind crossover evaluation. Pediatrics 84:595–602
Johnstone DE, Roghmann KJ (1993) Recommendations for soy infant formula: a review of the literature and a survey of pediatric allergists. Pediatr Asthma Allergy Immunol 7:77–88
Hill LW (1942) The production of nonetiological skin hypersensitivity to foods by natural means in atopic persons. J Allergy 13:366–370
Cantani A, Lucenti P (1997) Natural history of soy allergy and/or intolerance in children, and clinical use of soy protein formulas. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 8:59–74
Sampson HA (1988) The role of food hypersensitivity and mediator release in atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 81:635–645
Sampson HA (1999) Food allergy. Part 2: diagnosis and management. J Allergy Clin Immunol 103:981–989
Robinson KA, Dickersin K (2002) Development of a high sensitive search strategy for the retrieval of reports of controlled trials using PubMed. Int J Epidemiol 31:150–153
Wilczynski NL, Haynes RB, the Hedges Team (2004) Developing optimal search strategies for detecting clinically sound prognostic studies in MEDLINE: an analytic survey. BMC Med 2:23
GRADE Working Group (2004) Grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 328:1490–1498
Bock SA, Atkins FM (1990) Patterns of food hypersensitivity during sixteen years of double-blind, placebo-controlled food challenges. J Pediatr 117(4):561–567
Bruno G, Giampietro PG, Del Guercio MJ et al (1997) Soy allergy is not common in atopic children: a multicenter study. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 8(4):190–193
Zeiger RS, Sampson HA, Bock SA et al (1999) Soy allergy in infants and children with IgE-associated cow's milk allergy. J Pediatr 134(5):614–622
Roehr CC, Edenharter G, Reimann S et al (2004) Food allergy and non-allergic food hypersensitivity in children and adolescents. Clin Exp Allergy 34:1534–1541
Osterballe M, Hansen TK, Mortz CG, Høst A, Bindslev-Jensen C (2005) The prevalence of food hypersensitivity in an unselected population of children and adults. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 16:567–573
Caminiti L, Passalacqua G, Barberi S et al (2009) A new protocol for specific oral tolerance induction in children with IgE-mediated cow’s milk allergy. Allergy Asthma Proc 30:443–448
Klemola T, Kalimo K, Poussa T et al (2005) Feeding a soy formula to children with cow's milk allergy: the development of immunoglobulin E-mediated allergy to soy and peanuts. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 16:641–646
Niggemann B, Sielaff B, Beyer K, Binder C, Whan U (1999) Outcome of double-blind, placebo-controlled food challenge test in 107 children with atopic dermatitis. Clinical Exp Allergy 29:91–96
Dias A, Santos A, Pinheiro JA (2010) Persistence of cow's milk allergy beyond two years of age. Allergol Immunopathol 38(1):8–12, Madr
Antunes J, Borrego LM, Queiroz A et al (2009) Allergy to extensively hydrolysed formulas. Allergol Immunopathol 37(5):272–278, Madr
Buts JP, Di Sano C, Hansdorffer S (1993) Clinical evaluation of the tolerance for a soy-based special milk formula in children with cow's milk protein intolerance/allergy (CMPI/CMPA). Minerva Pediatr 45(5):209–213
Berger-Achituv S, Shohat T, Romano-Zelekha O et al (2005) Widespread use of soy-based formula without clinical indications. JPGN 41:660–666
Mehr SS, Kemp AS (2008) Feeding choice for children with immediate allergic reactions to cow's milk protein. MJA 189:178–179
Nachmias N, Landman Y, Danon YL, Levy Y (2010) Soy allergy following early soy feeding in neonates. IMAJ 12:684–686
Sladkevicius E, Nagy E, Lack G, Guest JF (2010) Resource implications and budget impact of managing cow milk allergy in the UK. J Med Econ 13:119–128
Klemola T, Vanto T, Juntunen-Backman K, Kalimo K, Korpela R, Varjonen E (2002) Allergy to soy formula and to extensively hydrolyzed whey formula in infants with cow's milk allergy: a prospective, randomized study with a follow-up to the age of 2 years. J Pediatr 140:219–224
Terracciano L, Bouygue GR, Sarratud T, Veglia F, Martelli A, Fiocchi A (2010) Impact of dietary regimen on the duration of cow's milk allergy: a random allocation study. Clin Exp Allergy 40:637–642
Agostoni C, Fiocchi A, Riva E et al (2007) Growth of infants with IgE-mediated cow's milk allergy fed different formulas in the complementary feeding period. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 18:599–606
Arató A, Horváth J (1995) Soy formula in the feeding of infants with milk allergy. Orv Hetil 136(27):1433–1437
Katz Y, Rajuan N, Goldberg MR et al (2010) Early exposure to cow's milk protein is protective against IgE-mediated cow's milk protein allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 126:77–82
Dalal I, Binson R, Reifen Z et al (2002) Food allergy is a matter of geography after all: sesame as a major cause of severe IgE-mediated food allergic reactions among infants and young children in Israel. Allergy 57:362–365
Brugman E, Meulmeester JF, Spee-van der Wekke A, Beuker RJ, Radder JJ, Verloove-Vanhorick SP (1998) Prevalence of self-reported food hypersensitivity among school children in The Netherlands. Eur J Clin Nutr 52:577–581
van Bockel-Geelkerken M, Meulmeester JF (1992) Prevalence of putative food hypersensitivity in young children. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 136:1351–1356
Eggesbo M, Halvorsen R, Tambs K, Botten G (1999) Prevalence of parentally perceived adverse reactions to food in young children. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 10:122–132
Altan DR, Chiaramonte LT (1996) Public perception of food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 97:1247–1251
Jirapinyo P, Densupsoontorn N, Wongarn R, Thamonsiri N (2007) Comparisons of a chicken-based formula with soy-based formula in infants with cow milk allergy. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 16(4):711–715
Ahrens B, Niggemann B, Whan U, Beyer K (2012) Organ-specific symptoms during oral food challenge in children with food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 130:549–551
Masilamani M, Wei J, Bhatt S, Paul M, Yakir S, Sampson HA (2011) Soybean isoflavins regulate dendritic cell function and suppress allergic sensitization to peanut. J Allergy Clin Immunol 128:1242–1250
Greer FR, Sicherer SH, Bruks AW (2008) Effects of early nutritional interventions on the development of atopic diseases in infants and children: the role of maternal dietary restrictions, breastfeeding, timing of introduction of complementary foods, and hydrolyzed formulae. Pediatrics 121:183–191
Koletzko S, Niggemann B, Arato A et al (2012) Diagnostic approach and management of cow's milk protein allergy in infants and children: ESPGHAN GI committee practical guidelines. JPGN 55:221–229
Arshad SH, Tariq SM, Matthews S, Hakim E (2001) Sensitization to common allergens and its association with allergic disorders at age 4 years: a whole population birth cohort study. Pediatrics 108:e33
Rance F, Grandmottet X, Grandjean H (2005) Prevalence and main characteristics of schoolchildren diagnosed with food allergies in France. Clin Exp Allergy 35:167–172
Roberts G, Peckitt C, Northstone K et al (2005) Relationship between aeroallergen and food allergen sensitization in childhood. Clin Exp Allergy 35:933–940
Chiang WC, Kidon MI, Liew WK, Goh A, Tang J, Chay OM (2007) The changing face of food hypersensitivity in an Asian community. Clin Exp Allergy 37:1055–1061
Baatenburg de Jong A, Dikkeschei LD, Brand PLP (2011) Sensitization patterns to food and inhalant allergens in childhood: a comparison of non-sensitized, monosensitized and polysensitized children. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 22:166–171
Matricardi PM, Bockelbrink A, Beyer K et al (2007) Primary versus secondary immunoglobulin E sensitization to soy and wheat in the Multi-Centre Allergy Study cohort. Clin Exp Allergy 38:493–500
Ferrari GG, Eng PA (2011) IgE-mediated food allergies in Swiss infants and children. Swiss Med Wkly 141:w13269
Kristjansson I, Ardal B, Jonsson JS, Sigurdsson JA, Foldevi M, Bjorksten B (1999) Adverse reactions to food and food allergy in young children in Iceland and Sweden. Scand J Prim Health Care 17:30–34
Katz Y, Goldberg MR, Zadik-Mnuhin G, Leshno M, Heyman E (2008) Cross-sensitization between milk proteins: reactivity to a “kosher” epitope? IMAJ 10:85–88
Ahn KM, Han YS, Nam SY, Park HY, Shin MY, Lee SI (2003) Prevalence of soy protein hypersensitivity in cow's milk protein-sensitive children in Korea. J Korean Med Sci 18:473–477
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katz, Y., Gutierrez-Castrellon, P., González, M.G. et al. A Comprehensive Review of Sensitization and Allergy to Soy-Based Products. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol 46, 272–281 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-013-8404-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-013-8404-9