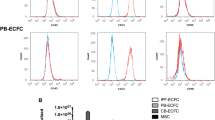
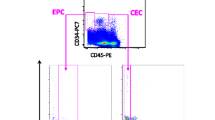
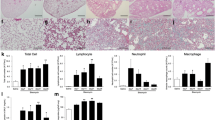
Abstract
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a devastating disease characterized by obliteration of alveolar architecture, resulting in declining lung function and ultimately death. Pathogenic mechanisms remain unclear but involve a concomitant accumulation of scar tissue together with myofibroblasts activation. Microparticles (MPs) have been investigated in several human lung diseases as possible pathogenic elements, prognosis markers and therapeutic targets. We postulated that levels and cellular origins of circulating MPs might serve as biomarkers in IPF patients and/or as active players of fibrogenesis. Flow cytometry analysis showed a higher level of Annexin-V positive endothelial and platelet MPs in 41 IPF patients compared to 22 healthy volunteers. Moreover, in IPF patients with a low diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO<40%), endothelial MPs (EMPs) were found significantly higher compared to those with DLCO>40% (p = 0.02). We then used EMPs isolated from endothelial progenitor cells (ECFCs) extracted from IPF patients or controls to modulate normal human lung fibroblast (NHLF) properties. We showed that EMPs did not modify proliferation, collagen deposition and myofibroblast transdifferentiation. However, EMPs from IPF patients stimulated migration capacity of NHLF. We hypothesized that this effect could result from EMPs fibrinolytic properties and found indeed higher plasminogen activation potential in total circulating MPs and ECFCs derived MPs issued from IPF patients compared to those isolated from healthy controls MPs. Our study showed that IPF is associated with an increased level of EMPs in the most severe patients, highlighting an active process of endothelial activation in the latter. Endothelial microparticles might contribute to the lung fibroblast invasion mediated, at least in part, by a fibrinolytic activity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raghu, G., Rochwerg, B., Zhang, Y., Garcia, C. A. C., Azuma, A., Behr, J., et al. (2015). An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline: treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. An update of the 2011 clinical practice guideline. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 192(2), e3–19.
Smadja, D. M., Mauge, L., Nunes, H., d’Audigier, C., Juvin, K., Borie, R., et al. (2013). Imbalance of circulating endothelial cells and progenitors in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Angiogenesis, 16(1), 147–157.
Toshner, M., Voswinckel, R., Southwood, M., Al-Lamki, R., Howard, L. S. G., Marchesan, D., et al. (2009). Evidence of dysfunction of endothelial progenitors in pulmonary arterial hypertension. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 180(8), 780–787.
Malli, F., Koutsokera, A., Paraskeva, E., Zakynthinos, E., Papagianni, M., Makris, D., et al. (2013). Endothelial progenitor cells in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: an evolving concept. PloS One, 8(1), e53658.
Amabile, N., Guignabert, C., Montani, D., Yeghiazarians, Y., Boulanger, C. M., & Humbert, M. (2013). Cellular microparticles in the pathogenesis of pulmonary hypertension. The European Respiratory Journal, 42(1), 272–279.
Nieri, D., Neri, T., Petrini, S., Vagaggini, B., Paggiaro, P., & Celi, A. (2016). Cell-derived microparticles and the lung. European Respiratory Review: an Official Journal of European Respiratory Society, 25(141), 266–277.
Bakouboula, B., Morel, O., Faure, A., Zobairi, F., Jesel, L., Trinh, A., et al. (2008). Procoagulant membrane microparticles correlate with the severity of pulmonary arterial hypertension. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 177(5), 536–543.
Amabile, N., Heiss, C., Real, W. M., Minasi, P., McGlothlin, D., Rame, E. J., et al. (2008). Circulating endothelial microparticle levels predict hemodynamic severity of pulmonary hypertension. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 177(11), 1268–1275.
Iversen, L. V., Ullman, S., Østergaard, O., Nielsen, C. T., Halberg, P., Karlsmark, T., et al. (2015). Cross-sectional study of soluble selectins, fractions of circulating microparticles and their relationship to lung and skin involvement in systemic sclerosis. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 16, 191.
Nomura, S., Inami, N., Ozaki, Y., Kagawa, H., & Fukuhara, S. (2008). Significance of microparticles in progressive systemic sclerosis with interstitial pneumonia. Platelets, 19(3), 192–198.
Ratajczak, J., Wysoczynski, M., Hayek, F., Janowska-Wieczorek, A., & Ratajczak, M. Z. (2006). Membrane-derived microvesicles: important and underappreciated mediators of cell-to-cell communication. Leukemia, 20(9), 1487–1495.
Ratajczak, M. Z., & Ratajczak, J. (2016). Horizontal transfer of RNA and proteins between cells by extracellular microvesicles: 14 years later. Clinical and Translational Medicine, 5(1), 7.
Mauge, L., Sabatier, F., Boutouyrie, P., D’Audigier, C., Peyrard, S., Bozec, E., et al. (2014). Forearm ischemia decreases endothelial colony-forming cell angiogenic potential. Cytotherapy, 16(2), 213–224.
Evrard, S. M., d’Audigier, C., Mauge, L., Israël-Biet, D., Guerin, C. L., Bieche, I., et al. (2012). The profibrotic cytokine transforming growth factor-β1 increases endothelial progenitor cell angiogenic properties. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 10(4), 670–679.
Amabile, N., Cheng, S., Renard, J. M., Larson, M. G., Ghorbani, A., McCabe, E., et al. (2014). Association of circulating endothelial microparticles with cardiometabolic risk factors in the Framingham Heart Study. European Heart Journal, 35(42):2972–2979.
Empana, J.-P., Boulanger, C. M., Tafflet, M., Renard, J. M., Leroyer, A. S., Varenne, O., et al. (2015). Microparticles and sudden cardiac death due to coronary occlusion. The TIDE (Thrombus and Inflammation in Sudden Death) study. European Heart Journal. Acute Cardiovascular Care, 4(1), 28–36.
Poncelet, P., Robert, S., Bouriche, T., Bez, J., Lacroix, R., & Dignat-George, F. (2016). Standardized counting of circulating platelet microparticles using currently available flow cytometers and scatter-based triggering: forward or side scatter? Cytometry Part A: the Journal of the International Society for Analytical Cytology, 89(2), 148–158.
Yoder, M. C., Mead, L. E., Prater, D., Krier, T. R., Mroueh, K. N., Li, F., et al. (2007). Redefining endothelial progenitor cells via clonal analysis and hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell principals. Blood, 109(5), 1801–1809.
Silvestre, J. S., Smadja, D. M., & Levy, B. I. (2013). Postisch-emic revascularization: from cellular and molecular mechanisms to clinical applications. Physiological Reviews, 93, 1743–1802.
Sapet, C., Simoncini, S., Loriod, B., Puthier, D., Sampol, J., Nguyen, C., et al. (2006). Thrombin-induced endothelial microparticle generation: identification of a novel pathway involving ROCK-II activation by caspase-2. Blood, 108(6):1868–1876.
Smadja, D. M., Bièche, I., Silvestre, J.-S., Germain, S., Cornet, A., Laurendeau, I., et al. (2008). Bone morphogenetic proteins 2 and 4 are selectively expressed by late outgrowth endothelial progenitor cells and promote neoangiogenesis. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 28(12), 2137–2143.
Smadja, D. M., Levy, M., Huang, L., Rossi, E., Blandinières, A., Israel-Biet, D., et al. (2015). Treprostinil indirectly regulates endothelial colony forming cell angiogenic properties by increasing VEGF-A produced by mesenchymal stem cells. Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 114(4), 735–747.
Sabatier, F., Roux, V., Anfosso, F., Camoin, L., Sampol, J., & Dignat-George, F. (2002). Interaction of endothelial microparticles with monocytic cells in vitro induces tissue factor-dependent procoagulant activity. Blood, 99(11):3962–3970.
Abid Hussein, M. N., Böing, A. N., Biró, E., Hoek, F. J., Vogel, G. M. T., Meuleman, D. G., et al. (2008). Phospholipid composition of in vitro endothelial microparticles and their in vivo thrombogenic properties. Thrombosis Research, 121(6), 865–871.
Lacroix, R., Plawinski, L., Robert, S., Doeuvre, L., Sabatier, F., Martinez de Lizarrondo, S., et al. (2012). Leukocyte- and endothelial-derived microparticles: a circulating source for fibrinolysis. Haematologica, 97(12), 1864–1872.
Crooks, M. G., & Hart, S. P. (2015). Coagulation and anticoagulation in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. European Respiratory Review: an Official Journal of European Respiratory Society, 24(137), 392–399.
Novelli, F., Neri, T., Tavanti, L., Armani, C., Noce, C., Falaschi, F., et al. (2014). Procoagulant, tissue factor-bearing microparticles in bronchoalveolar lavage of interstitial lung disease patients: an observational study. PloS One, 9(4), e95013.
Lin, C., Borensztajn, K., & Spek, C. A. (2017). Targeting coagulation factor receptors - protease-activated receptors in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 15(4), 597–607.
Scotton, C. J., Krupiczojc, M. A., Königshoff, M., Mercer, P. F., Lee, Y. C. G., Kaminski, N., et al. (2009). Increased local expression of coagulation factor X contributes to the fibrotic response in human and murine lung injury. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 119(9), 2550–2563.
Cointe, S., Judicone, C., Robert, S., Mooberry, M. J., Poncelet, P., Wauben, M., et al. (2017). Standardization of microparticle enumeration across different flow cytometry platforms: results of a multicenter collaborative workshop. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 15(1), 187–193.
Renzoni, E. A., Walsh, D. A., Salmon, M., Wells, A. U., Sestini, P., Nicholson, A. G., et al. (2003). Interstitial vascularity in fibrosing alveolitis. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 167(3), 438–443.
Ratajczak, J., Kucia, M., Mierzejewska, K., Marlicz, W., Pietrzkowski, Z., Wojakowski, W., et al. (2013). Paracrine proangiopoietic effects of human umbilical cord blood-derived purified CD133 + cells–implications for stem cell therapies in regenerative medicine. Stem Cells and Development, 22(3), 422–430.
Wang, J., Chen, S., Ma, X., Cheng, C., Xiao, X., Chen, J., et al. (2013). Effects of endothelial progenitor cell-derived microvesicles on hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced endothelial dysfunction and apoptosis. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2013, 572729.
Bitzer, M., Ben-Dov, I. Z., & Thum, T. (2012). Microparticles and microRNAs of endothelial progenitor cells ameliorate acute kidney injury. Kidney International, 82(4), 375–377.
Doeuvre, L., & Angles-Cano, E. (2009). Cell-derived microparticles unveil their fibrinolytic and proteolytic function. Medical Science, 25(1), 37–44.
Gobin, A. S., & West, J. L. (2002). Cell migration through defined, synthetic ECM analogs. FASEB Journal: an Official Publication Federation American Society Experimental Biology, 16(7), 751–753.
Warejcka, D. J., Narayan, M., & Twining, S. S. (2011). Maspin increases extracellular plasminogen activator activity associated with corneal fibroblasts and myofibroblasts. Experimental Eye Research, 93(5), 618–627.
Strieter, R. M., Keeley, E. C., Hughes, M. A., Burdick, M. D., & Mehrad, B. (2009). The role of circulating mesenchymal progenitor cells (fibrocytes) in the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis. Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 86(5), 1111–1118.
Ruehl, M., Muche, M., Freise, C., Erben, U., Neumann, U., Schuppan, D., et al. (2011). Hydroxyproline-containing collagen analogs trigger the release and activation of collagen-sequestered proMMP-2 by competition with prodomain-derived peptide P33-42. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair, 4(1), 1.
Phillips, R. J., Burdick, M. D., Hong, K., Lutz, M. A., Murray, L. A., Xue, Y. Y., et al. (2004). Circulating fibrocytes traffic to the lungs in response to CXCL12 and mediate fibrosis. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 114(3), 438–446.
Moore, B. B., Murray, L., Das, A., Wilke, C. A., Herrygers, A. B., & Toews, G. B. (2006). The role of CCL12 in the recruitment of fibrocytes and lung fibrosis. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology, 35(2), 175–181.
Smadja, D. M., Dorfmüller, P., Guerin, C. L., Bieche, I., Badoual, C., Boscolo, E., et al. (2014). Cooperation between human fibrocytes and endothelial colony-forming cells increases angiogenesis via the CXCR4 pathway. Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 112(5), 1002–1013.
Smadja, D. M., Bièche, I., Emmerich, J., Aiach, M., & Gaussem, P. (2006). PAR-1 activation has different effects on the angiogenic activity of endothelial progenitor cells derived from human adult and cord blood. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 4(12), 2729–2731.
Ingram, D. A., Mead, L. E., Tanaka, H., Meade, V., Fenoglio, A., Mortell, K., et al. (2004). Identification of a novel hierarchy of endothelial progenitor cells using human peripheral and umbilical cord blood. Blood, 104(9):2752–2760.
Nadaud, S., Poirier, O., Girerd, B., Blanc, C., Montani, D., Eyries, M., et al. (2013). Small platelet microparticle levels are increased in pulmonary arterial hypertension. European Journal of Clinical Investigation, 43(1), 64–71.
Simoncini, S., Chateau, A.-L., Robert, S., Todorova, D., Yzydorzick, C., Lacroix, R., et al. (2017). Biogenesis of pro-senescent microparticles by endothelial colony forming cells from premature neonates is driven by SIRT1-dependent epigenetic regulation of MKK6. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 8277.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants of Chancellerie des Universities (Legs Poix) and Coeny-maeva charitable foundation.
Nour C. Bacha is supported by a grant from « Fonds de dotation pour la Recherche en Santé Respiratoire ».
We thank the technicians and engineers of hematology department of Georges Pompidou hospital, in particular Sebastien Bertil, Alexandre Kisaoglou, Florence Desvard, Nadège Ochat and Yann Burnel.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Declaration of Interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest related to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bacha, N.C., Blandinieres, A., Rossi, E. et al. Endothelial Microparticles are Associated to Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Stem Cell Rev and Rep 14, 223–235 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-017-9778-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-017-9778-5