Abstract
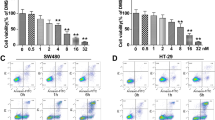
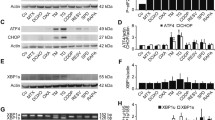
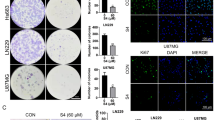
Disulfiram/copper complex (DSF/Cu) was found to have anti-tumor effects in a range of malignancies, including oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), yet its precise mechanism remains unknown. It has been shown that ER stress enhances immunogenic cell death (ICD) in tumor cells, as it can influence the anti-cancer immune system favorably. In this study, we reported that DSF/Cu exhibited a marked inhibitory effect on the growth of OSCC cells, accompanied by cell apoptosis. OSCC cells treated with DSF/Cu showed the hallmarks of immunogenic cell death (ICD), including surface expression of calreticulin (CRT), heat shock protein 70 (HSP70), high mobility-group box 1 (HMGB-1) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), thus, eliciting the maturation and activation of dendritic cells. Furthermore, we showed DSF/Cu-induced endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in OSCC cells. In vivo, results demonstrate that DSF/Cu inhibits tumor growth locally and alters the intratumoral immune cell infiltration and response. In conclusion, DSF/Cu suppresses OSCC development by inducing ICD and ER stress. DSF/Cu has the potential to be a new anti-tumor immunotherapy concept because of its ability to elicit ICD.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Johnson, D. E., Burtness, B., Leemans, C. R., Lui, V. W. Y., Bauman, J. E., & Grandis, J. R. (2020). Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 6, 92.
Chamoli, A., Gosavi, A. S., Shirwadkar, U. P., Wangdale, K. V., Behera, S. K., Kurrey, N. K., Kalia, K., & Mandoli, A. (2021). Overview of oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma: Risk factors, mechanisms, and diagnostics. Oral Oncology, 121, 105451.
Dhanuthai, K., Rojanawatsirivej, S., Thosaporn, W., Kintarak, S., Subarnbhesaj, A., Darling, M., Kryshtalskyj, E., Chiang, C. P., Shin, H. I., Choi, S. Y., Lee, S. S., & Aminishakib, P. (2018). Oral cancer: A multicenter study. Medicina Oral Patologica Oral Y Cirugia Bucal, 23, e23–e29.
Yang, H., Wei, Y. C., Li, W. C., Chen, H. Y., Lin, H. Y., Chiang, C. P., & Chen H. M. (2020). Natural compounds modulate drug transporter mediated oral cancer treatment. Biomolecules, 10, 1335.
Li, H., Zhang, Y., Xu, M., & Yang, D. (2022). Current trends of targeted therapy for oral squamous cell carcinoma. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology, 148, 2169–2186.
Kitamura, N., Sento, S., Yoshizawa, Y., Sasabe, E., Kudo, Y. & Yamamoto, T. (2020). Current trends and future prospects of molecular targeted therapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22, 240.
Birmpilis, A. I., Paschalis, A., Mourkakis, A., Christodoulou, P., Kostopoulos, I. V., Antimissari, E., Terzoudi, G. (2022). Immunogenic cell death, DAMPs and prothymosin α as a putative anticancer immune response biomarker. Cells, 11, 1415.
Andersson, U., Wang, H., Palmblad, K., Aveberger, A. C., Bloom, O., Erlandsson-Harris, H., Janson, A., Kokkola, R., Zhang, M., Yang, H., & Tracey, K. J. (2000). High mobility group 1 protein (HMG-1) stimulates proinflammatory cytokine synthesis in human monocytes. The Journal of Experimental Medicine, 192, 565–570.
Lewis, D. J., Deshmukh, P., Tedstone, A. A., Tuna, F., & O’Brien, P. (2014). On the interaction of copper(II) with disulfiram. Chemical Communication, 50, 13334–13337.
Ni, Y., Chien, H., Hsieh, H., Shen, H., Lee, S., & Chen, W. (2022). Disulfiram/copper suppresses cancer stem cell activity in differentiated thyroid cancer cells by inhibiting BMI1 expression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23, 13276.
Gao, X., Huang, H., Pan, C., Mei, Z., Yin, S., Zhou, L., & Zheng, S. (2022). Disulfiram/copper induces immunogenic cell death and enhances CD47 blockade in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers, 14, 4715.
Yang, Y., Li, M., Sun, X., Zhou, C., Wang, Y., Wang, L., Chen, L., Liang, Z., Zhu, L., & Yang, H. (2017). The selective cytotoxicity of DSF-Cu attributes to the biomechanical properties and cytoskeleton rearrangements in the normal and cancerous nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. The International Journal of Biochemical & Cell Biology, 84, 96–108.
Chen, D., Cui, Q. C., Yang, H., & Dou, Q. P. (2006). Disulfiram, a clinically used anti-alcoholism drug and copper-binding agent, induces apoptotic cell death in breast cancer cultures and xenografts via inhibition of the proteasome activity. Cancer Research, 66, 10425–10433.
Zhao, Y., & Zhu, S. (2023). Nrf2/HO-1 alleviates disulfiram/copper-induced ferroptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Biochemical Genetics, 62, 144–155.
Sun, T., Yang, W., Toprani, S. M., Guo, W., He, L., DeLeo, A. B., Ferrone, S., Zhang, G., Wang, E., Lin, Z., Hu, P., Wang, X. (2020). Induction of immunogenic cell death in radiation-resistant breast cancer stem cells by repurposing anti-alcoholism drug disulfiram. Cell Communication and Signaling, 18, 36.
You, S. Y., Rui, W., Chen, S. T., Chen, H. C., Liu, X. W., Huang, J., & Chen, H. Y. (2019). Process of immunogenic cell death caused by disulfiram as the anti-colorectal cancer candidate. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communication, 513, 891–897.
Sagar, V., Vatapalli, R., Lysy, B., Pamarthy, S., Anker, J. F., Rodriguez, Y., Han, H., Unno, K., Stadler, W. M., Catalona, W. J., Hussain, M., Gill, P. S., & Abdulkadir, S. A. (2019). EPHB4 inhibition activates ER stress to promote immunogenic cell death of prostate cancer cells. Cell Death & Disease, 10, 801.
Yuan, Y., Li, X., Chu, Y., Ye, G., Yang, L., & Dong, Z. (2021). Long non-coding RNA H19 augments hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced renal tubular epithelial cell apoptosis and injury by the miR-130a/BCL2L11 pathway. Frontiers in Physiology, 12, 632398.
Wang, Y., Drum, D. L., Sun, R., Zhang, Y., Chen, F., Sun, F., Dal, E., Yu, L., Jia, J., Arya, S., Jia, L., & Fan, S. (2023). Stressed target cancer cells drive nongenetic reprogramming of CAR T cells and solid tumor microenvironment. Nature Communications, 14, 5727.
Pozzi, C., Cuomo, A., Spadoni, I., Magni, E., Silvola, A., Conte, A., Sigismund, S., Ravenda, P. S., Bonaldi, T., Zampino, M. G., Cancelliere, C., Di Fiore, P. P., Bardelli, A., Penna, G., & Rescigno, M. (2016). The EGFR-specific antibody cetuximab combined with chemotherapy triggers immunogenic cell death. Nature Medicione, 22, 624–631.
Tang, D., Kepp, O. (2020). Ferroptosis becomes immunogenic: implications for anticancer treatments. Oncoimmunology, 10, 1862949.
Yip, N. C., Fombon, I. S., Liu, P., Brown, S., Kannappan, V., Armesilla, A. L., Xu, B., Cassidy, J., Darling, J. L., & Wang, W. (2011). Disulfiram modulated ROS-MAPK and NFκB pathways and targeted breast cancer cells with cancer stem cell-like properties. British Journal of Cancer, 104, 1564–1574.
Zhang, X., Hu, P., Ding, S. Y., Sun, T., Liu, L., Han, S., DeLeo, A. B., Sadagopan, A., Guo, W., & Wang, X. (2019). Induction of autophagy-dependent apoptosis in cancer cells through activation of ER stress: an uncovered anti-cancer mechanism by anti-alcoholism drug disulfiram. American Journal of Cancer Research, 9, 1266–1281.
Krysko, D. V., Garg, A. D., Kaczmarek, A., Krysko, O., Agostinis, P., & Vandenabeele, P. (2012). Immunogenic cell death and DAMPs in cancer therapy. Nature Reviews Cancer, 12, 860–875.
Shah O’Brien, P., Xi, Y., Miller, J. R., Brownell, A. L., Zeng, Q., Yoo, G. H., Garshott, D. M., O’Brien, M. B., Galinato, A. E., Cai, P., Narula, N., Callaghan, M. U., Kaufman, R. J. (2019). Disulfiram (Antabuse) activates ROS-dependent ER stress and apoptosis in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8, 611.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the reviewers for their helpful comments on this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.Z. and S.Z. designed and performed the research; Y.Z. and B.Z. analyzed the data; Y.Z. wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
All animal experiments have been reviewed and approved by the Institutional Ethics Review Committee of the Tianjin First Central Hospital.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Zhao, B. & Zhu, S. Disulfiram/Copper Activates ER Stress to Promote Immunogenic Cell Death of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cell Biochem Biophys (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-024-01283-z
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-024-01283-z