Abstract
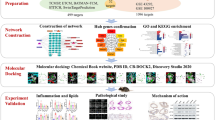
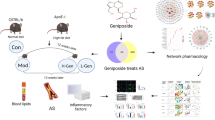
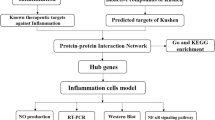
We investigated the mechanisms underlying the effects of Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam. (ZCL) on atherosclerosis (AS) using network pharmacology and in vitro validation.We collected the active components of ZCL and predicted their targets in AS. We constructed the protein-protein interaction, compound-target, and target-compound-pathway networks, and performed GO and KEGG analyses. Molecular docking of the active components and key targets was constructed with Autodock and Pymol software. Validation was performed with qRT-PCR, ELISA, and Western blot.We obtained 80 components of ZCL. The network analysis identified that 14 components and 37 genes were involved in AS. Then, 10 key nodes in the PPI network were identified as the key targets of ZCL because of their importance in network topology. The binding energy of 8 components (Cynaroside, α-Spinasterol, Linarin, Kaempferide, Acacetin, Genkwanin, Chrysin, and Apiin) to 4 targets (MMP9, TP53, AKT1, SRC) was strong and <−1 kJ/mol. In addition, 13 of the 14 components were flavonoids and thus total flavonoids of Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam. (ZCF) were used for in vitro validation. We found that ZCF reduced eNOS, P22phox, gp91phox, and PCSK9 at mRNA and protein levels, as well as the levels of IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6 proteins in vitro (P < 0.05).We successfully predicted the active components, targets, and mechanisms of ZCL in treating AS using network pharmacology. We confirmed that ZCF may play a role in AS by modulating oxidative stress, lipid metabolism, and inflammatory response via Cynaroside, Linarin, Kaempferide, Acacetin, Genkwanin, Chrysin, and Apiin.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AS:
-
Atherosclerosis;
- ZCL:
-
Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam.;
- GO:
-
Gene Ontology;
- PPI:
-
protein-protein interaction;
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes;
- ZCF:
-
flavonoids of Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam.;
- HUVEC:
-
Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells;
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde;
- SOD:
-
superoxide dismutase;
- NO:
-
nitric oxide;
- ADME:
-
absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion;
- TCMSP:
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database;
- DL:
-
drug-likeness;
- OB:
-
oral bioavailability;
- VC:
-
Vitamin C
References
Libby, P., Buring, J. E., & Badimon, L., et al. (2019). Atherosclerosis. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 5(1), 56.
Zhang, Y., Gu, Y., & Chen, Y., et al. (2021). Dingxin Recipe IV attenuates atherosclerosis by regulating lipid metabolism through LXR-α/SREBP1 pathway and modulating the gut microbiota in ApoE(-/-) mice fed with HFD. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 266, 113436.
Schaftenaar, F., Frodermann, V., Kuiper, J., & Lutgens, E. (2016). Atherosclerosis: the interplay between lipids and immune cells. Current Opinion in Lipidology, 27(3), 209–215.
Aguilar-Ballester, M., Herrero-Cervera, A., Vinue, A., Martinez-Hervas, S. & Gonzalez-Navarro, H. (2020). Impact of Cholesterol Metabolism in Immune Cell Function and Atherosclerosis. Nutrients, 12(7), 2021
Saigusa, R., Winkels, H., & Ley, K. (2020). T cell subsets and functions in atherosclerosis. Nature Reviews Cardiology, 17(7), 387–401.
Meschia, J. F., Klaas, J. P., Brown, Jr., R. D., & Brott, T. G. (2017). Evaluation and Management of Atherosclerotic Carotid Stenosis. Mayo Clinic Proceedings, 92(7), 1144–1157.
Kazi, D. S., Penko, J. M., & Bibbins-Domingo, K. (2017). Statins for Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: Review of Evidence and Recommendations for Clinical Practice. The Medical Clinics of North America, 101(4), 689–699.
Jian, X., Liu, Y., Zhao, Z., Zhao, L., Wang, D., & Liu, Q. (2019). The role of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of atherosclerosis through the regulation of macrophage activity. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & Pharmacotherapie, 118, 109375.
Wei, J., Huang, L., & Li, D., et al. (2021). Total Flavonoids of Engelhardia roxburghiana Wall. Leaves Alleviated Foam Cells Formation through AKT/mTOR-Mediated Autophagy in the Progression of Atherosclerosis. Chemistry & Biodiversity, 18(9), e2100308.
Shi, X., Huang, H., Zhou, M., Liu, Y., Wu, H., & Dai, M. (2021). Paeonol Attenuated Vascular Fibrosis Through Regulating Treg/Th17 Balance in a Gut Microbiota-Dependent Manner. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 12, 765482.
Li, T. T., Wang, Z. B., Li, Y., Cao, F., Yang, B. Y., & Kuang, H. X. (2019). The mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine underlying the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis. Chinese Journal of Natural Medicines, 17(6), 401–412.
Li, Y., Zhang, L., & Ren, P., et al. (2021). Qing-Xue-Xiao-Zhi formula attenuates atherosclerosis by inhibiting macrophage lipid accumulation and inflammatory response via TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway regulation. Phytomedicine : International Journal of Phytotherapy and Phytopharmacology, 93, 153812.
Guo, H. Y., Lu, Z. Y., Zhao, B., Jiang, W. W., Xiong, Y. H., & Wang, K. (2021). Effects of Bunao-Fuyuan decoction serum on proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerotic. Chinese Journal of Natural Medicines, 19(1), 36–45.
Tian, S., Yu, Q., Wang, D., & Upur, H. (2012). Development of a rapid resolution liquid chromatography-diode array detector method for the determination of three compounds in Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam from different origins of Xinjiang. Pharmacognosy Magazine, 8(32), 280–284.
Tian, S., Shi, Y., Zhou, X., Ge, L., & Upur, H. (2011). Total polyphenolic (flavonoids) content and antioxidant capacity of different Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam. extracts. Pharmacognosy Magazine, 7(25), 65–68.
Behravan, J., Ramezani, M., & Hassanzadeh, M. K. (2007). Composition, Antimycotic and Antibacterial Activity of Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam. Essential Oil from Iran. Journal of Essential Oil Bearing Plants, 10(4), 339–345.
Ding, W., Yang, T., Liu, F., & Tian, S. (2014). Effect of different growth stages of Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam. on its chemical composition. Pharmacognosy Magazine, 10(Suppl 1), S1–S5.
Tian, S., Shi, Y., & Yu, Q. & Upur, H. (2010). Determination of oleanolic acid and ursolic acid contents in Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam. by HPLC method. Pharmacognosy Magazine, 6(22), 116–119.
Senejoux, F., Demougeot, C., & Kerram, P., et al. (2012). Bioassay-guided isolation of vasorelaxant compounds from Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam. (Lamiaceae). Fitoterapia, 83(2), 377–382.
Zhang, H., Ma, X. K., & Wang, S. J., et al. (2020). Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam. Attenuates Atherosclerosis in Mice via Modulating TLR4/ NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Chinese Circulation Journal, 35(04), 395–400.
Zhang, X. M., & An, D. Q. (2018). Research progress on chemical constituents, pharmacology and clinical application of Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam. Journal of Emergency in Traditional Chinese Medicine, 27(03), 548–551.
Zhang, X., An, D., & Guo, L. (2019). Preliminary screening of active components in regulating autophagy in Ziziphora clinopodioide Lam. Pakistan Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 32(6), 2611–2615.
Senejoux, F., Girard, C., & Kerram, P., et al. (2010). Mechanisms of vasorelaxation induced by Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam. (Lamiaceae) extract in rat thoracic aorta. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 132(1), 268–273.
Wu, Y., Wang, Y., & Liu, X., et al. (2020). Ziziphora clinopodioides flavonoids based on network pharmacology attenuates atherosclerosis in rats induced by high-fat emulsion combined with vitamin D3 by down-regulating VEGF/AKT/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & Pharmacotherapie, 129, 110399.
Lan, W., Guo, Y. T., & Wu, Y. N. (2014). Study on the technology of microwave extraction of total flavonoids content from Uygur medicine Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam. Journal of Xinjiang Medical University, 37(03), 261–262.
Xu, Y. Z., Meng, Q. Y., Liu, W. J., Liu, Y., Lu, Y. L., & Jin, Y. X. (2013). Optimization of the Extraction Method of the Volatile Components from Ziziphora clinopodioides. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medicine Form, 19(06), 108–112.
Li, G. Z., Zhang, Y. Y., & Meng, Q. Y. (2013). Drug purification technology of the total flavonoids from Ziziphora linopodioides Lam. China Brewing, 32(10), 22–25.
Zhang, X. M., An, D. Q., Guo, L. L., Yang, N. H., & Zhang, H. (2019). Identification and screening of active components from Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam. in regulating autophagy. Natural Product Research, 33(17), 2549–2553.
Li, Q., Tursun, D., Shi, C., Heyrulla, M., Zhang, X., & Yang, W. (2018). Ziziphora clinopodioides Flavonoids Protect Myocardial Cell Damage from Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2018, 8495010.
Šmejkal, K., Malaník, M. & Zhaparkulova, K, et al. (2016). Kazakh Ziziphora Species as Sources of Bioactive Substances. Molecules, 21(7), 826
Li, G., Meng, Q., Luo, B., Ge, Z., & Liu, W. (2015). [Isolation of chemical constituents from Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam. with recycling preparative high performance liquid chromatography]. Se pu = Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 33(1), 84–89.
Tiana, S., Yu, Q., Xin, L., Zhou, Z. S., & Upur, H. (2012). Chemical fingerprinting by RP-RRLC-DAD and principal component analysis of Ziziphora clinopodioides from different locations. Natural Product Communications, 7(9), 1181–1184.
Shahbazi, Y. (2017). Chemical compositions, antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam. essential oils collected from different parts of Iran. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 54(11), 3491–3503.
Liu, J., Nile, S. H., Xu, G., Wang, Y., & Kai, G. (2021). Systematic exploration of Astragalus membranaceus and Panax ginseng as immune regulators: Insights from the comparative biological and computational analysis. Phytomedicine : International Journal of Phytotherapy and Phytopharmacology, 86, 153077.
Li, L., Qiu, H., Liu, M., & Cai, Y. (2020). A Network Pharmacology-Based Study of the Molecular Mechanisms of Shaoyao-Gancao Decoction in Treating Parkinson’s Disease. Interdisciplinary Sciences, Computational Life Sciences, 12(2), 131–144.
Wang, W., Liu, T., & Yang, L., et al. (2019). Study on the multi-targets mechanism of triphala on cardio-cerebral vascular diseases based on network pharmacology. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & Pharmacotherapie, 116, 108994.
Li, Y., Qin, R., & Yan, H., et al. (2018). Inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cells premature senescence with rutin attenuates and stabilizes diabetic atherosclerosis. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 51, 91–98.
Cho, B. O., Che, D. N., Shin, J. Y., Kang, H. J., Kim, J. H., & Jang, S. I. (2020). Anti-obesity effects of enzyme-treated celery extract in mice fed with high-fat diet. Journal of Food Biochemistry, 44(1), e13105.
Li, Q., Tian, Z., & Wang, M., et al. (2019). Luteoloside attenuates neuroinflammation in focal cerebral ischemia in rats via regulation of the PPARgamma/Nrf2/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. International Immunopharmacology, 66, 309–316.
Tai, J., Zou, J., & Zhang, X., et al. (2019). Using Network Pharmacology to Explore Potential Treatment Mechanism for Coronary Heart Disease Using Chuanxiong and Jiangxiang Essential Oils in Jingzhi Guanxin Prescriptions. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2019, 7631365.
Gong, B., Kao, Y., Zhang, C., Sun, F., & Zhao, H. (2018). Systematic Investigation of Scutellariae Barbatae Herba for Treating Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on Network Pharmacology. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2018, 4365739.
Chen, S., Xiao, Y., Ponnusamy, R., Tan, J., Lei, J., & Hilgenfeld, R. (2011). X-ray structure of the SH3 domain of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase p85beta subunit. Acta Crystallographica Section F, Structural Biology and Crystallization Communications., 67(Pt 11), 1328–1333.
Heffron, T. P., Heald, R. A., & Ndubaku, C., et al. (2016). The Rational Design of Selective Benzoxazepin Inhibitors of the α-Isoform of Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Culminating in the Identification of (S)-2-((2-(1-Isopropyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[f]imidazo[1,2-d][1,4]oxazepin-9-yl)oxy)propanamide (GDC-0326). Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 59(3), 985–1002.
Yasuda, H., Park, E., & Yun, C. H., et al. (2013). Structural, biochemical, and clinical characterization of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 20 insertion mutations in lung cancer. Science Translational Medicine 5(216), 216ra177.
Hennequin, L. F., Allen, J. & & Breed, J. et al. (2006). N-(5-chloro-1,3-benzodioxol-4-yl)-7-[2-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)ethoxy]-5- (tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-yloxy)quinazolin-4-amine, a novel, highly selective, orally available, dual-specific c-Src/Abl kinase inhibitor. Journal of medicinal chemistry, 49(22), 6465–6488.
Xia, Q. D., Xun, Y., & Lu, J. L., et al. (2020). Network pharmacology and molecular docking analyses on Lianhua Qingwen capsule indicate Akt1 is a potential target to treat and prevent COVID-19. Cell Proliferation, 53(12), e12949.
Milburn, C. C., Deak, M., Kelly, S. M., Price, N. C., Alessi, D. R., & Van Aalten, D. M. (2003). Binding of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate to the pleckstrin homology domain of protein kinase B induces a conformational change. The Biochemical Journal, 375(Pt 3), 531–538.
Sari, D. R. T., Cairns, J. R. K., Safitri, A., & Fatchiyah, F. (2019). Virtual Prediction of the Delphinidin-3-O-glucoside and Peonidin-3-O-glucoside as Anti-inflammatory of TNF-α Signaling. Acta Informatica Medica : AIM : Journal of the Society for Medical Informatics of Bosnia & Herzegovina : Casopis Drustva za medicinsku informatiku BiH, 27(3), 152–157.
Song, X., Zhang, Y., Dai, E., Wang, L., & Du, H. (2020). Prediction of triptolide targets in rheumatoid arthritis using network pharmacology and molecular docking. International Immunopharmacology, 80, 106179.
Chang, Y., Levy, D., & Horton, J. R., et al. (2011). Structural basis of SETD6-mediated regulation of the NF-kB network via methyl-lysine signaling. Nucleic Acids Research, 39(15), 6380–6389.
Zheng, Y., Lv, P., Huang, J., Ke, J., & Yan, J. (2020). GYY4137 exhibits anti-atherosclerosis effect in apolipoprotein E (-/-) mice via PI3K/Akt and TLR4 signalling. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology & Physiology, 47(7), 1231–1239.
Fang, S., Wan, X., & Zou, X., et al. (2021). Arsenic trioxide induces macrophage autophagy and atheroprotection by regulating ROS-dependent TFEB nuclear translocation and AKT/mTOR pathway. Cell Death & Disease, 12(1), 88.
Karshovska, E., Wei, Y., & Subramanian, P., et al. (2020). HIF-1α (Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α) Promotes Macrophage Necroptosis by Regulating miR-210 and miR-383. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 40(3), 583–596.
Han, X., Ma, W., Zhu, Y., Sun, X., & Liu, N. (2020). Advanced glycation end products enhance macrophage polarization to the M1 phenotype via the HIF-1alpha/PDK4 pathway. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 514, 110878.
Cheng, X., Liu, Z., Zhang, H., & Lian, Y. (2021). Inhibition of LOXL1-AS1 alleviates oxidative low-density lipoprotein induced angiogenesis via downregulation of miR-590-5p mediated KLF6/VEGF signaling pathway. Cell Cycle (Georgetown, Tex), 20(17), 1663–1680.
Gomes de Almeida Schirmer, B., Crucet, M., & Stivala, S., et al. (2020). The NO-donor MPC-1011 stimulates angiogenesis and arteriogenesis and improves hindlimb ischemia via a cGMP-dependent pathway involving VEGF and SDF-1alpha. Atherosclerosis, 304, 30–38.
Choi, H., Dey, A. K., & Priyamvara, A., et al. (2021). Role of Periodontal Infection, Inflammation and Immunity in Atherosclerosis. Current Problems in Cardiology, 46(3), 100638.
Kwiatkowska, M., Oldakowska-Jedynak, U., Wojtaszek, E., Glogowski, T., & Malyszko, J. (2021). Potential Effects of Immunosuppression on Oxidative Stress and Atherosclerosis in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2021, 6660846.
Wang, X., Du, H., & Li, X. (2022). Artesunate attenuates atherosclerosis by inhibiting macrophage M1-like polarization and improving metabolism. International Immunopharmacology, 102, 108413.
Long, X., You, G., & Wu, Q., et al. (2021). HomeoboxC6 affects the apoptosis of human vascular endothelial cells and is involved in atherosclerosis. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 236(3), 1913–1925.
Dong, G., Yu, J., Shan, G., Su, L., Yu, N., & Yang, S. (2021). N6-Methyladenosine Methyltransferase METTL3 Promotes Angiogenesis and Atherosclerosis by Upregulating the JAK2/STAT3 Pathway via m6A Reader IGF2BP1. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 9, 731810.
Hargreaves, C. E., Dhalla, F., & Patel, A. M., et al. (2022). Resolving the polygenic aetiology of a late onset combined immune deficiency caused by NFKB1 haploinsufficiency and modified by PIK3R1 and TNFRSF13B variants. Clinical Immunology (Orlando, Fla), 234, 108910.
Zhan, H., Huang, F., & Niu, Q., et al. (2021). Downregulation of miR-128 Ameliorates Ang II-Induced Cardiac Remodeling via SIRT1/PIK3R1 Multiple Targets. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2021, 8889195.
Tiemin, P., Fanzheng, M., & Peng, X., et al. (2020). MUC13 promotes intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma progression via EGFR/PI3K/AKT pathways. Journal of Hepatology, 72(4), 761–773.
Yueh, P. F., Lee, Y. H., & Chiang, I. T., et al. (2021). Suppression of EGFR/PKC-δ/NF-κB Signaling Associated With Imipramine-Inhibited Progression of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Frontiers in Oncology, 11, 735183.
Wei, S. G., Yu, Y., & Felder, R. B. (2021). TNF-α-induced sympathetic excitation requires EGFR and ERK1/2 signaling in cardiovascular regulatory regions of the forebrain. American Journal of Physiology Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 320(2), H772–h786.
Nilsson, M. B., Robichaux, J., & Herynk, M. H., et al. (2021). Altered Regulation of HIF-1α in Naive- and Drug-Resistant EGFR-Mutant NSCLC: Implications for a Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-Dependent Phenotype. Journal of Thoracic Oncology : Official Publication of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, 16(3), 439–451.
Brian, B. F. & Freedman, T. S. (2021). The Src-family Kinase Lyn in Immunoreceptor Signaling. Endocrinology, 162(10), 1–13.
Xia, X., Chen, Y., Xu, J., Yu, C., & Chen, W. (2021). SRC-3 deficiency protects host from Listeria monocytogenes infection through increasing ROS production and decreasing lymphocyte apoptosis. International Immunopharmacology, 96, 107625.
Strzeszewska-Potyrała, A., Staniak, K., & Czarnecka-Herok, J., et al. (2021). Chromatin-Directed Proteomics Identifies ZNF84 as a p53-Independent Regulator of p21 in Genotoxic Stress Response. Cancers., 13(9), 2115.
Ren, Q., Guo, F., Tao, S., Huang, R., Ma, L., & Fu, P. (2020). Flavonoid fisetin alleviates kidney inflammation and apoptosis via inhibiting Src-mediated NF-kappaB p65 and MAPK signaling pathways in septic AKI mice. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & Pharmacotherapie, 122, 109772.
Abu El-Asrar, A. M., Nawaz, M. I., & Ahmad, A., et al. (2021). CD146/Soluble CD146 Pathway Is a Novel Biomarker of Angiogenesis and Inflammation in Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, 62(9), 32.
Li, H., Sun, F. & Bai, S, et al. (2022). The DR1‑CSE/H(2)S system inhibits renal fibrosis by downregulating the ERK1/2 signaling pathway in diabetic mice. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 49(1), 1–10.
Akad Dincer, S., Sahin, F. I., Terzi, Y. K., Gulleroglu, K., Baskin, E. & Haberal, M. (2020). Impact of Matrix Metalloproteinases 2 and 9 and Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase 2 Gene Polymorphisms on Allograft Rejection in Pediatric Renal Transplant Recipients. Experimental and clinical Transplantation : Official Journal of the Middle East Society for Organ Transplantation, 21(4), 333–337.
Todd, J. L., Vinisko, R., & Liu, Y., et al. (2020). Circulating matrix metalloproteinases and tissue metalloproteinase inhibitors in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in the multicenter IPF-PRO Registry cohort. BMC Pulmonary Medicine, 20(1), 64.
Timokhina, E., Strizhakov, A., & Ibragimova, S., et al. (2020). Matrix Metalloproteinases MMP-2 and MMP-9 Occupy a New Role in Severe Preeclampsia. Journal of Pregnancy, 2020, 8369645.
Lee, E. J., Zheng, M., Craft, C. M., & Jeong, S. (2021). Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1 (TIMP-1) are localized in the nucleus of retinal Muller glial cells and modulated by cytokines and oxidative stress. PloS ONE, 16(7), e0253915.
Ding, M., Jiang, C. Y., Zhang, Y., Zhao, J., Han, B. M., & Xia, S. J. (2020). SIRT7 depletion inhibits cell proliferation and androgen-induced autophagy by suppressing the AR signaling in prostate cancer. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 39(1), 28.
Rangel, N., Rondon-Lagos, M. & Annaratone, L, et al. (2020). AR/ER Ratio Correlates with Expression of Proliferation Markers and with Distinct Subset of Breast Tumors. Cells, 9(4), 1064.
Zhang, G., Chen, H. X., Yang, S. N., & Zhao, J. (2020). MAGI1-IT1 stimulates proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer by upregulating AKT1 as a ceRNA. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 24(2), 691–698.
Peng, Z., Aggarwal, R. & Zeng, N, et al. (2020). AKT1 Regulates Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Mediates the Adaptive Response of Pancreatic beta Cells. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 40(11), e00031–20.
Tripathy, A. S., Vishwakarma, S., & Trimbake, D., et al. (2021). Pro-inflammatory CXCL-10, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6: biomarkers of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Archives of Virology, 166(12), 3301–3310.
Ferrara, A. L., Galdiero, M. R., & Fiorelli, A., et al. (2021). Macrophage-polarizing stimuli differentially modulate the inflammatory profile induced by the secreted phospholipase A2 group IA in human lung macrophages. Cytokine 138, 155378.
Chen, J. S., Alfajaro, M. M. & Chow, R. D, et al. (2021). Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs dampen the cytokine and antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Journal of Virology, 95(7), e00014–21.
Piasecka, D., Braun, M., & Mieszkowska, M., et al. (2020). Upregulation of HIF1-α via an NF-κB/COX2 pathway confers proliferative dominance of HER2-negative ductal carcinoma in situ cells in response to inflammatory stimuli. Neoplasia 22(11), 576–589.
Meriwether, D., Jones, A. E., & Ashby, J. W., et al. (2022). Macrophage COX2 Mediates Efferocytosis, Resolution Reprogramming, and Intestinal Epithelial Repair. Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 13(4), 1095–1120.
Iqbal, S., Shah, F. A. & Naeem, K, et al. (2020). Succinamide Derivatives Ameliorate Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress in Scopolamine-Induced Neurodegeneration. Biomolecules, 10(3), 443.
Zarate, M. A., Nguyen, L. M., De Dios, R. K., Zheng, L., & Wright, C. J. (2020). Maturation of the Acute Hepatic TLR4/NF-κB Mediated Innate Immune Response Is p65 Dependent in Mice. Frontiers in Immunology, 11, 1892.
Chawla, M., Mukherjee, T. & Deka, A, et al. (2021). An epithelial Nfkb2 pathway exacerbates intestinal inflammation by supplementing latent RelA dimers to the canonical NF-kappaB module. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 118(25), e20248281.
Peng, L., Wen, L., & Shi, Q. F., et al. (2020). Scutellarin ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis through inhibiting NF-κB/NLRP3-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and inflammation. Cell Death & Disease, 11(11), 978.
Song, L., Chen, X., & Mi, L., et al. (2020). Icariin-induced inhibition of SIRT6/NF-κB triggers redox mediated apoptosis and enhances anti-tumor immunity in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Science, 111(11), 4242–4256.
Zhou, J., Jiang, Y. Y., Chen, H., Wu, Y. C., & Zhang, L. (2020). Tanshinone I attenuates the malignant biological properties of ovarian cancer by inducing apoptosis and autophagy via the inactivation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Cell Proliferation, 53(2), e12739.
Guan, J., Lin, H., & Xie, M., et al. (2019). Higenamine exerts an antispasmodic effect on cold-induced vasoconstriction by regulating the PI3K/Akt, ROS/alpha2C-AR and PTK9 pathways independently of the AMPK/eNOS/NO axis. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 18(2), 1299–1308.
Yu, M., Liu, W., & Li, J., et al. (2020). Exosomes derived from atorvastatin-pretreated MSC accelerate diabetic wound repair by enhancing angiogenesis via AKT/eNOS pathway. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 11(1), 350.
He, H., Wang, L., & Qiao, Y., et al. (2019). Doxorubicin Induces Endotheliotoxicity and Mitochondrial Dysfunction via ROS/eNOS/NO Pathway. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 10, 1531.
Huang, C., Huang, W., Wang, R., & He, Y. (2020). Ulinastatin Inhibits the Proliferation, Invasion and Phenotypic Switching of PDGF-BB-Induced VSMCs via Akt/eNOS/NO/cGMP Signaling Pathway. Drug Design, Development and Therapy, 14, 5505–5514.
Man, A. W. C., Li, H., & Xia, N. (2019). The Role of Sirtuin1 in Regulating Endothelial Function, Arterial Remodeling and Vascular Aging. Frontiers in Physiology, 10, 1173.
Movafagh, S., Crook, S., & Vo, K. (2015). Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1a by reactive oxygen species: new developments in an old debate. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 116(5), 696–703.
Yang, Z., Huang, Y., & Zhu, L., et al. (2021). SIRT6 promotes angiogenesis and hemorrhage of carotid plaque via regulating HIF-1alpha and reactive oxygen species. Cell Death & Disease, 12(1), 77.
Kerber, E. L., Padberg, C., Koll, N., Schuetzhold, V., Fandrey, J. & Winning, S. (2020). The Importance of Hypoxia-Inducible Factors (HIF-1 and HIF-2) for the Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(22), eci.13459.
Ragusa, R., Basta, G., Neglia, D., De Caterina, R., Del Turco, S., & Caselli, C. (2021). PCSK9 and atherosclerosis: Looking beyond LDL regulation. European Journal of Clinical Investigation, 51(4), e13459.
Funding
This research was funded by Open Research Funding of the Key Laboratory of Xinjiang Uighur Autonomous Region [grant number 2016D03025].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.A. and H.L. designed the research study and revised the paper. H.L., J.Z., and X.Y. performed the research and analyzed the data. H.L. and J.Z. wrote the paper. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the paper. All authors read and approved the final paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Zhang, J., Yan, X. et al. The Anti-atherosclerosis Mechanism of Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam. Based On Network Pharmacology. Cell Biochem Biophys 81, 515–532 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-023-01151-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-023-01151-2