Abstract
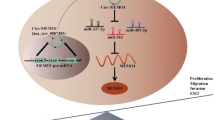
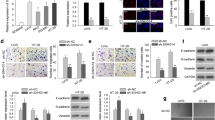
Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a malignant cancer with a high mortality. Accumulating studies have revealed that mRNAs involved in ceRNA (competing endogenous RNA) network are implicated in the tumorigenesis and development of CRC. Here, we aimed to elucidate the ceRNA network involving Src kinase associated phosphoprotein 1 (SKAP1) in the biological characteristics of CRC. Methods: Expression levels of genes in colon adenocarcinoma (COAD) samples and prognosis of COAD patients were predicted using publicly available online tool. 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT), clony formation and Transwell assays were conducted to test the biological functions of SKAP1 and THUMPD3 antisense RNA 1 (THUMPD3-AS1) in CRC cells. Western blot was used to measure the protein levels of SKAP1. Gene expression in CRC cells was detected by reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). The interaction between miR-218-5p and THUMPD3-AS1 (or SKAP1) was verified by RNA pulldown and luciferase reporter assays. Results: SKAP1 was upregulated in COAD tissues and CRC cells and it reflected a poor prognosis in patients with COAD. SKAP1 knockdown inhibited CRC (HT-29 and HCT-116) cell proliferation, migration and invasion. Mechanistically, THUMPD3-AS1 acted as a ceRNA to sponge miR-218-5p and subsequently upregulated SKAP1 expression in CRC cells. SKAP1 overexpression reversed the suppressive effect of THUMPD3-AS1 knockdown on proliferation, migration and invision of CRC cells. Conclusions:THUMPD3-AS1 promotes CRC cell growth and aggressiveness by regulating the miR-218-5p/SKAP1 axis.






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
27 November 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-023-01199-0
Abbreviations
- CRC:
-
colorectal cancer
- COAD:
-
colon adenocarcinoma
- SKAP1:
-
Src kinase associated phosphoprotein 1
- THUMPD3-AS1:
-
THUMPD3 antisense RNA 1, miR-218-5p, microRNA-218-5p
- ceRNA:
-
competing endogenous RNA
- RT-qPCR:
-
reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- ncRNA:
-
noncoding RNA
- DFS:
-
disease free survival
- OS:
-
overall survival
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium
- FBS:
-
fetal bovine serum
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- Wt:
-
wild type
- Mut:
-
mutant type
- NC:
-
negative control
- GAPDH:
-
glyceraldehyde-3phosphate dehydrogenase.
References
Ferlay, J., Soerjomataram, I., Dikshit, R., Eser, S., Mathers, C., Rebelo, M., Parkin, D. M., Forman, D., & Bray, F. (2015). Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer, 136(5), E359–86.
Bray, F., Ferlay, J., Soerjomataram, I., Siegel, R. L., Torre, L. A., & Jemal, A. (2018). Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin, 68(6), 394–424.
Zhang, Z., Qian, W., Wang, S., Ji, D., Wang, Q., Li, J., Peng, W., Gu, J., Hu, T., Ji, B., Zhang, Y., Wang, S., & Sun, Y. (2018). Analysis of lncRNA-associated ceRNA network reveals potential lncRNA biomarkers in human colon adenocarcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem, 49(5), 1778–1791.
Poursheikhani, A., Abbaszadegan, M. R., Nokhandani, N., & Kerachian, M. A. (2020). Integration analysis of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) role in tumorigenesis of colon adenocarcinoma. BMC Med Genomics, 13(1), 108.
Ruan, G. T., Wang, S., Zhu, L. C., Liao, X. W., Wang, X. K., Liao, C., Yan, L., Xie, H. L., Gong, Y. Z., Gan, J. L., & Gao, F. (2021). Investigation and verification of the clinical significance and perspective of natural killer group 2 member D ligands in colon adenocarcinoma. Aging (Albany NY), 13(9), 12565–12586.
Li, Z., Sun, Y., He, M., & Liu, J. (2021). Differentially-expressed mRNAs, microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs in intervertebral disc degeneration identified by RNA-sequencing. Bioengineered., 12(1), 1026–1039.
Shi, Z., Shen, C., Yu, C., Yang, X., Shao, J., Guo, J., Zhu, X., & Zhou, G. (2021). Long non-coding RNA LINC00997 silencing inhibits the progression and metastasis of colorectal cancer by sponging miR-512-3p. Bioengineered., 12(1), 627–639.
Micallef, I., & Baron, B. (2021). The mechanistic roles of ncRNAs in promoting and supporting chemoresistance of colorectal cancer. Noncoding RNA, 7, 2.
Salmena, L., Poliseno, L., Tay, Y., Kats, L., & Pandolfi, P. P. (2011). A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell., 146(3), 353–8.
Liu, J., Sun, Y., Zhu, B., Lin, Y., Lin, K., Sun, Y., Yao, Z., & Yuan, L. (2021). Identification of a potentially novel LncRNA-miRNA-mRNA competing endogenous RNA network in pulmonary arterial hypertension via integrated bioinformatic analysis. Life Sci, 277, 119455.
Zhang, D., An, X., Yu, H., & Li, Z. (2021). The regulatory effect of 6-TG on lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA network in triple-negative breast cancer cell line. Biosci Rep, 41, 2.
Luan, Y., Li, X., Luan, Y., Zhao, R., Li, Y., Liu, L., Hao, Y., Oleg Vladimir, B., & Jia, L. (2020). Circulating lncRNA UCA1 promotes malignancy of colorectal cancer via the miR-143/MYO6 axis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 19, 790–803.
Chen, D. L., Lu, Y. X., Zhang, J. X., Wei, X. L., Wang, F., Zeng, Z. L., Pan, Z. Z., Yuan, Y. F., Wang, F. H., Pelicano, H., Chiao, P. J., Huang, P., Xie, D., Li, Y. H., Ju, H. Q., & Xu, R. H. (2017). Long non-coding RNA UICLM promotes colorectal cancer liver metastasis by acting as a ceRNA for microRNA-215 to regulate ZEB2 expression. Theranostics., 7(19), 4836–4849.
Xu, M., Chen, X., Lin, K., Zeng, K., Liu, X., Xu, X., Pan, B., Xu, T., Sun, L., He, B., Pan, Y., Sun, H., & Wang, S. (2019). lncRNA SNHG6 regulates EZH2 expression by sponging miR-26a/b and miR-214 in colorectal cancer. J Hematol Oncol, 12(1), 3.
Raab, M., Strebhardt, K., & Rudd, C. E. (2018). Immune adaptor protein SKAP1 (SKAP-55) forms homodimers as mediated by the N-terminal region. BMC Res Notes, 11(1), 869.
van Doorn, R., van Kester, M. S., Dijkman, R., Vermeer, M. H., Mulder, A. A., Szuhai, K., Knijnenburg, J., Boer, J. M., Willemze, R., & Tensen, C. P. (2009). Oncogenomic analysis of mycosis fungoides reveals major differences with Sezary syndrome. Blood., 113(1), 127–36.
Schulte, I., Batty, E. M., Pole, J. C., Blood, K. A., Mo, S., Cooke, S. L., Ng, C., Howe, K. L., Chin, S. F., Brenton, J. D., Caldas, C., Howarth, K. D., & Edwards, P. A. (2012). Structural analysis of the genome of breast cancer cell line ZR-75-30 identifies twelve expressed fusion genes. BMC Genomics, 13, 719.
Kosco, K. A., Cerignoli, F., Williams, S., Abraham, R. T., & Mustelin, T. (2008). SKAP55 modulates T cell antigen receptor-induced activation of the Ras-Erk-AP1 pathway by binding RasGRP1. Mol Immunol, 45(2), 510–22.
Shen, J., Li, L., Yang, T., Cheng, N., & Sun, G. (2019). Drug sensitivity screening and targeted pathway analysis reveal a multi-driver proliferative mechanism and suggest a strategy of combination targeted therapy for colorectal cancer cells. Molecules., 24, 3.
Mokutani, Y., Uemura, M., Munakata, K., Okuzaki, D., Haraguchi, N., Takahashi, H., Nishimura, J., Hata, T., Murata, K., Takemasa, I., Mizushima, T., Doki, Y., Mori, M., & Yamamoto, H. (2016). Down-Regulation of microRNA-132 is Associated with Poor Prognosis of Colorectal Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol., 23(Suppl 5), 599–608.
Despotovic, J., Dragicevic, S., & Nikolic, A. (2021). Effects of chemotherapy for metastatic colorectal cancer on the TGF-β signaling and related miRNAs hsa-miR-17-5p, hsa-miR-21-5p and hsa-miR-93-5p. Cell Biochem Biophys, 79(4), 757–767.
Gu, X., Jin, R., Mao, X., Wang, J., Yuan, J., & Zhao, G. (2018). Prognostic value of miRNA-181a/b in colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. Biomark Med, 12(3), 299–308.
Baltruskeviciene, E., Schveigert, D., Stankevicius, V., Mickys, U., Zvirblis, T., Bublevic, J., Suziedelis, K., & Aleknavicius, E. (2017). Down-regulation of miRNA-148a and miRNA-625-3p in colorectal cancer is associated with tumor budding. BMC Cancer, 17(1), 607.
Chen, K., Gan, J. X., Huang, Z. P., Liu, J., & Liu, H. P. (2021). Clinical significance of long noncoding RNA MNX1-AS1 in human cancers: a meta-analysis of cohort studies and bioinformatics analysis based on TCGA datasets. Bioengineered., 12(1), 875–885.
Cheng, X. B., Zhang, T., Zhu, H. J., Ma, N., Sun, X. D., Wang, S. H., & Jiang, Y. (2021). Knockdown of lncRNA SNHG4 suppresses gastric cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by targeting miR-204-5p. Neoplasma, 68(3), 546–556.
Jin, L., Pan, Y. L., Zhang, J., & Cao, P. G. (2021). LncRNA HOTAIR recruits SNAIL to inhibit the transcription of HNF4α and promote the viability, migration, invasion and EMT of colorectal cancer. Transl Oncol, 14(4), 101036.
Yan, T., Shen, C., Jiang, P., Yu, C., Guo, F., Tian, X., Zhu, X., Lu, S., Han, B., Zhong, M., Chen, J., Liu, Q., Chen, Y., Zhang, J., Hong, J., Chen, H., & Fang, J. Y. (2021). Risk SNP-induced lncRNA-SLCC1 drives colorectal cancer through activating glycolysis signaling. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 6(1), 70.
Wang, G., Ye, Q., Ning, S., Yang, Z., Chen, Y., Zhang, L., Huang, Y., Xie, F., Cheng, X., Chi, J., Lei, Y., Guo, R., & Han, J. (2021). LncRNA MEG3 promotes endoplasmic reticulum stress and suppresses proliferation and invasion of colorectal carcinoma cells through the MEG3/miR-103a-3p/PDHB ceRNA pathway. Neoplasma., 68(2), 362–374.
Xu, J., Wu, G., Zhao, Y., Han, Y., Zhang, S., Li, C., & Zhang, J. (2020). Long noncoding RNA DSCAM-AS1 facilitates colorectal cancer cell proliferation and migration via miR-137/Notch1 axis. J Cancer, 11(22), 6623–6632.
Zheng, X. Y., Cao, M. Z., Ba, Y., Li, Y. F., & Ye, J. L. (2020). LncRNA testis-specific transcript, Y-linked 15 (TTTY15) promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells via regulating miR-29a-3p/DVL3 axis. Cancer Biomark, 31(1), 1–11.
Zhang, X., Yao, J., Shi, H., Gao, B., & Zhang, L. (2019). LncRNA TINCR/microRNA-107/CD36 regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis in colorectal cancer via PPAR signaling pathway based on bioinformatics analysis. Biol Chem, 400(5), 663–675.
Sun, J., Hu, J., Wang, G., Yang, Z., Zhao, C., Zhang, X., & Wang, J. (2018). LncRNA TUG1 promoted KIAA1199 expression via miR-600 to accelerate cell metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 37(1), 106.
Xie, J. J., Li, W. H., Li, X., Ye, W., & Shao, C. F. (2019). LncRNA MALAT1 promotes colorectal cancer development by sponging miR-363-3p to regulate EZH2 expression. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents, 33(2), 331–343.
Yan, Z., Bi, M., Zhang, Q., Song, Y., & Hong, S. (2020). LncRNA TUG1 promotes the progression of colorectal cancer via the miR-138-5p/ZEB2 axis. Biosci Rep, 40, 6.
le Petit, G. F. (1976). Medazepam pKa determined by spectrophotometric and solubility methods. J Pharm Sci, 65(7), 1094–5.
Lin, J., Zhang, Y., Zeng, X., Xue, C., & Lin, X. (2020). CircRNA CircRIMS acts as a microRNA sponge to promote gastric cancer metastasis. ACS Omega, 5(36), 23237–23246.
Su, Y. K., Lin, J. W., Shih, J. W., Chuang, H. Y., Fong, I. H., Yeh, C. T., & Lin, C. M. (2020). Targeting BC200/miR218-5p signaling axis for overcoming temozolomide resistance and suppressing glioma stemness. Cells., 9, 8.
Tan, J. J., Long, S. Z. & Zhang, T. (2020). Effects of LncRNA UNC5B-AS1 on adhesion, invasion and migration of lung cancer cells and its mechanism. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi, 36(6), 622–627.
Li, Y., Shi, B., Dong, F., Zhu, X., Liu, B., & Liu, Y. (2020). LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 facilitates the progression of bladder cancer by targeting MiR-218-5p/HS3ST3B1. Cancer Gene Ther, 28(3-4), 212–220.
Li, L., Yu, H., & Ren, Q. (2020). MiR-218-5p suppresses the progression of retinoblastoma through targeting NACC1 and inhibiting the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Cancer Manag Res, 12, 6959–6967.
Jia, G., Wang, Y., Yu, Y., Li, Z., & Wang, X. (2020). Long non‑coding RNA NR2F1‑AS1 facilitates the osteosarcoma cell malignant phenotype via the miR‑485‑5p/miR‑218‑5p/BIRC5 axis. Oncol Rep, 44(4), 1583–1595.
Li, J., Zhong, Y., Cai, S., Zhou, P., & Yao, L. (2019). MicroRNA expression profiling in the colorectal normal-adenoma-carcinoma transition. Oncol Lett., 18(2), 2013–2018.
Zhou, X. G., Huang, X. L., Liang, S. Y., Tang, S. M., Wu, S. K., Huang, T. T., Mo, Z. N., & Wang, Q. Y. (2018). Identifying miRNA and gene modules of colon cancer associated with pathological stage by weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Onco Targets Ther, 11, 2815–2830.
Liu, M., Yin, K., Guo, X., Feng, H., Yuan, M., Liu, Y., Zhang, J., Guo, B., Wang, C., Zhou, G., Zhou, Z., Zhang, C. Y., & Chen, X. (2017). Diphthamide Biosynthesis 1 is a Novel Oncogene in Colorectal Cancer Cells and is Regulated by MiR-218-5p. Cell Physiol Biochem, 44(2), 505–514.
Chen, R., Wu, J., Lu, C., Yan, T., Qian, Y., Shen, H., Zhao, Y., Wang, J., Kong, P., & Zhang, X. (2020). Systematic transcriptome analysis reveals the inhibitory function of cinnamaldehyde in non-small cell lung cancer. Front Pharmacol, 11, 611060.
Hu, J., Chen, Y., Li, X., Miao, H., Li, R., Chen, D., & Wen, Z. (2019). THUMPD3-AS1 Is Correlated With Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer And Regulates Self-Renewal Through miR-543 And ONECUT2. Onco Targets Ther, 12, 9849–9860.
Zhao, X., Bai, Z., Li, C., Sheng, C., & Li, H. (2020). Identification of a novel eight-lncRNA prognostic signature for HBV-HCC and analysis of their functions based on coexpression and ceRNA networks. Biomed Res Int, 2020, 8765461.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pu, Y., Wei, J., Wu, Y. et al. THUMPD3-AS1 facilitates cell growth and aggressiveness by the miR-218-5p/SKAP1 axis in colorectal cancer. Cell Biochem Biophys 80, 483–494 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-022-01074-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-022-01074-4