Abstract
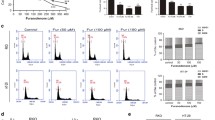
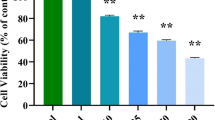
Colorectal cancer is one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers in the world. Currently, drug resistance of cancer cell to chemotherapy is a major cause for cancer recurrence and death of the patients; therefore, new therapeutic strategy is required to improve the care of colorectal cancer patients. The Chinese herb, Isodon eriocalyx, has been used a therapeutic for a long time in China. In this study, we showed that Epieriocalyxin A (EpiA), a diterpenoid isolated from I. eriocalyx, suppressed Caco-2 colon cancer cell growth. EpiA induced annexin V flipping in cell membrane and DNA fragment. We also showed that EpiA induced the generation of ROS in cells, as well as damage of the mitochondrial membrane. Western blot results showed that both JNK and ERK1/2 activation was decreased after EpiA treatment in a dose-dependent manner. EpiA increased the expression of caspase 3 and Bax, and decreased Bcl2 expression. Our results suggest that EpiA is a novel compound that induces colon cancer apoptosis. EpiA could be a potential drug for colon cancer therapy in the future.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal, A., Bray, F., Center, M. M., Ferlay, J., Ward, E., & Forman, D. (2011). Global cancer statistics. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 61, 69–90.
Sun, H. D., Lin, Z. W., Niu, F. D., et al. (1995). Diterpenoids from Isodon eriocalyx var. laxiflora. Phytochemistry, 38, 1451–1455.
Chen, S. N., Yue, J. M., Chen, S. Y., et al. (1999). Diterpenoids from isodon eriocalyx. Journal of Natural Products, 62, 782–784.
Wang, L., Zhao, W. L., Yan, J. S., et al. (2007). Eriocalyxin B induces apoptosis of t(8;21) leukemia cells through NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathways and triggers degradation of AML1-ETO oncoprotein in a caspase-3-dependent manner. Cell Death and Differentiation, 14, 306–317.
Zhang, Y. W., Jiang, X. X., Chen, Q. S., et al. (2010). Eriocalyxin B induces apoptosis in lymphoma cells through multiple cellular signaling pathways. Experimental Hematology, 38, 191–201.
Wang, L., Gala, M., Yamamoto, M., et al. (2014). Adrenomedullin is a therapeutic target in colorectal cancer. International journal of cancer Journal international du cancer, 134, 2041–2050.
Li, L., Yue, G. G., Lau, C. B., et al. (2012). Eriocalyxin B induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells through caspase- and p53-dependent pathways. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 262, 80–90.
Lu, Y., Chen, B., Song, J. H., et al. (2013). Eriocalyxin B ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by suppressing Th1 and Th17 cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110, 2258–2263.
Han, Q. B., Cheung, S., Tai, J., et al. (2006). Maoecrystal Z, a cytotoxic diterpene from Isodon eriocalyx with a unique skeleton. Organic Letters, 8, 4727–4730.
Wang, W. G., Li, X. N., Du, X., et al. (2012). Laxiflorolides A and B, epimeric bishomoditerpene lactones from Isodon eriocalyx. Journal of Natural Products, 75, 1102–1107.
Han, Q. B., Yu, T., Lai, F., et al. (2010). Quick identification of apoptosis inducer from Isodon eriocalyx by a drug discovery platform composed of analytical high-speed counter-current chromatography and the fluorescence-based caspase-3 biosensor detection. Talanta, 82, 1521–1527.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Xu, Z., Niu, Z. et al. Epieriocalyxin A Induces Cell Apoptosis Through JNK and ERK1/2 Signaling Pathways in Colon Cancer Cells. Cell Biochem Biophys 73, 559–564 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-015-0687-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-015-0687-4