Abstract
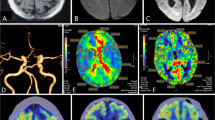
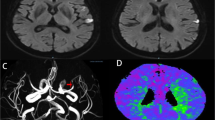
Movement disorders are a recognized complication of stroke. Here we present a case of hemichorea-hemiballism (HCHB) after stroke. Basal ganglia and thalamus are typically recognized as sites responsible for HCHB. The MRI scan showed acute infarction which was unexpectedly present in both sides of corona radiate and cortex, but not in basal ganglia. This cortical HCHB could have evolved due to hypoperfusion of basal ganglia undetectable at the MRI scan or due to interruption of excitatory connections from the cerebral cortex to basal ganglia.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ghika, J., & Bogousslavsky, J. (2001). Abnormal movements. In J. Bogousslavsky & L. Caplan (Eds.), Stroke syndromes (pp. 162–181). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Handley, A., Medcalf, P., Hellier, K., & Dutta, D. (2009). Movement disorders after stroke. Age and Ageing, 38, 260–266.
Hwang, K. J., Hong, I. K., Ahn, T. B., Yi, S. H., Lee, D., & Kim, D. Y. (2013). Cortical hemichorea-hemiballism. Journal of Neurology, 260, 2986–2992.
Martin, J. P., & Alcock, N. S. (1934). Hemichorea associated with a lesion of the corpus Luysii. Brain, 57, 504–516.
Whittier, J. R. (1947). Ballism and the subthalamic nucleus hypothalamicus; corpus luysi) review of the literature and study of 30 cases. Archives of Neurology & Psychiatry, 58, 672–692.
Alarcon, F., Zijlmans, J. C., Duenas, G., & Cevallos, N. (2004). Post-stroke movement disorders: report of 56 patients. Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 75, 1568–1574.
Chung, S. J., Im, J. H., Lee, M. C., & Kim, J. S. (2004). Hemichorea after stroke: Clinical-radiological correlation. Journal of Neurology, 251, 725–729.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, M., Qin, X. & Gao, H. A case of Hemichorea-Hemiballism Induced by Acute Infarction of Bilateral Corona Radiata and Cortex. Cell Biochem Biophys 73, 171–174 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-015-0608-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-015-0608-6