Abstract
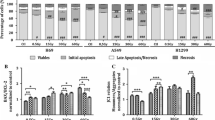
The aim of the study is to explore the bystander effects in A549 cells that have been exposed to 6MV X-ray. Control group, irradiated group, irradiated conditioned medium (ICM)-received group, and fresh medium group were designed in this study. A549 cells in the logarithmic growth phase were irradiated with 6MV X-ray at 0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, and 2. In ICM-received group, post-irradiation A549 cells were cultured for 3 h and were transferred into non-irradiated A549 cells for further cultivation. Clone forming test was applied to detect the survival fraction of cells. Annexin V-FITC/PI double-staining assay was used to detect the apoptosis of A549 cells 24, 48, 72, and 96 h after 2-Gy 6MV X-ray irradiation, and the curves of apoptosis were drawn. The changes in the cell cycles 4, 48, 72, and 96 h after 2-Gy 6MV X-ray irradiation were detected using PI staining flow cytometry. With the increase of irradiation dose, the survival fraction of A549 cells after the application of 0.5 Gy irradiation was decreasing continuously. In comparison to the control group, the apoptosis rate of the ICM-received group was increased in a time-dependent pattern, with the highest apoptosis rate observed at 72 h (p < 0.05). Cell count in G2/M stages was obviously increased compared with that of the control group (p < 0.05), with the highest count observed at 72 h, after which G2/M stage arrest was diminished. ICM can cause apparent A549 cell damage, indicating that 6MV X-ray irradiation can induce bystander effect on A549 cells, which reaches a peak at 72 h.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mothersill, C., & Seymour, C. B. (2003). Radiation-induced bystander effects, carcinogenesis and models. Oncogene, 22, 7028–7033.
Morgan, W. F., & Sowa, M. B. (2007). Non-targeted bystander effects induced by ionizing radiation. Mutation Research, 616, 159–164.
Wang X, X., Yang, Y., Danny, R. Moore, et al. (2012). 4-Hydroxy-2-nonenal mediates genotoxicity and bystander effects caused by Enterococcus faecalis–infected macrophages. Gastroenterology, 142(3), 543–551.
Hamada, N., Maeda, M., Otsuka, K., & Tomita, M. (2011). Signaling pathways underpinning the manifestations of ionizing radiation-induced bystander effects. Current Molecular Pharmacology, 2, 79–95.
Nagasawa, H., & Little, J. B. (2002). Bystander effect for chromosomal aberrations induced in wild-type and repair CHO cells by low fluences of alpha particles. Mutation Research, 508(1/2), 121–129.
Prise, K. M., Belyakov, O. V., Folkard, M., et al. (1998). Studies of bystander effects in human fibroblasts using a charged particle microbeam. International Journal of Radiation Biology, 74(5), 793.
Tu, X. M., Lei, S. W., Wang, J. F., et al. (2005). Chinese Journal of Radiological Medicine and Protection, 25(4), 33–35.
Koukourakis, M. I. (2012). Radiation damage and radioprotectants: new concepts in the era of molecular medicine. British Journal of Radiology, 1012(85), 313–330.
Mothersill, C., & Seymour, C. (1997). Medium from irradiated human epithelial cells but not human fibroblasts reduces the clonogenic survival of unirradiated cells. International Journal of Radiation Biology, 71(4), 421–427.
Yang, H., Anzenberg, V., & Held, K. D. (2007). Effects of heavy ions and energetic protons on normal human fibroblasts. Radiation Research, 168(3), 292–298.
Xiao, H., Zhang, Q., Lin, Y., et al. (2008). Combination of atorvastatin and celecoxib synergistically induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in colon cancer cells. International Journal of Cancer, 22(9), 2115–2124.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, S., Xu, J., Shao, W. et al. Radiation-Induced Bystander Effects in A549 Cells Exposed to 6 MV X-rays. Cell Biochem Biophys 72, 877–882 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-015-0555-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-015-0555-2