Abstract
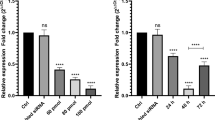
We sought to determine the expression levels of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) in the bone marrow chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) patients. We also tried to determine the roles HIF-1α in the proliferation of CML cells by small interfering RNA (siRNA) knockdown. Real-time PCR was performed to determine the expression levels of HIF-1α in the bone marrows of CML patients and healthy volunteers. HIF-1α knockdown by siRNA in K562 cells was confirmed by RT-PCR. Proliferation and colony formation of the treated cells were determined by CCK8 after HIF-1α knockdown. RT-PCR and western blotting were performed to detect mRNA and protein levels of p21 and p53 in K562 cells. HIF-1α mRNA expression in the bone marrow of CML patients was significantly higher than that in the control, which was statistically significant (P < 0.05). HIF-1α knockdown dramatically reduced the proliferation of K562 cells, which was also statistically significant (P < 0.05). HIF-1α knockdown markedly reduced the colony formation ability of K562 cells, which was also statistically significant (P < 0.05). The mRNA and protein expression of p21 were significantly reduced in K562 cell after HIF-1α knockdown with affecting the mRNA and protein levels of p53. HIF-α promotes chronic CML cell proliferation by up-regulating p21 expression




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Esteban, M. A., & Maxwell, P. H. (2005). HIF, a missing link between metabolism and cancer. Nature Medicine, 11, 1047–1048.
Brogi, E., Schatteman, G., Wu, T., Kim, E. A., Varticovski, L., Keyt, B., & Isner, J. M. (1996). Hypoxia-induced paracrine regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor expression. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 97, 469–476.
Janssen, H. L., Haustermans, K. M., Sprong, D., Blommestijn, G., Hofland, I., Hoebers, F. J., et al. (2002). HIF-1A, pimonidazole, and iododeoxyuridine to estimate hypoxia and perfusion in human head-and-neck tumors. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics, 54, 1537–1549.
Kitajima, Y., & Miyazaki, K. (2013). The critical impact of HIF-1a on gastric cancer biology. Cancers (Basel), 5, 15–26.
Kelly, B. D., Hackett, S. F., Hirota, K., Oshima, Y., Cai, Z., Berg-Dixon, S., et al. (2003). Cell type-specific regulation of angiogenic growth factor gene expression and induction of angiogenesis in nonischemic tissue by a constitutively active form of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Circulation Research, 93, 1074–1081.
Huang, J. H., Lee, F. S., Pasha, T. L., Sammel, M. D., Karakousis, G., Xu, G., et al. (2010). Analysis of HIF-1a and its regulator, PHD2, in retroperitoneal sarcomas: Clinico-pathologic implications. Cancer Biology & Therapy, 9, 303–311.
Oladipupo, S. S., Hu, S., Santeford, A. C., Yao, J., Kovalski, J. R., Shohet, R. V., et al. (2011). Conditional HIF-1 induction produces multistage neovascularization with stage-specific sensitivity to VEGFR inhibitors and myeloid cell independence. Blood, 117, 4142–4153.
Kaidi, A., Williams, A. C., & Paraskeva, C. (2007). Interaction between beta-catenin and HIF-1 promotes cellular adaptation to hypoxia. Nature Cell Biology, 9, 210–217.
Chomel, J. C., Sorel, N., Guilhot, J., Guilhot, F., & Turhan, A. G. (2012). BCR-ABL expression in leukemic progenitors and primitive stem cells of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood, 119, 2964–2965. author reply 2965–2966.
Makino, Y., Uenishi, R., Okamoto, K., Isoe, T., Hosono, O., Tanaka, H., et al. (2007). Transcriptional up-regulation of inhibitory PAS domain protein gene expression by hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1): A negative feedback regulatory circuit in HIF-1-mediated signaling in hypoxic cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 282, 14073–14082.
O’Donnell, J. L., Joyce, M. R., Shannon, A. M., Harmey, J., Geraghty, J., & Bouchier-Hayes, D. (2006). Oncological implications of hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha) expression. Cancer Treatment Reviews, 32, 407–416.
Gort, E. H., Groot, A. J., Derks van de Ven, T. L., van der Groep, P., Verlaan, I., van Laar, T., et al. (2006). Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha expression requires PI 3-kinase activity and correlates with Akt1 phosphorylation in invasive breast carcinomas. Oncogene, 25, 6123–6127.
Lee, J. Y., Choi, J. Y., Lee, K. M., Park, S. K., Han, S. H., Noh, D. Y., et al. (2008). Rare variant of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1A) and breast cancer risk in Korean women. Clinica Chimica Acta, 389, 167–170.
Bardos, J. I., & Ashcroft, M. (2004). Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and oncogenic signalling. BioEssays, 26, 262–269.
Jiang, Y. A., Fan, L. F., Jiang, C. Q., Zhang, Y. Y., Luo, H. S., Tang, Z. J., et al. (2003). Expression and significance of PTEN, hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha in colorectal adenoma and adenocarcinoma. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 9, 491–494.
Nakatsuka, A., Wada, J., Hida, K., Hida, A., Eguchi, J., Teshigawara, S., et al. (2012). RXR antagonism induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and ameliorates obesity by up-regulating the p53-p21(Cip1) pathway in adipocytes. Journal of Pathology, 226, 784–795.
Yang, X., Wang, W., Qin, J. J., Wang, M. H., Sharma, H., Buolamwini, J. K., et al. (2012). JKA97, a novel benzylidene analog of harmine, exerts anti-cancer effects by inducing G1 arrest, apoptosis, and p53-independent up-regulation of p21. PLoS One, 7, e34303.
Wu, G., Lin, N., Xu, L., Liu, B., & Feitelson, M. A. (2013). UCN-01 induces S and G2/M cell cycle arrest through the p53/p21(waf1) or CHK2/CDC25C pathways and can suppress invasion in human hepatoma cell lines. BMC Cancer, 13, 167.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Shen, Y., Gong, F. et al. HIF-α Promotes Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Cell Proliferation by Upregulating p21 Expression. Cell Biochem Biophys 72, 179–183 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0434-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0434-2