Abstract
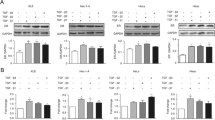
Previous research has reported that IGFBP7 functions as a tumor suppressor gene in different tumors, but its role in the trophoblast has not been elucidated. In this research, we studied the regulation mechanism of IGFBP7 in trophoblast proliferation and invasion in HTR-8 and JEG-3 cell lines. We found that IGFBP7 was abundantly expressed in normal human syncytiotrophoblast tissue samples but that this was lacking in hydatidiform moles. The proliferation and invasion capacities of HTR-8 and JEG-3 cells were significantly inhibited by recombinant IGFBP7. Estrogen (E2) stimulated the expression of IGFBP7 at a concentration of 5–10 ng/mL. This stimulation was inhibited by the estrogen receptor antagonist Fulvestrant (ICI182.780) and a TGFβ-neutralizing antibody. In conclusion, our data reveals that estrogen stimulates the expression of IGFBP7 through estrogen receptors and TGFβ. The expression of IGFBP7 could be stimulated by TGFβ in a dose-dependent manner and inhibited by IFNγ in HTR-8 and JEG-3 cells. IGFBP7 could also inhibit the phosphorylation of ERK and the expression of PCNA, MMP2 and MMP9 in HTR-8 and JEG-3 cells. These findings suggest that IGFBP7 is a key regulator of E2-induced trophoblast proliferation and invasion.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hwa, V., Oh, Y., & Rosenfeld, R. G. (1999). The insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP) superfamily. Endocrine Reviews, 20(6), 761–787.
Yamashita, S., Tsujino, Y., Moriguchi, K., Tatematsu, M., & Ushijima, T. (2006). Chemical genomic screening for methylation-silenced genes in gastric cancer cell lines using 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine treatment and oligonucleotide microarray. Cancer Science, 97(1), 64–71. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00136.x.
Heesch, S., Bartram, I., Neumann, M., Reins, J., Mossner, M., Schlee, C., Stroux, A., Haferlach, T., Goekbuget, N., Hoelzer, D., Hofmann, W. -K., Thiel, E., & Baldus, C. D. (2010). Expression of IGFBP7 in acute leukemia is regulated by DNA methylation. Cancer Science, 102, 253–259. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01760.x.
Ye, F., Chen, Y., Knosel, T., Schluns, K., Pacyna-Gengelbach, M., Deutschmann, N., et al. (2007). Decreased expression of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 in human colorectal carcinoma is related to DNA methylation. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology, 133(5), 305–314. doi:10.1007/s00432-006-0171-z.
Wajapeyee, N., Serra, R. W., Zhu, X., Mahalingam, M., & Green, M. R. (2008). Oncogenic BRAF induces senescence and apoptosis through pathways mediated by the secreted protein IGFBP7. Cell, 132(3), 363–374. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.12.032.
Dominguez, F., Avila, S., Cervero, A., Martin, J., Pellicer, A., Castrillo, J. L., et al. (2003). A combined approach for gene discovery identifies insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-related protein 1 as a new gene implicated in human endometrial receptivity. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 88(4), 1849–1857. doi:10.1210/jc.2002-020724.
Tamura, K., Hara, T., Kutsukake, M., Iwatsuki, K., Yanagida, M., Yoshie, M., et al. (2004). Expression and the biological activities of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein related protein 1 in rat uterus during the preimplantation period. Endocrinology, 145(11), 5243–5251. doi:10.1210/en.2004-0415.
Kutsukake, M., Ishihara, R., Yoshie, M., Kogo, H., & Tamura, K. (2007). Involvement of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-related protein 1 in decidualization of human endometrial stromal cells. Molecular Human Reproduction, 13(10), 737–743. doi:10.1093/molehr/gam058.
Guibourdenche, J., Handschuh, K., Tsatsaris, V., Gerbaud, P., Leguy, M. C., Muller, F., et al. (2010). Hyperglycosylated hCG is a marker of early human trophoblast invasion. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 95(10), E240–E244. doi:10.1210/jc.2010-0138.
Udayashankar, R., Baker, D., Tuckerman, E., Laird, S., Li, T. C., & Moore, H. D. (2011). Characterization of invasive trophoblasts generated from human embryonic stem cells. Human Reproduction, 26(2), 398–406. doi:10.1093/humrep/deq350.
Blomberg, L., Hashizume, K., & Viebahn, C. (2008). Blastocyst elongation, trophoblastic differentiation, and embryonic pattern formation. Reproduction, 135(2), 181–195. doi:10.1530/rep-07-0355.
Norwitz, E. R., Schust, D. J., & Fisher, S. J. (2001). Implantation and the survival of early pregnancy. New England Journal of Medicine, 345(19), 1400–1408. doi:10.1056/NEJMra000763.
Riquelme, G. (2009). Placental chloride channels: a review. Placenta, 30(8), 659–669. doi:10.1016/j.placenta.2009.06.002.
Mendelson, C. R., Jiang, B., Shelton, J. M., Richardson, J. A., & Hinshelwood, M. M. (2005). Transcriptional regulation of aromatase in placenta and ovary. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 95(1–5), 25–33. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2005.04.016.
Ringler, G. E., & Strauss, J. F. (1990). In vitro systems for the study of human placental endocrine function. Endocrine Reviews, 11(1), 105–123. doi:10.1210/edrv-11-1-105.
Pijnenborg, R., Bland, J. M., Robertson, W. B., & Brosens, I. (1983). Uteroplacental arterial changes related to interstitial trophoblast migration in early human pregnancy. Placenta, 4(4), 397–413. doi:10.1016/s0143-4004(83)80043-5.
Pollheimer, J., & Knöfler, M. (2005). Signalling pathways regulating the invasive differentiation of human trophoblasts: A review. Placenta, 26(Supplement 1), S21–S30. doi:10.1016/j.placenta.2004.11.013.
Koc, S., Ozdegirmenci, O., Tulunay, G., Ozgul, N., Kose, M. F., & Bulbul, D. (2006). Recurrent partial hydatidiform mole: A report of a patient with three consecutive molar pregnancies. International Journal of Gynecological Cancer, 16(2), 940–943. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1438.2006.00232.x.
Yang, X., Zhang, Z., Jia, C., Li, J., Yin, L., & Jiang, S. (2002). The relationship between expression of c-ras, c-erbB-2, nm23, and p53 gene products and development of trophoblastic tumor and their predictive significance for the malignant transformation of complete hydatidiform mole. Gynecologic Oncology, 85(3), 438–444. doi:10.1006/gyno.2002.6652.
Tuncer, Z. S., Vegh, G. L., Fulop, V., Genest, D. R., Mok, S. C., & Berkowitz, R. S. (2000). Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor-related family products in gestational trophoblastic diseases and normal placenta and its relationship with development of postmolar tumor. Gynecologic Oncology, 77(3), 389–393. doi:10.1006/gyno.2000.5777.
Seckl, M. J., Fisher, R. A., Salerno, G., Rees, H., Paradinas, F. J., Foskett, M., et al. (2000). Choriocarcinoma and partial hydatidiform moles. The Lancet, 356(9223), 36–39. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(00)02432-6.
Cui, J. Q., Shi, Y. F., Zhou, H. J., & Li, J. Q. (2004). The changes of gene expression profiles in hydatidiform mole and choriocarcinoma with hyperplasia of trophoblasts. International Journal of Gynecological Cancer, 14(5), 984–997. doi:10.1111/j.1048-891X.2004.14539.x.
Yashwanth, R., Rama, S., Anbalagan, M., & Rao, A. J. (2006). Role of estrogen in regulation of cellular differentiation: A study using human placental and rat Leydig cells. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 246(1–2), 114–120. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2005.11.007.
Caniggia, I., Grisaru-Gravnosky, S., Kuliszewsky, M., Post, M., & Lye, S. J. (1999). Inhibition of TGF-β3 restores the invasive capability of extravillous trophoblasts in preeclamptic pregnancies. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 103(12), 1641–1650.
MacPhee, D. J., Mostachfi, H., Han, R., Lye, S. J., Post, M., & Caniggia, I. (2001). Focal adhesion kinase is a key mediator of human trophoblast development. Laboratory Investigation, 81(11), 1469–1483.
Ilic, D., Genbacev, O., Jin, F., Caceres, E., Almeida, E. A. C., Bellingard-Dubouchaud, V., et al. (2001). Plasma membrane-associated pY397FAK is a marker of cytotrophoblast invasion in vivo and in vitro. American Journal of Pathology, 159(1), 93–108.
Bifulco, G., Trencia, A., Caruso, M., Tommaselli, G. A., Miele, C., di Carlo, C., et al. (2003). Leptin induces mitogenic effect on human choriocarcinoma cell line (JAr) via MAP kinase activation in a glucose-dependent fashion. Placenta, 24(4), 385–391. doi:10.1053/plac.2002.0905.
Cartwright, J. E., Tse, W. K., & Whitley, G. S. (2002). Hepatocyte growth factor induced human trophoblast motility involves phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase, mitogen-activated protein kinase, and inducible nitric oxide synthase. Experimental Cell Research, 279(2), 219–226. doi:10.1006/excr.2002.5616.
Maymó, J. L., Pérez Pérez, A., Gambino, Y., Calvo, J. C., Sánchez-Margalet, V., & Varone, C. L. (2011). Review: Leptin gene expression in the placenta—Regulation of a key hormone in trophoblast proliferation and survival. Placenta 32, Supplement 2(0):S146–S153. doi:10.1016/j.placenta.2011.01.004.
Gambino, Y. P., Maymó, J. L., Pérez Pérez, A., Calvo, J. C., Sánchez-Margalet, V., & Varone, C. L. (2012). Elsevier trophoblast research award lecture: Molecular mechanisms underlying estrogen functions in trophoblastic cells—Focus on leptin expression. Placenta. doi:10.1016/j.placenta.2011.12.001.
Ramathal, C. Y., Bagchi, I. C., Taylor, R. N., & Bagchi, M. K. (2010). Endometrial decidualization: of mice and men. Seminars in Reproductive Medicine, 28 (01), 017–026. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1242989.
Leonard, S., Murrant, C., Tayade, C., van den Heuvel, M., Watering, R., & Croy, B. A. (2006). Mechanisms regulating immune cell contributions to spiral artery modification—Facts and hypotheses—A review. Placenta, 27, Supplement(0), 40–46. doi:10.1016/j.placenta.2005.11.007.
Paulesu, L., Romagnoli, R., Cintorino, M., Grazia Ricci, M., & Garotta, G. (1994). First trimester human trophoblast expresses both interferon-γ and interferon-γ-receptor. Journal of Reproductive Immunology, 27(1), 37–48. doi:10.1016/0165-0378(94)90013-2.
Roberts, R. M., Chen, Y., Ezashi, T., & Walker, A. M. (2008). Interferons and the maternal-conceptus dialog in mammals. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology, 19(2), 170–177. doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2007.10.007.
Rajaraman, G., Murthi, P., Pathirage, N., Brennecke, S. P., & Kalionis, B. (2010). Downstream targets of homeobox gene HLX show altered expression in human idiopathic fetal growth restriction. The American Journal of Pathology, 176(1), 278–287. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2010.090187.
Wickert, L., Chatain, N., Kruschinsky, K., & Gressner, A. (2007). Glucocorticoids activate TGF-beta induced PAI-1 and CTGF expression in rat hepatocytes. Comparative Hepatology, 6(1), 5.
Jovanovic, M., & Vicovac, L. (2009). Interleukin-6 stimulates cell migration, invasion and integrin expression in HTR-8/SVneo cell line. Placenta, 30(4), 320–328. doi:10.1016/j.placenta.2009.01.013.
Suman, P., Poehlmann, T. G., Prakash, G. J., Markert, U. R., & Gupta, S. K. (2009). Interleukin-11 increases invasiveness of JEG-3 choriocarcinoma cells by modulating STAT3 expression. Journal of Reproductive Immunology, 82(1), 1–11. doi:10.1016/j.jri.2009.07.002.
Zhang, X., Green, K. E., Yallampalli, C., & Dong, Y. L. (2005). Adrenomedullin enhances invasion by trophoblast cell lines. Biology of Reproduction, 73(4), 619–626. doi:10.1095/biolreprod.105.040436.
King, A., Thomas, L., & Bischof, P. (2000). Cell culture models of trophoblast II: Trophoblast cell lines—A workshop report. Placenta, 21, S113–S119.
Bukovsky, A., Cekanova, M., Caudle, M., Wimalasena, J., Foster, J., Henley, D., et al. (2003). Expression and localization of estrogen receptor-alpha protein in normal and abnormal term placentae and stimulation of trophoblast differentiation by estradiol. Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology, 1(1), 1–18. doi:10.1186/1477-7827-1-13.
Ma, W. G., Song, H., Das, S. K., Paria, B. C., & Dey, S. K. (2003). Estrogen is a critical determinant that specifies the duration of the window of uterine receptivity for implantation. Proceedings of the National Academy of the United States of America, 100(5), 2963–2968. doi:10.1073/pnas.0530162100.
Damon, S. E., Haugk, K. L., Swisshelm, K., & Quinn, L. S. (1997). Developmental regulation of Mac25/insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-7 expression in skeletal myogenesis. Experimental Cell Research, 237(1), 192–195. doi:10.1006/excr.1997.3787.
Pen, A., Moreno, M. J., Durocher, Y., Deb-Rinker, P., & Stanimirovic, D. B. (2008). Glioblastoma-secreted factors induce IGFBP7 and angiogenesis by modulating Smad-2-dependent TGF-beta signaling. Oncogene, 27(54), 6834–6844. doi:10.1038/onc.2008.287.
Hwa, V., Tomasini-Sprenger, C., Bermejo, A. L., Rosenfeld, R. G., & Plymate, S. R. (1998). Characterization of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-related protein-1 in prostate cells. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 83(12), 4355–4362.
Graham, C. H., & Lala, P. K. (1991). Mechanism of control of trophoblast invasion in situ. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 148(2), 228–234. doi:10.1002/jcp.1041480207.
Graham, C. H. (1997). Effect of transforming growth factor-[beta] on the plasminogen activator system in cultured first trimester human cytotrophoblasts. Placenta, 18(2–3), 137–143. doi:10.1016/s0143-4004(97)90085-0.
Ashkar, A. A., Di Santo, J. P., & Croy, B. A. (2000). Interferon γ contributes to initiation of uterine vascular modification, decidual integrity, and uterine natural killer cell maturation during normal murine pregnancy. The Journal of Experimental Medicine, 192(2), 259–270. doi:10.1084/jem.192.2.259.
Choi, J. C., Holtz, R., Petroff, M. G., Alfaidy, N., & Murphy, S. P. (2007). Dampening of IFN-γ-inducible gene expression in human choriocarcinoma cells is due to phosphatase-mediated inhibition of the JAK/STAT-1 pathway. The Journal of Immunology, 178(3), 1598–1607.
Irving, J. A., Lysiak, J. J., Graham, C. H., Hearn, S., Han, V. K. M., & Lala, P. K. (1995). Characteristic’s of trophoblast cells migrating from first trimester chorionic villus explants and propagated in culture. Placenta, 16(5), 413–433. doi:10.1016/0143-4004(95)90100-0.
Tomimaru, Y., Eguchi, H., Wada, H., Noda, T., Murakami, M., Kobayashi, S., Marubashi, S., Takeda, Y., Tanemura, M., Umeshita, K., Doki, Y., Mori, M., & Nagano, H. (2010) Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7 alters the sensitivity to interferon-based anticancer therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. British Journal of Cancer, 102 (10), 1483–1490. doi:http://www.nature.com/bjc/journal/v102/n10/suppinfo/6605669s1.html.
Librach, C. L., Werb, Z., Fitzgerald, M. L., Chiu, K., Corwin, N. M., Esteves, R. A., et al. (1991). 92-kD type IV collagenase mediates invasion of human cytotrophoblasts. The Journal of Cell Biology, 113(2), 437–449. doi:10.1083/jcb.113.2.437.
Cohen, M., Meisser, A., Haenggeli, L., & Bischof, P. (2006). Involvement of MAPK pathway in TNF-α-induced MMP-9 expression in human trophoblastic cells. Molecular Human Reproduction, 12(4), 225–232. doi:10.1093/molehr/gal023.
Bischoff, P., Meisser, A., & Campana, A. (2000). Paracrine and autocrine regulators of trophoblast invasion—A review. Placenta, 21(Supplement 1), S55–S60. doi:10.1053/plac.2000.0521.
Takahashi, T., & Caviness, V. S. (1993). PCNA-binding to DNA at the G1/S transition in proliferating cells of the developing cerebral wall. Journal of Neurocytology, 22(12), 1096–1102. doi:10.1007/bf01235751.
Kortylewski, M., Heinrich, P. C., Kauffmann, M. E., Böhm, M., MacKiewicz, A., & Behrmann, I. (2001). Mitogen-activated protein kinases control p27/Kip1 expression and growth of human melanoma cells. Biochemical Journal, 357(1), 297–303.
Dworakowska, D., Wlodek, E., Leontiou, C. A., Igreja, S., Cakir, M., Teng, M., et al. (2009). Activation of RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways in pituitary adenomas and their effects on downstream effectors. Endocrine-Related Cancer, 16(4), 1329–1338. doi:10.1677/erc-09-0101.
Cho, A., Graves, J., & Reidy, M. A. (2000). Mitogen-activated protein kinases mediate matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 20(12), 2527–2532. doi:10.1161/01.atv.20.12.2527.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2011CB944402), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31171435), and the Knowledge Innovation Program in Chinese Academy of Sciences (KSCX2-EW-R-06).
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, ZK., Liu, HY., Fang, WN. et al. Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 7 Modulates Estrogen-Induced Trophoblast Proliferation and Invasion in HTR-8 and JEG-3 Cells. Cell Biochem Biophys 63, 73–84 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-012-9342-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-012-9342-5