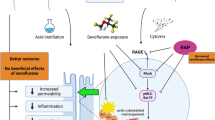
Abstract
Preconditioning with sevoflurane (SPC) diminishes effusion of rat alveolar membrane during inflammation. It is not clear whether this preconditioning directly inhibits permeability of pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell (PMVEC) monolayer. In this article, we evaluated effects of SPC on permeability of PMVEC monolayer and identified signaling pathways involved in these effects. PMVEC monolayer was exposed to different conditions (5-hydroxydecanoate (5-HD), TNF-α, SPC, SPC with subsequent exposure to TNF-α and 5-HD, and SPC with subsequent exposure to TNF-α alone), and the permeability of PMVEC monolayer was assessed using FITC-bovine serum albumin (ELISA). Expression of ICAM-1 (Western blot and RT-PCR) and activation of p38 MAPK (Western blot) were also assessed. Compared to the TNF-α group, permeability of PMVEC monolayer in the SPC + TNF-α group was significantly lower. Activation of p38 MAPK was also diminished in the TNF-α group. Pre-treatment with 5-HD reverted beneficial effects of SPC. Expression of ICAM-1 was not modulated by any of the tested experimental exposures. The results of this study demonstrate that SPC is capable of diminishing the TNF-α-induced increase of permeability of PMVEC monolayer, and that this beneficial effect is partly reversed by 5-HD. Further, SPC suppresses activation of p38 MAPK.





Similar content being viewed by others
Bibliography
Zimmerman, G. A., Albertine, K. H., Carveth, H. J., Gill, E. A., Grissom, C. K., Hoidal, J. R., et al. (1999). Endothelial activation in ARDS. Chest, 116, 18S–24S.
Asaduzzaman, M., Wang, Y., & Thorlacius, H. (2008). Critical role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in septic lung injury. Critical Care Medicine, 36, 482–488.
Borbiev, T., Birukova, A., Liu, F., Nurmukhambetova, S., Gerthoffer, W. T., Garcia, J. G., et al. (2004). p38 MAP kinase-dependent regulation of endothelial cell permeability. American Journal of Physiology Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology, 287, L911–L918.
Nwariaku, F. E., Chang, J., Zhu, X., Liu, Z., Duffy, S. L., Halaihel, N. H., et al. (2002). The role of p38 map kinase in tumor necrosis factor-induced redistribution of vascular endothelial cadherin and increased endothelial permeability. Shock, 18, 82–85.
Sniecinski, R., & Liu, H. (2004). Reduced efficacy of volatile anesthetic preconditioning with advanced age in isolated rat myocardium. Anesthesiology, 100, 589–597.
Yonemochi, H., Ichinose, M., Anan, F., Taniguti, Y., Shinohara, T., Takahashi, N., et al. (2006). Diazoxide-induced cardioprotection via DeltaPsim loss depending on timing of application. Life Science, 79, 1906–1912.
Tanaka, K., Ludwig, L. M., Krolikowski, J. G., Alcindor, D., Pratt, P. F., Kersten, J. R., et al. (2004). Isoflurane produces delayed preconditioning against myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury: Role of cyclooxygenase-2. Anesthesiology, 100, 525–531.
Xiong, L., Zheng, Y., Wu, M., Hou, L., Zhu, Z., Zhang, X., et al. (2003). Preconditioning with isoflurane produces dose-dependent neuroprotection via activation of adenosine triphosphate-regulated potassium channels after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Anesthesia and Analgesia, 96, 233–237. table.
Plachinta, R. V., Hayes, J. K., Cerilli, L. A., & Rich, G. F. (2003). Isoflurane pretreatment inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in rats. Anesthesiology, 98, 89–95.
Allen, M., Svensson, L., Roach, M., Hambor, J., McNeish, J., & Gabel, C. A. (2000). Deficiency of the stress kinase p38alpha results in embryonic lethality: characterization of the kinase dependence of stress responses of enzyme-deficient embryonic stem cells. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 191, 859–870.
Sun, Y. H., Zhang, Q., Wang, J. K., & Cui, Y. (2004). Effects of sevoflurane on membrane permeability of alveolar capillaries in rats with acute lung injury caused by endotoxin. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi, 42, 1014–1017.
Chen, S. F., Fei, X., & Li, S. H. (1995). A new simple method for isolation of microvascular endothelial cells avoiding both chemical and mechanical injuries. Microvascular Research, 50, 119–128.
Nooteboom, A., Hendriks, T., Otteholler, I., & van der Linden, C. J. (2000). Permeability characteristics of human endothelial monolayers seeded on different extracellular matrix proteins. Mediators Inflammation, 9, 235–241.
Predescu, D., & Palade, G. E. (1993). Plasmalemmal vesicles represent the large pore system of continuous microvascular endothelium. American Journal of Physiology, 265, H725–H733.
Michel, C. C., & Curry, F. E. (1999). Microvascular permeability. Physiological Reviews, 79, 703–761.
Malik, A. B., & Horgan, M. J. (1987). Mechanisms of thrombin-induced lung vascular injury and edema. American Review of Respiratory Disease, 136, 467–470.
Malik, A. B., & Lo, S. K. (1996). Vascular endothelial adhesion molecules and tissue inflammation. Pharmacological Reviews, 48, 213–229.
Bates, D. O., Hillman, N. J., Pocock, T. M., & Neal, C. R. (2002). Regulation of microvascular permeability by vascular endothelial growth factors. Journal of Anatomy, 200, 529–530.
Michel, C. C., & Neal, C. R. (1999). Openings through endothelial cells associated with increased microvascular permeability. Microcirculation, 6, 45–54.
van Hinsbergh, W. M. (1997). Endothelial permeability for macromolecules. Mechanistic aspects of pathophysiological modulation. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 17, 1018–1023.
Garcia, J. G., Davis, H. W., & Patterson, C. E. (1995). Regulation of endothelial cell gap formation and barrier dysfunction: role of myosin light chain phosphorylation. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 163, 510–522.
van Nieuw Amerongen, G. P., Draijer, R., Vermeer, M. A., & van Hinsbergh, V. W. (1998). Transient and prolonged increase in endothelial permeability induced by histamine and thrombin: role of protein kinases, calcium, and RhoA. Circulation Research, 83, 1115–1123.
Vuong, P. T., Malik, A. B., Nagpala, P. G., & Lum, H. (1998). Protein kinase C beta modulates thrombin-induced Ca2+ signaling and endothelial permeability increase. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 175, 379–387.
Angelini, D. J., Hyun, S. W., Grigoryev, D. N., Garg, P., Gong, P., Singh, I. S., et al. (2006). TNF-alpha increases tyrosine phosphorylation of vascular endothelial cadherin and opens the paracellular pathway through fyn activation in human lung endothelia. American Journal of Physiology Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology, 291, L1232–L1245.
van Hinsbergh, V. W., & van Nieuw Amerongen, G. P. (2002). Intracellular signalling involved in modulating human endothelial barrier function. Journal of Anatomy, 200, 549–560.
Leeper-Woodford, S. K., Carey, P. D., Byrne, K., Jenkins, J. K., Fisher, B. J., Blocher, C., et al. (1991). Tumor necrosis factor. Alpha and beta subtypes appear in circulation during onset of sepsis-induced lung injury. American Review of Respiratory Disease, 143, 1076–1082.
Goldblum, S. E., Ding, X., & Campbell-Washington, J. (1993). TNF-alpha induces endothelial cell F-actin depolymerization, new actin synthesis, and barrier dysfunction. American Journal of Physiology, 264, C894–C905.
Hildt, E., & Oess, S. (1999). Identification of Grb2 as a novel binding partner of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor I. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 189, 1707–1714.
Petrache, I., Verin, A. D., Crow, M. T., Birukova, A., Liu, F., & Garcia, J. G. (2001). Differential effect of MLC kinase in TNF-alpha-induced endothelial cell apoptosis and barrier dysfunction. American Journal of Physiology Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology, 280, L1168–L1178.
Deyhimy, D. I., Fleming, N. W., Brodkin, I. G., & Liu, H. (2007). Anesthetic preconditioning combined with postconditioning offers no additional benefit over preconditioning or postconditioning alone. Anesthesia and Analgesia, 105, 316–324.
Chiari, P. C., Pagel, P. S., Tanaka, K., Krolikowski, J. G., Ludwig, L. M., Trillo, R. A., Jr., et al. (2004). Intravenous emulsified halogenated anesthetics produce acute and delayed preconditioning against myocardial infarction in rabbits. Anesthesiology, 101, 1160–1166.
Zaugg, M., Lucchinetti, E., Spahn, D. R., Pasch, T., & Schaub, M. C. (2002). Volatile anesthetics mimic cardiac preconditioning by priming the activation of mitochondrial K(ATP) channels via multiple signaling pathways. Anesthesiology, 97, 4–14.
Kaneda, K., Miyamae, M., Sugioka, S., Okusa, C., Inamura, Y., Domae, N., et al. (2008). Sevoflurane enhances ethanol-induced cardiac preconditioning through modulation of protein kinase C, mitochondrial KATP channels, and nitric oxide synthase, in guinea pig hearts. Anesthesia and Analgesia, 106, 9–16. table.
Zhou, Z., Connell, M. C., & MacEwan, D. J. (2007). TNFR1-induced NF-kappaB, but not ERK, p38MAPK or JNK activation, mediates TNF-induced ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression on endothelial cells. Cellular Signalling, 19, 1238–1248.
Paul, A., Wilson, S., Belham, C. M., Robinson, C. J., Scott, P. H., Gould, G. W., et al. (1997). Stress-activated protein kinases: activation, regulation and function. Cellular Signalling, 9, 403–410.
Hu, J. H., Chen, T., Zhuang, Z. H., Kong, L., Yu, M. C., Liu, Y., et al. (2007). Feedback control of MKP-1 expression by p38. Cellular Signalling, 19, 393–400.
Acknowledgments
We thank all the lab members for helpful discussion. This study is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (project 30872430).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, SX., Ge, BX. & Miao, CH. Effects of Preconditioning with Sevoflurane on TNF-α-Induced Permeability and Activation of p38 MAPK in Rat Pulmonary Microvascular Endothelial Cells. Cell Biochem Biophys 61, 123–129 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-011-9168-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-011-9168-6