Abstract
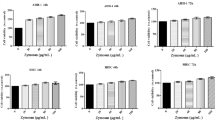
The objective is to study the effect of zymosan on antioxidant and immune function of S180 tumor-bearing mice. Seventy Kunming mice were randomly divided into seven groups: a normal control group (NC), a tumor control group (TC), three dose groups of zymosan (low, medium, high), a cyclophosphamide (Cy) group, and a combination of zymosan and Cy group. The S180 tumor-bearing mice model was established by the inoculation of cancer cell suspension subcutaneously in the mouse’s right anterior limb. At the 19th day, malondialdehyde (MDA), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity in liver homogenate were analyzed. The reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction was used to determine the mRNA expression levels of IL-2, TNF-α, and TGF-β1. The activity of GSH-Px and SOD in the liver increased with the dose of zymosan, whereas the activity of MDA significantly decreased in the higher-dose groups of zymosan, compared to the TC group (P < 0.01). In the zymosan groups, mRNA expression levels in tissues of S180 tumor-bearing mice were significantly higher for TNF-α and IL-2, but lower for TGFβ1 than in the Cy or TC group (P < 0.01). The high-dose of zymosan markedly showed a depressant effect on S180 tumor, enhanced by the action of Cy that increased mRNA expression levels of TNF-α and IL-2. The mechanism of zymosan on the inhibition of tumor growth may be due to its ability to enhance the antioxidant and immune function in a dose-dependent manner.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Cy:
-
Cyclophosphamide
- GSH-Px:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- H:
-
High-dose
- L:
-
Low-dose
- M:
-
Medium-dose
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- NC:
-
Normal control
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- TC:
-
Tumor control
References
Wasowicz, W., Reszka, E., Gromadzinska, J., & Rydzynski, K. (2003). The role of essential elements in oxidative stress. Comments on Toxicology, 9, 39–48.
Mates, J. M., Perez-Gomez, C., & Nunez dC, I. (1999). Antioxidant enzymes and human diseases. Clinical Biochemistry, 32, 595–603.
Gracy, R. W., Talent, J. M., Kong, Y., & Conrad, C. C. (1999). Reactive oxygen species: The unavoidable environmental insult? Mutation Research, 428, 17–22.
Woutersen, R.A. & Appel, M.J. (1998). Food and chemical toxicology. Symposium on antioxidants and health Bordeaux, France (pp. 981–984).
Estrada, A., Yun, C. H., Van Kessel, A., Li, B., Hauta, S., & Laarveld, B. (1997). Immunomodulatory activities of oat beta-glucan in vitro and in vivo. Microbiology and Immunology, 41, 991–998.
Li, F., & Li, Y. (1998). Effect of polysaccharides of brewers yeast on the immune cells in mice. Journal of Norman Bethune University of Medicine and Science, 24, 124–126.
Zhang, J., Liu, J., & Dang, X. (2000). Effect of yeast competence products and zymosan A on erythrocyte immune adherence. Journal of Xi’an Medical University, 21, 18–19.
Xu, J., Hou, G., Huang, D., & Lu, S. (2002). Effects of zymosan on the production of nitric oxide and interleukin-1 in mouse peritoneal macrophages. Chinese Journal of Biochemical Pharmaceuticals, 23, 67–68.
Williams, N. (1996). Tumor cells fight back to beat immune system. Science. 274, 1302.
Li, X., Liu, F., & Zhang, H. (2006). Effect of Traditional Chinese medicine FGC-6 on tumor inhibition and immune regulation on H22 tumor bearing mice. Chinese Journal of Gerontology, 6, 92–93.
Bosscher, D., Breynaert, A., Pieters, L., & Hermans, N. (2009). Food-based strategies to modulate the composition of the intestinal microbiota and their associated health effects. Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology, 60(6), 5–11.
Troy, E. B., & Kasper, D. L. (2010). Beneficial effects of Bacteroides fragilis polysaccharides on the immune system. Frontiers in Bioscience, 15, 25–34.
Kimura, K., Bowen, C., Spiegel, S., & Gelmann, E. P. (1999). Tumor necrosis factor-alpha sensitizes prostate cancer cells to gamma-irradiation-induced apoptosis. Cancer Research, 59, 1606–1614.
Capelli, E., Barni, S., Vaccarone, R., Fortis, C., & Nano, R. (1996). Cell activation and death (apoptosis) induced by IL-2: Ultrastructural evidence. Anticancer Research, 16, 1775–1780.
Zhou, Z., Wu, X., & Zhu, Y. (2003). Clinical significance of measured expression level of cytokine in peripheral blood cells from patients with malignant carcinoma. Henan Journal of Oncology, 16, 159.
Schuster, N., & Krieglstein, K. (2002). Mechanisms of TGF-beta-mediated apoptosis. Cell and Tissue Research, 307, 1–14.
Perlman, R., Schiemann, W. P., Brooks, M. W., Lodish, H. F., & Weinberg, R. A. (2001). TGF-beta-induced apoptosis is mediated by the adapter protein Daxx that facilitates JNK activation. Nature Cell Biology, 3, 708–714.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. L. V. Xiang for assistance in animal modeling. The support of Dr. Yao Lu for manuscript editing is also gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xiao-li Liu and Ning Lin contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Xl., Lin, N., Zan, D. et al. Effect of Zymosan on Antioxidant and Immune Function of S180 Tumor-Bearing Mice. Cell Biochem Biophys 60, 225–229 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-010-9143-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-010-9143-7