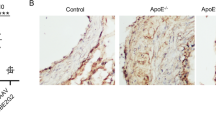
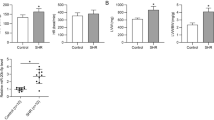
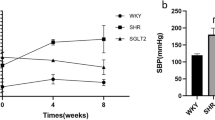
Abstract
Hypertension is a pathological state of the metabolic syndrome that increases the risk of cardiovascular disease. Managing hypertension is challenging, and we aimed to identify the pathogenic factors and discern therapeutic targets for metabolic hypertension (MHR). An MHR rat model was established with the combined treatment of a high-sugar, high-fat diet and ethanol. Histopathological observations were performed using hematoxylin–eosin and Sirius Red staining. Transcriptome sequencing was performed to screen differentially expressed genes. The role of ubiquitin-specific protease 18 (USP18) in the proliferation, apoptosis, and oxidative stress of HUVECs was explored using Cell Counting Kit-8, flow cytometry, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. Moreover, USP18 downstream signaling pathways in MHR were screened, and the effects of USP18 on these signaling pathways were investigated by western blotting. In the MHR model, total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein levels increased, while high-density lipoprotein levels decreased. Moreover, high vessel thickness and percentage of collagen were noted along with increased malondialdehyde, decreased superoxide dismutase and catalase levels. The staining results showed that the MHR model exhibited an irregular aortic intima and disordered smooth muscle cells. There were 78 differentially expressed genes in the MHR model, and seven hub genes, including USP18, were identified. USP18 overexpression facilitated proliferation and reduced apoptosis and oxidative stress in HUVECs treated with Ang in vitro. In addition, the JAK/STAT pathway was identified as a USP18 downstream signaling pathway, and USP18 overexpression inhibited the expression of JAK/STAT pathway-related proteins. Conclusively, USP18 restrained MHR progression by promoting cell proliferation, reversing apoptosis and oxidative stress, and suppressing the JAK/STAT pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Garg, P. K., Biggs, M. L., Carnethon, M., Ix, J. H., Criqui, M. H., Britton, K. A., Djousse, L., Sutton-Tyrrell, K., Newman, A. B., Cushman, M., & Mukamal, K. J. (2014). Metabolic syndrome and risk of incident peripheral artery disease: The cardiovascular health study. Hypertension, 63, 413–419.
Wang, J., Ma, M. C., Mennie, A. K., Pettus, J. M., Xu, Y., Lin, L., Traxler, M. G., Jakoubek, J., Atanur, S. S., Aitman, T. J., et al. (2015). Systems biology with high-throughput sequencing reveals genetic mechanisms underlying the metabolic syndrome in the Lyon hypertensive rat. Circulation Cardiovascular Genetics, 8, 316–326.
Franco, C., Sciatti, E., Favero, G., Bonomini, F., Vizzardi, E., & Rezzani, R. (2022). Essential hypertension and oxidative stress: Novel future perspectives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23, 14489.
Iqbal, A.M., & Jamal, S.F. (2022). Essential hypertension. In StatPearls. Treasure Island.
Pandi-Perumal, S. R., BaHammam, A. S., Ojike, N. I., Akinseye, O. A., Kendzerska, T., Buttoo, K., Dhandapany, P. S., Brown, G. M., & Cardinali, D. P. (2017). Melatonin and human cardiovascular disease. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 22, 122–132.
Kostov, K. (2021). The causal relationship between endothelin-1 and hypertension: Focusing on endothelial dysfunction, arterial stiffness, vascular remodeling, and blood pressure regulation. Life, 11, 986.
Stump, M., Mukohda, M., Hu, C., & Sigmund, C. D. (2015). PPARgamma regulation in hypertension and metabolic syndrome. Current Hypertension Reports, 17, 89.
Carella, A. M., Antonucci, G., Conte, M., Di Pumpo, M., Giancola, A., & Antonucci, E. (2010). Antihypertensive treatment with beta-blockers in the metabolic syndrome: A review. Current Diabetes Review, 6, 215–221.
Yin, Y., Butler, C., & Zhang, Q. (2021). Challenges in the application of NGS in the clinical laboratory. Human Immunology, 82, 812–819.
Saeidian, A. H., Youssefian, L., Vahidnezhad, H., & Uitto, J. (2020). Research techniques made simple: Whole-transcriptome sequencing by RNA-Seq for diagnosis of monogenic disorders. The Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 140, 1117–1126.
Lacy, S. E., Barrans, S. L., Beer, P. A., Painter, D., Smith, A. G., Roman, E., Cooke, S. L., Ruiz, C., Glover, P., Van Hoppe, S. J. L., et al. (2020). Targeted sequencing in DLBCL, molecular subtypes, and outcomes: A Haematological Malignancy Research Network report. Blood, 135, 1759–1771.
Wu, H., Zhu, S., Yuan, R., Yi, Y., Wang, H., Gu, B., Zhen, T., Xing, K., & Ma, J. (2019). Transcriptome sequencing to detect the potential role of long noncoding RNAs in salt-sensitive hypertensive rats. BioMed Research International, 2019, 2816959.
Musunuru, K. (2012). Exome sequencing to identify novel genes in hypertension. Circulation Cardiovascular Genetics, 5, 267–268.
Hou, J., Han, L., Zhao, Z., Liu, H., Zhang, L., Ma, C., Yi, F., Liu, B., Zheng, Y., & Gao, C. (2021). USP18 positively regulates innate antiviral immunity by promoting K63-linked polyubiquitination of MAVS. Nature Communications, 12, 2970.
Dziamalek-Macioszczyk, P., Harazna, J., & Stompor, T. (2019). Versatility of USP18 in physiology and pathophysiology. Acta Biochimica Polonica, 66, 389–392.
Malakhov, M. P., Malakhova, O. A., Kim, K. I., Ritchie, K. J., & Zhang, D. E. (2002). UBP43 (USP18) specifically removes ISG15 from conjugated proteins. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277, 9976–9981.
Friedrich, S. K., Schmitz, R., Bergerhausen, M., Lang, J., Cham, L. B., Duhan, V., Haussinger, D., Hardt, C., Addo, M., Prinz, M., et al. (2020). Usp18 expression in CD169(+) macrophages is important for strong immune response after vaccination with VSV-EBOV. Vaccines, 8, 142.
Luo, X., Zhou, Z., Wu, J., Zhang, L., Zhang, J., & Li, J. (2022). Integrated RNA- and miRNA-sequencing analysis identifies molecular basis for stress-induced heart injury in mouse models. International Journal of Cardiology, 349, 115–122.
Dziamalek-Macioszczyk, P., Harazny, J. M., Kwella, N., Wojtacha, P., Jung, S., Dienemann, T., Schmieder, R. E., & Stompor, T. (2020). Relationship between ubiquitin-specific peptidase 18 and hypertension in polish adult male subjects: A cross-sectional pilot study. Medical Science Monitor, 26, e921919.
Xue, C., Yao, Q., Gu, X., Shi, Q., Yuan, X., Chu, Q., Bao, Z., Lu, J., & Li, L. (2023). Evolving cognition of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway: Autoimmune disorders and cancer. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 8, 204.
Pang, Q., You, L., Meng, X., Li, Y., Deng, T., Li, D., & Zhu, B. (2023). Regulation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway: The promising targets for cardiovascular disease. Biochemical Pharmacology, 213, 115587.
Li, B., He, X., Jin, H. Y., Wang, H. Y., Zhou, F. C., Zhang, N. Y., Jie, D. Y., Li, L. Z., Su, J., Zheng, X., et al. (2021). Beneficial effects of Dendrobium officinale on metabolic hypertensive rats by triggering the enteric-origin SCFA-GPCR43/41 pathway. Food & Function, 12, 5524–5538.
Su, J., Wang, Y., Yan, M., He, Z., Zhou, Y., Xu, J., Li, B., Xu, W., Yu, J., Chen, S., & Lv, G. (2022). The beneficial effects of Polygonatum sibiricum Red. Superfine powder on metabolic hypertensive rats via gut-derived LPS/TLR4 pathway inhibition. Phytomedicine, 106, 154404.
Katsimardou, A., Imprialos, K., Stavropoulos, K., Sachinidis, A., Doumas, M., & Athyros, V. (2020). Hypertension in metabolic syndrome: Novel insights. Current Hypertension Reviews, 16, 12–18.
McMaster, W. G., Kirabo, A., Madhur, M. S., & Harrison, D. G. (2015). Inflammation, immunity, and hypertensive end-organ damage. Circulation Research, 116, 1022–1033.
Crowley, S. D., & Jeffs, A. D. (2016). Targeting cytokine signaling in salt-sensitive hypertension. American Journal of Physiology Renal Physiology, 311, F1153–F1158.
Chen, N., Deng, J., Zhang, Z., Feng, X., Wang, H., Chen, J., Li, L., Cao, Y., Jia, C., & Cao, Y. (2022). Oxidative stress-triggered pyroptosis mediates Candida albicans susceptibility in diabetic foot. Microbial Pathogenesis, 172, 105765.
Martynowicz, H., Janus, A., Nowacki, D., & Mazur, G. (2014). The role of chemokines in hypertension. Advances in Clinical Experimental Medicine, 23, 319–325.
Mikolajczyk, T. P., Szczepaniak, P., Vidler, F., Maffia, P., Graham, G. J., & Guzik, T. J. (2021). Role of inflammatory chemokines in hypertension. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 223, 107799.
Yang, F., Qiu, R., Abudoubari, S., Tao, N., & An, H. (2022). Effect of interaction between occupational stress and polymorphisms of MTHFR gene and SELE gene on hypertension. PeerJ, 10, e12914.
Faruque, M. U., Chen, G., Doumatey, A., Huang, H., Zhou, J., Dunston, G. M., Rotimi, C. N., & Adeyemo, A. A. (2011). Association of ATP1B1, RGS5 and SELE polymorphisms with hypertension and blood pressure in African-Americans. Journal of Hypertension, 29, 1906–1912.
Hage, F. G. (2014). C-reactive protein and hypertension. Journal of Human Hypertension, 28, 410–415.
Lin, K., Luo, W., Yan, J., Shen, S., Shen, Q., Wang, J., Guan, X., Wu, G., Huang, W., & Liang, G. (2020). TLR2 regulates angiotensin II-induced vascular remodeling and EndMT through NF-κB signaling. Aging, 13, 2553–2574.
Lagor, W. R., Fields, D. W., Bauer, R. C., Crawford, A., Abt, M. C., Artis, D., Wherry, E. J., & Rader, D. J. (2014). Genetic manipulation of the ApoF/Stat2 locus supports an important role for type I interferon signaling in atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis, 233, 234–241.
Liu, L. Q., Ilaria, R., Jr., Kingsley, P. D., Iwama, A., van Etten, R. A., Palis, J., & Zhang, D. E. (1999). A novel ubiquitin-specific protease, UBP43, cloned from leukemia fusion protein AML1-ETO-expressing mice, functions in hematopoietic cell differentiation. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 19, 3029–3038.
Pan, A., Li, Y., Guan, J., Zhang, P., Zhang, C., Han, Y., Zhang, T., Cheng, Y., Sun, L., Lu, S., et al. (2021). USP18-deficiency in cervical carcinoma is crucial for the malignant behavior of tumor cells in an ERK signal-dependent manner. Oncology Letters, 21, 421.
Feng, L., Wang, K., Tang, P., Chen, S., Liu, T., Lei, J., Yuan, R., Hu, Z., Li, W., & Yu, X. (2020). Deubiquitinase USP18 promotes the progression of pancreatic cancer via enhancing the Notch1-c-Myc axis. Aging, 12, 19273–19292.
Diao, W., Guo, Q., Zhu, C., Song, Y., Feng, H., Cao, Y., Du, M., & Chen, H. (2020). USP18 promotes cell proliferation and suppressed apoptosis in cervical cancer cells via activating AKT signaling pathway. BMC Cancer, 20, 741.
Jiang, Z., Shen, J., Ding, J., Yuan, Y., Gao, L., Yang, Z., & Zhao, X. (2021). USP18 mitigates lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells through the TLR4/NF-kappaB/ROS signaling. Toxicology in Vitro, 75, 105181.
Huang, P. L. (2009). A comprehensive definition for metabolic syndrome. Disease Models & Mechanisms, 2, 231–237.
Dodington, D. W., Desai, H. R., & Woo, M. (2018). JAK/STAT—emerging players in metabolism. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism, 29, 55–65.
Collotta, D., Franchina, M. P., Carlucci, V., & Collino, M. (2023). Recent advances in JAK inhibitors for the treatment of metabolic syndrome. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 14, 1245535.
Dobrian, A. D., Galkina, E. V., Ma, Q., Hatcher, M., Aye, S. M., Butcher, M. J., Ma, K., Haynes, B. A., Kaplan, M. H., & Nadler, J. L. (2013). STAT4 deficiency reduces obesity-induced insulin resistance and adipose tissue inflammation. Diabetes, 62, 4109–4121.
Yao, Y., Luo, Z. P., Li, H. W., Wang, S. X., Wu, Y. C., Hu, Y., Hu, S., Yang, C. C., Yang, J. F., Wang, J. P., et al. (2023). P38γ modulates the lipid metabolism in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by regulating the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. The FASEB Journal, 37, e22716.
Shi, S. Y., Martin, R. G., Duncan, R. E., Choi, D., Lu, S. Y., Schroer, S. A., Cai, E. P., Luk, C. T., Hopperton, K. E., Domenichiello, A. F., et al. (2012). Hepatocyte-specific deletion of Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) protects against diet-induced steatohepatitis and glucose intolerance. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 287, 10277–10288.
Luo, J. W., Hu, Y., Liu, J., Yang, H., & Huang, P. (2021). Interleukin-22: A potential therapeutic target in atherosclerosis. Molecular Medicine, 27, 88.
Acknowledgements
Not Applicable.
Funding
Not Applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhihong Xie and Mingshan Huang: conception, design and analysis of data, performed the data analyses and wrote the manuscript; Wang Xu and Fuwei Liu: contributed to the conception of the study; wrote the manuscript; Donghua Huang: contributed significantly to analysis and manuscript preparation; wrote the manuscript; All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
The experiments conformed to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Animal study has been approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Ganzhou People’s Hospital (TY-DKY2023-009-01). All methods are reported in accordance with ARRIVE guidelines.
Consent for Publication
Not Applicable.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Daniel Conklin.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Z., Huang, M., Xu, W. et al. USP18 Curbs the Progression of Metabolic Hypertension by Suppressing JAK/STAT Pathway. Cardiovasc Toxicol 24, 576–586 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-024-09860-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-024-09860-7