Abstract
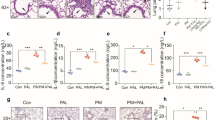
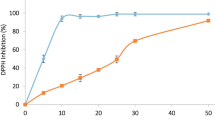
Chronic mixed toxicant exposure has been implicated in the aetiology of lung and heart failure through prolonged free radical generations. This study was carried out to assess the protective effect of naturally occurring phenolic components from Croton zambesicus (400 mg/kg C-ZAMB) leaves against cardiopulmonary toxicity induced by chronic mixed toxicant (0.5 mL EOMABRSL) in rats. Chronic cardiopulmonary injury via oral administration of 0.5 ml EOMABRSL for 98 days (non-withdrawal) and 70 days (withdrawal) caused unhealthy alteration in the levels of oxidative stress biomarkers [malondialdehyde (MDA), reduced glutathione (GSH), glutathione-S-transferase (GST), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase]. Similarly, both withdrawal and non-withdrawal approaches of EOMABRSL-exposed animals exhibited increase in the activity of eco-51-nucleotidase (51ENT) with corresponding diminution in the activity of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), i.e. the metabolic fuel for cardiopulmonary wellness. Ultimately, histology examination confirmed hyperplastic, bronchopneumonia and cloudy swelling of cardiovascular cells followed by the accumulation of cellular exudates and haemorrhage in the alveoli and bronchioles. The active antioxidants of 400 mg/kg C-ZAMB leaves were responsible for the biological protection of cardiopulmonary toxicity by modulating the activities of 51ENT and LDH. The oxidative stress was also reversed by 400 mg/kg phenolic C-ZAMB leaves in the heart and lungs. Hence, 400 mg/kg phenolic C-ZAMB leaves may be a natural therapy for the treatment of cardiovascular disorder associated with pulmonary dysfunction in rats.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, H., Khan, E., & Sajad, M. A. (2013). Phytoremediation of heavy metals-concepts and applications. Chemoshere, 91(7), 869–881.
Hashem, M. A., Nur-A-Tomal, M. S., Mondal, N. R., & Rahman, M. A. (2017). Hair burning and liming in tanneries is a source of pollution by arsenic, lead, zinc, manganese and iron. Environmental Chemistry and Letters, 15(3), 501–506.
Ogaga, A. A., Faith, A. M., & Sylvester, C. I. (2018). Impacts of anthropogenic activities on heavy metal levels in surface water of Nun River around Gbarantoru and Tombia Towns, Bayelsa State, Nigeria. Annals of Ecology and Environmental Science, 2(2), 1–8.
Nagajyoti, P. C., Lee, K. D., & Sreekanth, T. V. M. (2010). Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: A review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 8(3), 199–216.
Jaishankar, M., Mathew, B. B., Shah, M. S., & Gowda, K. R. S. (2014). Biosorption of few heavy metal ions using agricultural wastes. Journal of Environmental Pollution and Human Health, 2(1), 1–6.
He, Z. L., Yang, X. E., & Stoffella, P. J. (2005). Trace elements in agroecosystems and impacts on the environment. Journal of Trace Elementary Medicine and Biology, 19(2–3), 125–140.
Stern, B. R. (2010). Essentiality and toxicity in copper health risk assessment: Overview, update and regulatory considerations. Toxicological Environmental Health A, 73(2), 114–127.
Beyersmann, D., & Hartwig, A. (2008). Carcinogenic metal compounds: Recent insight into molecular and cellular mechanisms. Archive of Toxicology, 82(8), 493–512.
Tchounwou, P. B., Yedjou, C. G., Patlolla, A. K., & Sutton, D. J. (2012). Heavy metals toxicity and the environment. NHS Public Access, 101, 133–164.
Sheng, J. J., Wang, X. P., Gong, P., Tian, L. D., & Yao, T. D. (2012). Heavy metals of the Tibetan top soils Level, source, spatial distribution, temporal variation and risk assessment. Environmental Science and Pollution Resources, 19, 3362–3370.
Wieczorek-Dąbrowska, M., Tomza-Marciniak, A., Pilarczyk, B., & Balicka-Ramisz, A. (2013). Roe and red deer as bioindicators of heavy metals contamination in north-western Poland. Chemical Ecology, 29(2), 100–110.
Monisha, J., Tenzin, T., Naresh, A., Blessy, B. M., & Krishnamurthy, N. B. (2014). Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdisciplinary Toxicology, 7(2), 60–72.
Akintunde, J. K., & Oboh, G. (2015). Depletion of cellular adenosine triphosphate and hepatocellular damage in rat after sub-chronic exposure to leachate from anthropogenicrecycling site. Human and Experimental Toxicology, 34(11), 1083–1095.
Aleksandra, B., David, W., Vesna, M., Amie, S., Branislav, O., Dusan, M., & Vladimir, D. (2017). Cadmium exposure as a putative risk factor for the development of pancreatic Cancer: Three different lines of evidence. Biomedical Resources International, 1, 1981837.
Krishna, A. K., & Mohan, K. R. (2016). Distribution, correlation, ecological and health risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface soils around an industrial area, Hyderabad, India. Environmental Earth Science, 75, 411.
World Health Organization. (2017). Fact sheet: Lead poisoning and health. Retrieved December 10, 2017, from https://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs379/en/.
Sogl, M., Taeger, D., Pallapies, D., Brüning, T., Dufey, F., Schnelzer, M., et al. (2012). Quantitative relationship between silica exposure and lung cancer mortality in German uranium miners, 1946–2003. British Journal of Cancer, 107(7), 1188–1194.
Akintunde, J. K., Oboh, G., & Akindahunsi, A. A. (2015). Inhibition of key markers linked with spermatogenesis and cellular ATP by sub-chronic exposure to leachate in a rat model. Archive Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 68(1), 159–168.
French, I. T., & Muthusamy, K. A. (2018). A review of the pedunculopontine nucleus in parkinson’s disease. Frontier of Aging Neuroscience, 10, 99.
Ayanniyi, R. O., Olumoh-Abdul, H. A., Ojuade, F. I., Abdullahi, R., & Anafi, S. B. (2019). The protective effect of Croton zambesicus against carbon tetrachloride-induced renal toxicity in rats. International Journal of Toxicology, 1, 5–8.
Adam-Sharma, I. Y., & Ebtihal, A. S. (2013). Investigations on the effects of various oral doses of Croton zambesicus seeds’ in wistar rats. Journal of Pharmacology and Toxicology, 8(1), 19–27.
Okokon, J. E., & Nwafor, P. A. (2010). Anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic activities of ethanolic root extract of Croton zambesicus. Pakistan Journal of Pharmaceutical Science, 92(4), 385–392.
Ndhlala, A. R., Aderogba, M. A., Ncube, B., & Van Staden, J. (2013). Anti-oxidative and cholinesterase inhibitory effects of leaf extracts and their isolated compounds from two closely related Croton species. Molecules, 18(2), 1916–1932.
Aderogba, M. A., McGaw, L. J., Bezabih, M., & Abegaz, B. M. (2011). Isolation and characterisation of novel antioxidant constituents of Croton zambesicus leaf extract. Natural Product Resources, 25(13), 1224–1233.
Robert, S., Baccelli, C., Devel, P., Dogne, J. M., & Quetin-Leclercq, J. (2010). Effects of leaf extracts from Croton zambesicus Muell Arg. on hemostasis. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 128(3), 641–648.
Baccelli, C., Navarro, I., Block, S., Abad, A., Morel, N., & Quetin-Leclercq, J. (2007). Vasorelaxant activity of diterpenes from Croton zambesicus and synthetic trachylobanes and their structure-activity relationships. Journal of Natural Products, 70(6), 910–917.
Martinsen, A., Baccelli, C., Navarro, I., Abad, A., Quetin-Leclercq, J., & Morel, N. (2010). Vascular activity of a natural diterpene isolated from Croton zambesicus and of a structurally similar synthetic trachylobane. Vascular Pharmacology, 52(1), 63–69.
Asare, G. A., Adjei, S., Afriyie, D., Appiah-Danquah, A. B., Asia, J., Asiedu, B., et al. (2015). Croton membranaceus improves some biomarkers of cardiovascular disease and diabetes in genetic animal models. Journal Clinical Diagnosis Resources, 9(12), 1–5.
Akintunde, J., Ayeni, S., Adeoye, M., & Shittu, A. (2020). Rat liver and kidney post-mitochondrial dysfunction by addition of chronic mixed metal intoxication and hepatorenal wellness mediated by phenolic components from Croton zambiscus leaves. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 74, 103293.
Bello, M. O., Abdul-Hammed, M., Adekunle, S. A., & Fasogbon, O. T. (2014). Nutrient contents and fatty acids profiles of leaves and seeds of Croton zambesicus. Advance Journal of Food Science and Technology, 6(3), 398–402.
Chan, E. W. C., Lim, Y. Y., & Chew, Y. L. (2006). Antioxidant activity of Camellia sinensis leaves and tea from a lowland plantation in Malaysia. Food Chemistry, 102, 1214–1222.
Kale, A., Gaikwad, S., Mundhe, K., Deshpande, N., & Salvekar, J. (2010). Quantification of phenolics and flavonoids by spectrophotometer from Juglans regia. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Bioscience, 1, 1–4.
Padmaja, G. (1989). Evaluation of techniques to reduce assayable tannin and cyanide in cassava leaves. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 137, 712–716.
Makkar, H. P. S., Siddhuraju, P., & Becker, K. (2007). Plant secondary metabolites. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press.
Benderitter, M., Maupoil, V., Vergely, C., Dalloz, F., Briot, F., & Rochette, L. (1998). Studies by electron paramagnetic resonance of the importance of iron in the hydroxyl scavenging properties of ascorbic acid in plasma: Effects of iron chelators. Fundamental Clinical Pharmacology, 12, 510–516.
Ashwell, R. N., Mutalib, A. A., Bhekumthetho, N., & Johannes, V. S. (2013). Anti-oxidative and cholinesterase inhibitory effects of leaf extracts and their isolated compounds from two closely related croton species. Molecules, 18, 1916–1932.
Akintunde, J. K., Irondi, A. E., Ajani, E. O., & Olayemi, T. V. (2018). Neuroprotective effect of dietary black seed flour on key enzymes linked with neuronal signaling molecules in rats exposed to mixture of environmental metals. Journal of Food Biochemistry, 42(5), e12573.
Dauwe, T., Janssens, E., Kempernaers, B., & Eens, M. (2004). The effect of heavy metal exposure on egg size, egg shell thickness and the number of spermatozoa in blue tit parus caeruleus eggs. Environmental Pollution, 129, 125–129.
Heymann, D., Reddington, M., & Kreutzberg, G. (1984). Sub-cellular localization of 5I-nucleotidase in rat brain. Journal of Neurochemistry, 43, 971–978.
Weisshaar, H. D., Prasad, M. C., & Parker, R. S. (1975). Estimation of lactate dehydrogenase in serum/plasma. Medicine Welt, 26, 387.
Misra, H., & Fridovich, I. (1989). The role of superoxide anion in the auto-oxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay of superoxide dismutase. Toxicology and Biological Chemistry, 2417, 3170.
Clairborne, A. (1995). Catalase activity. In A. Greewald (Ed.), Handbook of methods for oxygen radical research (pp. 237–242). Florida: CRC Press.
Habig, W., Pabst, M., & Jacoby, W. (1974). Glutathione S-transferases. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. Journal of Biochemistry, 249, 7130–7139.
Jollow, D., Mitchell, J., Zampaglione, N., & Gillette, J. (1974). Bromobenzene induced liver necrosis: Protective role of glutathione and evidence for 3,4 bromobenzene oxide as the hepatotoxic metabolite. Pharmacology, 11, 151–169.
Akintunde, J. K., Akintola, T. E., Adenuga, G. O., Odugbemi, Z. A., Adetoye, R. O., & Akintunde, O. G. (2020). Naringin attenuates Bisphenol-A mediated neurotoxicity in hypertensive rats by abrogation of cerebral nucleotide depletion, oxidative damage and neuroinflammation. Nuerotoxicology, 81, 18–33.
Guan, D. S., Chen, Y. J., & Ruan, G. D. (2001). Study on heavy metal concentrations and the impact of human activity on them in urban and suburb soils of Guangzhou. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Unversitatis Sunyatseni, 40(4), 93–101.
Yan, J., Ye, Z. X., Yan, Y., & Huang, X. P. (2008). Study on heavy metals distribution in atmospheric particulate matter on both sides of the Cheng-Ya Expressway. Sichuan Environment, 2(2), 19–21.
Christoforidis, A., & Stamatis, N. (2009). Heavy metal contamination in street dust and roadside soil along the major national road in Kavala’s region, Greece. Geodermadrology, 151, 257–263.
Geiss, O., Bianchi, I., & Barrero-Moreno, J. (2016). Lung-deposited surface area concentration measurements in selected occupational and non-occupational environments. Journal of Aerosol Science, 96, 24–37.
Badding, M. A., Fix, N. R., Antonini, J. M., & Leonard, S. S. (2014). A comparison of cytotoxicity and oxidative stress from welding fumes generated with a new nickel-, copper-based consumable versus mild and stainless steel-based welding in RAW 264.7 mouse macrophages. PLoS ONE, 9(6), e101310.
Young-Seoub, H., Ki-Hoon, S., & Jin-Yong, C. (2014). Health effects of chronic arsenic exposure. Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health, 47(5), 245–252.
Richter, P., Faroon, O., & Pappas, R. S. (2017). Cadmium and cadmium/zinc ratios and tobacco related morbidities. International Journal of Environmental Resources and Public Health, 29, 10–14.
Duffus, J. H. (2002). Heavy metals-a meaningless term? Pure and Applied Chemistry, 74(5), 793–807.
Terzano, C., Di Stefano, F., Conti, V., Graziani, E., & Petroianni, A. (2010). Air pollution ultrafine particles: Toxicity beyond the lung. European Review Medicine and Pharmacological Science, 14, 809–821.
Grahame, T. J. (2011). Distinguishing health effects among different PM 2.5 components in urban airborne particulate matter. Eds Fathi Z, 1, 575–597.
Lu, X., Zhu, Y., Bai, R., Li, S., & Teng, X. (2015). The effect of manganese-induced toxicity on the cytokine mRNA expression of chicken spleen lymphocytes in vitro. Resources and Veterinary Science, 101, 165–167.
Li, Q., Liu, H., Alattar, M., Jiang, S., Han, J., Ma, Y., et al. (2015). The preferential accumulation of heavy metals in different tissues following frequent respiratory exposure to PM2.5 in rats. Scientific Reports, 5(1), 1–12.
Valko, M., Morris, H., & Cronin, M. T. D. (2005). Metals, toxicity and oxidative stress. Current Medicine and Chemistry, 12(10), 1161–1208.
Patra, R. C., Rautray, A. K., & Swarup, D. (2011). Oxidative stress in lead and cadmium toxicity and its amelioration. Veterinary Medicine International, 2011, 457327.
Leonard, S. S., Harris, G. K., & Shi, X. (2002). Metal-induced oxidative stress and signal transduction. Free Radical Biological Medicine, 37(12), 1921–1942.
Wagner, C., Vargas, A. P., Roos, D. H., Morel, A. F., Farina, M., Nogueira, C. W., et al. (2010). Comparative study of quercetin and its two glycoside derivatives quercitrin and rutin against methylmercury (MeHg)-induced ROS production in rat brain slices. Archive Toxicology, 84, 89–97.
Carvalho, C. M., Lu, J., Zhang, X., Arner, E. S., & Holmgren, A. (2010). Effects of selenite and chelating agents on mammalian thioredoxin reductase inhibited by mercury: Implications for treatment of mercury poisoning. FASEB Journal, 25, 370–381.
Bechan, S., Shweta, S., & Nikhat, J. S. (2014). Biomedical implications of heavy metals induced imbalances in redox systems. Biomedical Resources International, 2014, 640754.
Arif, T. J., Mudsser, A., Kehkashan, S., Arif, A., Inho, C., Qazi, M., et al. (2015). Heavy metals and human health: Mechanistic insight into toxicity and counter defense system of antioxidants. International Journal of Molecular Science, 2015(16), 29592–29630.
Mohamed, N. A., Amna, A., & Ahmed, S. K. (2016). In vitro antioxidant activity and phytochemical screening of Croton zambesicus. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, 5(6), 12–16.
Ajayi, A. O., & Omomagiowawi, I. E. (2018). Antimicrobial activity of Croton zambesicus on Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus species. SYLWAN, 160, 10.
Akintunde, J. K. (2017). Functional oil from black seed differentially inhibits aldose-reductase and ectonucleotidase activities by up-regulating cellular energy in haloperidol-induced hepatic toxicity in rat liver. Journal of Oleo Science, 66(9), 1051–1060.
Aho, J., Helenius, M., Vattulainen-Collanus, S., Alastalo, T. P., & Koskenvuo, J. (2016). Extracellular ATP protects endothelial cells against DNA damage. Purinergic Signalling, 12, 575–581.
Takahashi-Sato, K., Murakawa, M., & Kimura, J. (2013). Loss of ectonucleotidases from the coronary vascular bed after ischemia-reperfusion in isolated rat heart. BMC Cardiovascular Disorder, 13, 53.
Burnstock, G. (2015). Blood cells: An historical account of the roles of purinergic signalling. Purinergic Signalling, 11(4), 411–434.
Akintunde, J. K., Akintola, T. E., Aliu, F. H., Fajoye, M. O., & Adimchi, S. O. (2020). Naringin regulates erectile dysfunction by abolition of apoptosis and inflammation through NOS/cGMP/PKG signalling pathway on exposure to Bisphenol-A in hypertensive rat model. Reproductive Toxicology, 95, 123–136.
Deepak, J., Raju, K. P., & Hari, K. (2013). Non-respiratory functions of the lung, continuing education in anaesthesia. Critical Care & Pain, 13(3), 98–102.
Sha, L., Hor-Yue, T., Ning, W., Zhang-Jin, Z., Lixing, L., Chi-Woon, W., et al. (2015). The role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in liver diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(11), 26087–26124.
Akintunde, J. K., & Oboh, G. (2016). Nephritic cell damage and antioxidant status in rats exposed to leachate from battery recycling industry. Interdisciplinary Toxicology, 9(1), 1–11.
Jadhav, S. H., Sarkar, S. N., Patil, R. D., & Tripathi, H. C. (2007). Effects of subchronic exposure via drinking water to a mixture of eight water-contaminating metals: A biochemical and histopathological study in male rats. Archive Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 53, 667–677.
Hwang, K. Y., Schwartz, B. S., Lee, B. K., Strickland, P. T., Todd, A. C., & Bressler, J. P. (2001). Associations of lead exposure and dose measures with erythrocyte protein kinase C activity in 212 current Korean lead workers. Toxicological Science, 62, 280–288.
Westerink, R. H., Klompmkers, A. A., Westenberg, H. G., & Vijverberg, H. P. (2002). Signaling pathways involved in Ca and Pb-induced vesicular catecholamine release from rat PC12 cells. Brain Research, 957, 25–36.
Ndhlala, A., Ncube, B., & Van Staden, J. (2014). Antioxidants versus reactive oxygen species: A tug of war for human benefits? In I. Laher (Ed.), Systems biology of free radicals and antioxidants (pp. 3987–4002). New York: Springer.
Bernard, A. (2008). Cadmium and its adverse effects on human health. Indian Journal of Medicine Resources, 128, 557–564.
Bhattacharyya, A., Chattopadhyay, R., Mitra, S., & Crowe, S. E. (2014). Oxidative stress: An essential factor in the pathogenesis of gastrointestinal mucosal diseases. Physiological Review, 94, 329–354.
Chen, J. R., Ko, J., Yeh, W. J., Huang, W. C., & Yang, H. Y. (2018). Renoprotective effects of Antroquinonol in rats with Nω-Nitro-l-Arginine methyl ester-induced hypertension. Nutrients, 10(10), E1521.
Akintunde, J. K., Oboh, G., & Akindahunsi, A. A. (2013). Testicular membrane lipid damage by complex mixture of leachate from municipal battery recycling site as indication of idiopathic male infertility in rat. Interdisciplinary Toxicology, 6(4), 192–197.
Akintunde, J. K. A., & J.B., Ebinama O.N, . (2020). Potential protective effects of naringin on oculo-pulmonary injury induced by PM 10 (wood smoke) exposure by modulation of oxidative damage and acetylcholine esterase activity in a rat mode. Current Therapeutic Research, 92, 1005861.
Fernández-Martínez, E., Jiménez-Santana, M., Centeno-Álvarez, M., Torres-Valencia, J. M., Shibayama, M., & Cariño-Cortés, R. (2017). Hepatoprotective effects of nonpolar extracts from inflorescences of thistles Cirsium vulgare and Cirsium ehrenbergii on acute liver damage in rat. Pharmacognosy Magazine, 13(4), S860–S867.
Akintunde, J. K., Akintola, T. E., Hammed, M. O., Amoo, C. O., Adegoke, A. M., & Ajisafe, L. O. (2020). Naringin protects against Bisphenol-A induced oculopathy as implication of cataract in hypertensive rat model. Biomedical Pharmacotherapy, 126, 110043.
Murni, N. S., Qamar, U. A., Siti, Z., Mat, S., Alhassan, M. A., & Suganya, M. (2017). Antioxidant and antidiabetic effects of flavonoids: A structure-activity relationship based study. Biomedical Research International, 2017, 8386065.
Priya, B., & Anil, K. S. (2013). Anti-cancer potential of flavonoids: Recent trends and future perspectives. Biotechnology, 3(6), 439–459.
Mahmoud, A. M., Hernández Bautista, R. J., Sandhu, M. A., & Hussein, O. E. (2019). Beneficial effects of citrus flavonoids on cardiovascular and metabolic health. Oxidative Medicine Cellular Longevity, 1, 1–19.
Riaz, M. A., Nisa, Z. U., & Anjum, M. S. (2020). Assessment of metals induced histopathological and gene expression changes in different organs of non-diabetic and diabetic rats. Science Reports, 10, 5897.
Reena, S., Neetu, G., Anurag, Mi., & Rajiv, G. (2011). Heavy metals and living systems: An overview. Indian Journal of Pharmacology, 43(3), 246–253.
Bell, M. L., Zanobetti, A., & Dominici, F. (2013). Evidence on vulnerability and susceptibility to health risks associated with short-term exposure to particulate matter: A systematic review and meta-analysis. American Journal Epidemiology, 178(6), 865–876.
Markiewicz-Górka, I., Januszewska, L., Michalak, A., Prokopowicz, A., Januszewska, E., Pawlas, N., et al. (2018). Effects of chronic exposure to lead, cadmium, and manganese mixtures on oxidative stress in rat liver and heart. Archive High Rada Toksikology, 66, 51–62.
Cope, G., & Hodgson, E. (2010). Classes of toxicants: Use classes. In E. Hodgson (Ed.), Modern Toxicology (4th ed., pp. 49–50). New Jersey: Wiley.
Carneiro, M. F. H., Oliveira-Souza, J. M., Grotto, D., Batista, B. L., De Oliveira Souza, V. C., & Barbosa, F. (2014). A systemic study of the deposition and metabolism of mercury species in mice after exposure to low levels of Thimerosal (ethylmercury). Environmental Research, 134, 218–227.
Jan, A., Azam, M., Siddiqui, K., Ali, A., Choi, I., & Haq, Q. (2015). Heavy metals and human health: Mechanistic insight into toxicity and counter defense system of antioxidants. International Journal of Molecular Science, 16(12), 29592–29630.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Vittorio Fineschi.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akintunde, J.K., Oyedibu, G.O., Olanipekun, N.J. et al. Modulation of Cardiopulmonary Toxicity and Oxidative Stress by Phenolic-Rich Fraction of Croton zambiscus Leaves in Rat Exposed to Chronic Mixture of Environmental Toxicants. Cardiovasc Toxicol 21, 272–285 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-020-09618-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-020-09618-x