Abstract
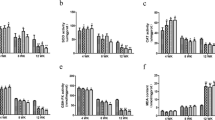
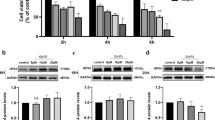
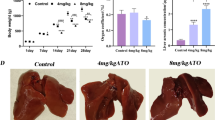
Copper (Cu) is one of the most significant trace elements in the body, but it is also a widespread environmental toxicant health. Ferroptosis is a newly identified programmed cell death, which involves various heavy metal–induced organ toxicity. Nevertheless, the role of ferroptosis in Cu-induced hepatotoxicity remains poorly understood. In this study, we found that 330 mg/kg Cu could disrupt the liver structure and cause characteristic morphological changes in mitochondria associated with ferroptosis. Additionally, Cu treatment increased MDA (malondialdehyde) and LPO (lipid peroxide) production while reducing GSH (reduced glutathione) content and GCL (glutamate cysteine ligase) activity. However, it is noticeable that there were no appreciable differences in liver iron content and key indicators of iron metabolism. Meanwhile, our further investigation found that 330 mg/kg Cu-exposure changed multiple ferroptosis-related indicators in chicken livers, including inhibition of the expression of SLC7A11, GPX4, FSP1, and COQ10B, whereas enhances the levels of ACLS4, LPCAT3, and LOXHD1. Furthermore, the changes in the expression of NCOA4, TXNIP, and Nrf2/Keap1 signaling pathway–related genes and proteins also further confirmed 330 mg/kg Cu exposure-induced ferroptosis. In conclusion, our results indicated that ferroptosis may play essential roles in Cu overload–induced liver damage, which offered new insights into the pathogenesis of Cu-induced hepatotoxicity.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Tsang T, Davis CI, Brady DC (2021) Copper biology. Curr Biol 31:R421–R427
Gao Y, Yang W, Che D, Adams S, Yang L (2020) Advances in the mechanism of high copper diets in restraining pigs growth. J Anim Physiol An N 104:667–678
Yang F, Liao J, Yu W, Qiao N, Guo J, Han Q, Li Y, Hu L, Pan J, Tang Z (2021) Exposure to copper induces mitochondria-mediated apoptosis by inhibiting mitophagy and the PINK1/parkin pathway in chicken (Gallus gallus) livers. J Hazard Mater 408:124888
Fagnano M, Agrelli D, Pascale A, Adamo P, Fiorentino N, Rocco C, Pepe O, Ventorino V (2020) Copper accumulation in agricultural soils: risks for the food chain and soil microbial populations. Sci Total Environ 734:139434
Li X, Zhang J, Gong Y, Liu Q, Yang S, Ma J, Zhao L, Hou H (2020) Status of copper accumulation in agricultural soils across China (1985-2016). Chemosphere 244:125516
Zhong G, He Y, Wan F, Wu S, Jiang X, Tang Z, Hu L (2021) Effects of long-term exposure to copper on the Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway and Msr-related redox status in the kidneys of rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 199:4205–4217
Cao P, Nie G, Luo J, Hu R, Li G, Hu G, Zhang C (2022) Cadmium and molybdenum co-induce pyroptosis and apoptosis via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT axis in the livers of Shaoxing ducks (Anas platyrhynchos). Food Funct 13:2142–2154
Michalopoulos GK, Bhushan B (2021) Liver regeneration: biological and pathological mechanisms and implications. Nat Rev Gastro Hepat 18:40–55
Linder MC (2020) Copper homeostasis in mammals, with emphasis on secretion and excretion. a review. Int J Mol Sci 21
Johncilla M, Mitchell KA (2011) Pathology of the liver in copper overload. Semin Liver Dis 31:239–244
Wang X, Wang H, Li J, Yang Z, Zhang J, Qin Z, Wang L, Kong X (2014) Evaluation of bioaccumulation and toxic effects of copper on hepatocellular structure in mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 159:312–319
Yang F, Pei R, Zhang Z, Liao J, Yu W, Qiao N, Han Q, Li Y, Hu L, Guo J, Pan J, Tang Z (2019) Copper induces oxidative stress and apoptosis through mitochondria-mediated pathway in chicken hepatocytes. Toxicol In Vitro 54:310–316
Yu W, Liao J, Yang F, Zhang H, Chang X, Yang Y, Bilal RM, Wei G, Liang W, Guo J, Tang Z (2021) Chronic tribasic copper chloride exposure induces rat liver damage by disrupting the mitophagy and apoptosis pathways. Ecotox Environ Safe 212:111968
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS, Morrison BR, Stockwell BR (2012) Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 149:1060–1072
Cepelak I, Dodig S, Dodig DC (2020) Ferroptosis: regulated cell death. Arh Hig Rada Toksiko 71:99–109
Tang D, Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G (2021) Ferroptosis: molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res 31:107–125
Xie Y, Hou W, Song X, Yu Y, Huang J, Sun X, Kang R, Tang D (2016) Ferroptosis: process and function. Cell Death Differ 23:369–379
Wei L, Zuo Z, Yang Z, Yin H, Yang Y, Fang J, Cui H, Du Z, Ouyang P, Chen X, Chen J, Geng Y, Zhu Y, Chen Z, Huang C, Wang F, Guo H (2022) Mitochondria damage and ferroptosis involved in Ni-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Toxicology 466:153068
Meng P, Zhang S, Jiang X, Cheng S, Zhang J, Cao X, Qin X, Zou Z, Chen C (2020) Arsenite induces testicular oxidative stress in vivo and in vitro leading to ferroptosis. Ecotox Environ Safe 194:110360
Xue Q, Yan D, Chen X, Li X, Kang R, Klionsky DJ, Kroemer G, Chen X, Tang D, Liu J (2023) Copper-dependent autophagic degradation of GPX4 drives ferroptosis. Autophagy 19:1982–1996
Yang F, Liao J, Pei R, Yu W, Han Q, Li Y, Guo J, Hu L, Pan J, Tang Z (2018) Autophagy attenuates copper-induced mitochondrial dysfunction by regulating oxidative stress in chicken hepatocytes. Chemosphere 204:36–43
Zhang C, Lin T, Nie G, Hu R, Pi S, Wei Z, Wang C, Li G, Hu G (2021) In vivo assessment of molybdenum and cadmium co-induce nephrotoxicity via causing calcium homeostasis disorder and autophagy in ducks (Anas platyrhyncha). Ecotox Environ Safe 230:113099
Wan F, Zhong G, Ning Z, Liao J, Yu W, Wang C, Han Q, Li Y, Pan J, Tang Z, Huang R, Hu L (2020) Long-term exposure to copper induces autophagy and apoptosis through oxidative stress in rat kidneys. Ecotox Environ Safe 190:110158
Dodson M, Castro-Portuguez R, Zhang DD (2019) NRF2 plays a critical role in mitigating lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. Redox Biol 23:101107
Liao J, Li Q, Hu Z, Yu W, Zhang K, Ma F, Han Q, Zhang H, Guo J, Hu L, Pan J, Li Y, Tang Z (2022) Mitochondrial miR-1285 regulates copper-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and mitophagy by impairing IDH2 in pig jejunal epithelial cells. J Hazard Mater 422:126899
Liu J, Kang R, Tang D (2021) Signaling pathways and defense mechanisms of ferroptosis. Febs J 289(22):7038–7050
Yan HF, Zou T, Tuo QZ, Xu S, Li H, Belaidi AA, Lei P (2021) Ferroptosis: mechanisms and links with diseases. Signal Transduct Tar 6:49
Chen X, Li J, Kang R, Klionsky DJ, Tang D (2021) Ferroptosis: machinery and regulation. Autophagy 17:2054–2081
Mu Y, Sun J, Li Z, Zhang W, Liu Z, Li C, Peng C, Cui G, Shao H, Du Z (2022) Activation of pyroptosis and ferroptosis is involved in the hepatotoxicity induced by polystyrene microplastics in mice. Chemosphere 291:132944
Xiao J, Zhang S, Tu B, Jiang X, Cheng S, Tang Q, Zhang J, Qin X, Wang B, Zou Z, Chen C (2021) Arsenite induces ferroptosis in the neuronal cells via activation of ferritinophagy. Food Chem Toxicol 151:112114
Bradley BD, Graber G, Condon RJ, Frobish LT (1983) Effects of graded levels of dietary copper on copper and iron concentrations in swine tissues. J Anim Sci 56:625–630
Stevenson MH, Jackson N (1980) Effects of level of dietary copper sulphate and period of feeding on the laying, domestic fowl, with special reference to tissue mineral content. Brit J Nutr 43:205–215
Theil EC, Calvert KT (1978) The effect of copper excess on iron metabolism in sheep. Biochem J 170:137–143
Fosset C, Danzeisen R, Gambling L, McGaw BA, McArdle HJ (2009) Cu loading alters expression of non-IRE regulated, but not IRE regulated, Fe dependent proteins in HepG2 cells. J Inorg Biochem 103:709–716
Jiang L, Garrick MD, Garrick LM, Zhao L, Collins JF (2013) Divalent metal transporter 1 (Dmt1) mediates copper transport in the duodenum of iron-deficient rats and when overexpressed in iron-deprived HEK-293 cells. J Nutr 143:1927–1933
Lane DJ, Merlot AM, Huang ML, Bae DH, Jansson PJ, Sahni S, Kalinowski DS, Richardson DR (2015) Cellular iron uptake, trafficking and metabolism: key molecules and mechanisms and their roles in disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1853:1130–1144
Stockwell BR et al (2017) Ferroptosis: a regulated cell death nexus linking metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell 171:273–285
Qiu Y, Cao Y, Cao W, Jia Y, Lu N (2020) The application of ferroptosis in diseases. Pharmacol Res 159:104919
Sachdev PK, Freeland-Graves J, Beretvas SN, Sanjeevi N (2018) Zinc, copper, and iron in oral submucous fibrosis: a meta-analysis. Int J Dent 2018:3472087
Ursini F, Maiorino M (2020) Lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis: the role of GSH and GPx4. Free Radical Bio Med 152:175–185
Liu Z, Lv X, Yang B, Qin Q, Song E, Song Y (2021) Tetrachlorobenzoquinone exposure triggers ferroptosis contributing to its neurotoxicity. Chemosphere 264:128413
Zhao L, Feng Y, Xu ZJ, Zhang NY, Zhang WP, Zuo G, Khalil MM, Sun LH (2021) Selenium mitigated aflatoxin B1-induced cardiotoxicity with potential regulation of 4 selenoproteins and ferroptosis signaling in chicks. Food Chem Toxicol 154:112320
Li J, Cao F, Yin HL, Huang ZJ, Lin ZT, Mao N, Sun B, Wang G (2020) Ferroptosis: past, present and future. Cell Death Dis 11:88
Bellezza I, Giambanco I, Minelli A, Donato R (2018) Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in oxidative and reductive stress. Bba-Mol Cell Res 1865:721–733
Fang Y, Xing C, Wang X, Cao H, Zhang C, Guo X, Zhuang Y, Hu R, Hu G, Yang F (2021) Activation of the ROS/HO-1/NQO1 signaling pathway contributes to the copper-induced oxidative stress and autophagy in duck renal tubular epithelial cells. Sci Total Environ 757:143753
Kerins MJ, Ooi A (2018) The roles of NRF2 in modulating cellular iron homeostasis. Antioxid Redox Sign 29:1756–1773
Yumnamcha T, Devi TS, Singh LP (2019) Auranofin mediates mitochondrial dysregulation and inflammatory cell death in human retinal pigment epithelial cells: implications of retinal neurodegenerative diseases. Front Neurosci-Switz 13:1065
Lu J, Zhao Y, Liu M, Lu J, Guan S (2021) Toward improved human health: Nrf2 plays a critical role in regulating ferroptosis. Food Funct 12:9583–9606
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 32072930 and 31572585).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Gaolong Zhong; methodology: Gaolong Zhong, Jianzhao Liao, and Feiyang Ma; formal analysis and investigation: Gaolong Zhong, Yuanxu Li, Feiyang Ma, and Yihui Huo; writing—original draft preparation: Gaolong Zhong; writing—review and editing: Qingyue Han and Lianmei Hu; funding acquisition: Zhaoxin Tang; resources: Zhaoxin Tang; supervision: Zhaoxin Tang.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The procedures of animal experiments were authorized and performed by the Ethics Committee of South China Agricultural University (Permit Number: 2017A087).
Consent for Publication
All the authors have consented for publication of this research.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, G., Li, Y., Ma, F. et al. Copper Exposure Induced Chicken Hepatotoxicity: Involvement of Ferroptosis Mediated by Lipid Peroxidation, Ferritinophagy, and Inhibition of FSP1-CoQ10 and Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4 Axis. Biol Trace Elem Res 202, 1711–1721 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-023-03773-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-023-03773-2