Abstract
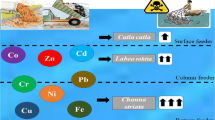
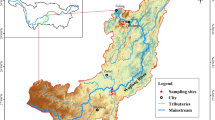
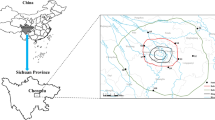
In order to assess the bioaccumulation and health risk of metals in a river reservoir, concentrations of copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd), arsenic (As), and mercury (Hg) in the water, sediments, two small-sized fish, and a freshwater mussel from the Zhoubai reservoir were examined. The results indicated that all of these metals conform with class one of environmental quality standards for surface water (State Environmental Protection Administration of China, GB 3838–2002). There were no significant differences for total metal concentrations in sediment between the three sampling sites (p > 0.05), but the bioavailable concentrations in S3 were the lowest. The Cd was dominated with exchangeable fraction and showed considerable risk. All metal concentrations except for Pb in Rhodeus sinensis were significantly higher than those in Ctenogobius giurinus (p < 0.05). The metal concentrations in Cristaria plicata showed a similar pattern of bioavailable metals in sediment, indicating that the metal concentrations in aquatic organisms were determined by the bioavailable forms of metals. Negative correlations were observed between the size of fish and concentrations of Cu, Zn, Pb, Cd, and As. However, significant positive correlations were found between the size of mussel and concentrations of Cd (p < 0.01), As (p < 0.05), and Hg (p < 0.01). Zn had the highest BCF values in fish and mussel. The aquatic organisms showed lower ability of metal bioaccumulation from the sediment. Low values of target hazard quotient (THQ), hazard index (HI), and carcinogenic risk (CR) indicated that these metals do not pose a health risk to public through fish and mussel consumption in this study area.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Sheikhzadeh H, Hamidian AH (2021) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in fish species of Iran: a review. Environ Geochem Hlth 43(10):3749–3869. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-00883-5
Hanfi MY, Mostafa MYA, Zhukovsky MV (2020) Heavy metal contamination in urban surface sediments: sources, distribution, contamination control, and remediation. Environ Monit Assess 192(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7947-5
Varol M, Karakaya G, Sünbül MR (2021) Spatiotemporal variations, health risks, pollution status and possible sources of dissolved trace metal(loid)s in the Karasu River, Turkey. Environ Res 202:111733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111733
Canpolat Ö, Varol M, Okan ÖÖ, Eriş KK, Çağlar M (2020) A comparison of trace element concentrations in surface and deep water of the Keban Dam Lake (Turkey) and associated health risk assessment. Environ Res 190:110012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.110012
Du Laing G, Rinklebe J, Vandecasteele B, Meers E, Tack FMG (2009) Trace metal behaviour in estuarine and riverine floodplain soils and sediments: a review. Sci Total Environ 407(13):3972–3985. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.07.025
Varol M, Ustaoğlu F, Tokatlı C (2022) Ecological risks and controlling factors of trace elements in sediments of dam lakes in the Black Sea Region (Turkey). Environ Res 205:112478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112478
Varol M, Canpolat Ö, Eriş KK, Çağlar M (2020) Trace metals in core sediments from a deep lake in eastern Turkey: Vertical concentration profiles, eco-environmental risks and possible sources. Ecotox Environ Safe 189:110060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110060
Nemati K, Bakar NKA, Abas MR, Sobhanzadeh E (2011) Speciation of heavy metals by modified BCR sequential extraction procedure in different depths of sediments from Sungai Buloh, Selangor. Malaysia J Hazard Mater 192(1):402–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.05.039
Xu L, Wang T, Wang J, Lu A (2017) Occurrence, speciation and transportation of heavy metals in 9 coastal rivers from watershed of Laizhou Bay, China. Chemosphere 173:61–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.01.046
Varol M (2011) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. J Hazard Mater 195:355–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.08.051
Lei P, Zhang H, Shan B, Lv S, Tang W (2016) Heavy metals in estuarine surface sediments of the Hai River Basin, variation characteristics, chemical speciation and ecological risk. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(8):7869–7879. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6059-9
Nemati K, Bakar NKA, Abas MR (2009) Investigation of heavy metals mobility in shrimp aquaculture sludge—Comparison of two sequential extraction procedures. Microchem J 91(2):227–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2008.12.001
Kumar M, Gupta N, Ratn A, Awasthi Y, Prasad R, Trivedi A, Trivedi SP (2020) Biomonitoring of heavy metals in River Ganga water, sediments, plant, and fishes of different trophic levels. Biol Trace Elem Res 193(2):536–547. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01736-0
Chua EM, Flint N, Wilson SP, Vink S (2018) Potential for biomonitoring metals and metalloids using fish condition and tissue analysis in an agricultural and coal mining region. Chemosphere 202:598–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.080
Varol M, Sünbül MR (2018) Biomonitoring of trace metals in the Keban Dam Reservoir (Turkey) Using mussels (Unio elongatulus eucirrus) and crayfish (Astacus leptodactylus). Biol Trace Elem Res 185(1):216–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1238-1
Jia Y, Wang L, Qu Z, Wang C, Yang Z (2017) Effects on heavy metal accumulation in freshwater fishes: species, tissues, and sizes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(10):9379–9386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8606-4
Jiang X, Wang J, Pan B, Li D, Wang Y, Liu X (2022) Assessment of heavy metal accumulation in freshwater fish of Dongting Lake, China: Effects of feeding habits, habitat preferences and body size. J Environ Sci 112:355–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2021.05.004
Lin Z, Xu XY, Xie MW, Chen R, Tan QG (2021) Measuring metal uptake and loss in individual organisms: A novel double stable isotope method and its application in explaining body size effects on cadmium concentration in mussels. Environ Sci Technol 55(14):9979–9988. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c01582
Merciai R, Guasch H, Kumar A, Sabater S, Garcia-Berthou E (2014) Trace metal concentration and fish size: Variation among fish species in a Mediterranean river. Ecotox Environ Safe 107:154–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.05.006
Saavedra Y, González A, Fernández P, Blanco J (2004) The effect of size on trace metal levels in raft cultivated mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis). Sci Total Environ 318(1):115–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(03)00402-9
Danabaş D, Kutluyer F, Ural M, Özçelik M, Kocabaş M (2022) Age- and sex-specific bioaccumulation of selected metals in freshwater mussel (Unio elangatulus eucirrus Bourguignat, 1860) populating from Keban dam lake (Elazig, Turkey). B Environ Contam Tox 108(2):366–371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03414-1
Balzani P, Kouba A, Tricarico E, Kourantidou M, Haubrock PJ (2022) Metal accumulation in relation to size and body condition in an all-alien species community. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(17):25848–25857. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17621-0
Yi YJ, Zhang SH (2012) Heavy metal (Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Pb, Zn) concentrations in seven fish species in relation to fish size and location along the Yangtze River. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19(9):3989–3996. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-0840-1
Varol M, Sünbül MR (2020) Macroelements and toxic trace elements in muscle and liver of fish species from the largest three reservoirs in Turkey and human risk assessment based on the worst-case scenarios. Environ Res 184:109298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109298
Olmedo P, Pla A, Hernández AF, Barbier F, Ayouni L, Gil F (2013) Determination of toxic elements (mercury, cadmium, lead, tin and arsenic) in fish and shellfish samples. Risk assessment for the consumers. Environ Int 59:63–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2013.05.005
Cai SW, Zhou SQ, Cheng JW, Wang QH, Dai Y (2021) Distribution, bioavailability and ecological risk of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Wujiang River Basin, southwest of China. Pol J Environ Stud 30(6):5479–5491. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/136185
Cai SW, Ni ZH, Liu B, Fan LL (2017) Metal concentrations and health risk assessment in the muscle of ten commercial fish species from the Chishui River. China Int J Environ Res 11(2):125–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-017-0013-7
Håkanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control.a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14(8):975–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
Yi Y, Yang Z, Zhang S (2011) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in fishes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River basin. Environ Pollut 159(10):2575–2585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.06.011
Bi B, Liu X, Guo X, Lu S (2018) Occurrence and risk assessment of heavy metals in water, sediment, and fish from Dongting Lake. China Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(34):34076–34090. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3329-8
Li R, Tang C, Li X, Jiang T, Shi Y, Cao Y (2019) Reconstructing the historical pollution levels and ecological risks over the past sixty years in sediments of the Beijiang River, South China. Sci Total Environ 649:448–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.283
Voigt CL, da Silva CP, Doria HB, Randi MAF, de Oliveira Ribeiro CA, de Campos SX (2015) Bioconcentration and bioaccumulation of metal in freshwater Neotropical fish Geophagus brasiliensis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(11):8242–8252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3967-4
Djikanović V, Skorić S, Spasić S, Naunovic Z, Lenhardt M (2018) Ecological risk assessment for different macrophytes and fish species in reservoirs using biota-sediment accumulation factors as a useful tool. Environ Pollut 241:1167–1174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.06.054
USEPA (2021) Risk-based concentration table. Washington, DC: United States Environmental Protection Agency. https://www.epa.gov/risk/regional-screening-levels-rsls-generic-tables. Accessed 20 Aug 2021
Buchet JP, Lison D, Ruggeri M, Foa V, Elia G, Maugeri S (1996) Assessment of exposure to inorganic arsenic, a human carcinogen, due to the consumption of seafood. Arch Toxicol 70(11):773–778. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050339
Brondi M, Dall’aglio M, Ghiara E, Gragnani R (1986) Analysis of trace elements in natural waters. Chem Ecol 2(4):289–299. https://doi.org/10.1080/02757548608080734
Gao Q, Li Y, Cheng Q, Yu M, Hu B, Wang Z, Yu Z (2016) Analysis and assessment of the nutrients, biochemical indexes and heavy metals in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China, from 2008 to 2013. Water Res 92:262–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.12.055
Lin L, Li C, Yang W, Zhao L, Liu M, Li Q, Crittenden JC (2020) Spatial variations and periodic changes in heavy metals in surface water and sediments of the Three Gorges Reservoir. China. Chemosphere 240:124837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124837
Gao L, Gao B, Xu D, Peng W, Lu J (2019) Multiple assessments of trace metals in sediments and their response to the water level fluctuation in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci Total Environ 648:197–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.112
Meng B, Feng XB, Qiu GL, Li ZG, Yao H, Shang LH, Yan HY (2016) The impacts of organic matter on the distribution and methylation of mercury in a hydroelectric reservoir in Wujiang river, southwest China. Environ Toxicol Chem 35(1):191–199. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.3181
Jiang H, Feng X, Li G, Qiu G, Yan H (2007) Seasonal distribution of total mercury and methylmercury in sediments of the Wujiangdu Reservoir, Guizhou, China. Chin J Geochem 26(4):414–417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-007-0414-y
Canpolat Ö, Varol M, Okan ÖÖ, Eriş KK (2022) Sediment contamination by trace elements and the associated ecological and health risk assessment: a case study from a large reservoir (Turkey). Environ Res 204:112145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112145
Lee P-K, Kang M-J, Yu S, Ko K-S, Ha K, Shin S-C, Park JH (2017) Enrichment and geochemical mobility of heavy metals in bottom sediment of the Hoedong reservoir, Korea and their source apportionment. Chemosphere 184:74–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.05.124
Baran A, Tarnawski M, Koniarz T (2016) Spatial distribution of trace elements and ecotoxicity of bottom sediments in Rybnik reservoir. Silesian-Poland Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(17):17255–17268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6678-1
Hiller E, Jurkovič Ľ, Šutriepka M (2010) Metals in the surface sediments of selected water reservoirs. Slovakia B Environ Contam Tox 84(5):635–640. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-010-0008-y
Wu Q, Zhou H, Tam NFY, Tian Y, Tan Y, Zhou S, Li Q, Chen Y, Leung JYS (2016) Contamination, toxicity and speciation of heavy metals in an industrialized urban river: Implications for the dispersal of heavy metals. Mar Pollut Bull 104(1):153–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.01.043
Saleem M, Iqbal J, Akhter G, Shah MH (2018) Fractionation, bioavailability, contamination and environmental risk of heavy metals in the sediments from a freshwater reservoir, Pakistan. J Geochem Explor 184:199–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2017.11.002
Ma X, Zuo H, Tian M, Zhang L, Meng J, Zhou X, Min N, Chang X, Liu Y (2016) Assessment of heavy metals contamination in sediments from three adjacent regions of the Yellow River using metal chemical fractions and multivariate analysis techniques. Chemosphere 144:264–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.08.026
Cai SW, Zhou SQ, Cheng JW, Wang QH, Dai Y (2022) Heavy metals speciation and distribution of microbial communities in sediments from the abandoned Mo-Ni polymetallic mines, southwest of China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(23):35350–35364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18697-y
Lin S, Liu X, Zhang Z, Zhang Q (2022) Speciation characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments from Caohai Lake, Guizhou Province. Stoch Env Res Risk A 36(11):3929–3944. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-022-02236-9
Kang MX, Tian YM, Peng S, Wang MQ (2019) Effect of dissolved oxygen and nutrient levels on heavy metal contents and fractions in river surface sediments. Sci Total Environ 648:861–870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.201
Xu D, Wang Y, Zhang R, Guo J, Zhang W, Yu K (2016) Distribution, speciation, environmental risk, and source identification of heavy metals in surface sediments from the karst aquatic environment of the Lijiang River. Southwest China Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(9):9122–9133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6147-x
Sundaray SK, Nayak BB, Lin S, Bhatta D (2011) Geochemical speciation and risk assessment of heavy metals in the river estuarine sediments—a case study: Mahanadi basin. India J Hazard Mater 186(2):1837–1846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.12.081
Yang Z, Wang Y, Shen Z, Niu J, Tang Z (2009) Distribution and speciation of heavy metals in sediments from the mainstream, tributaries, and lakes of the Yangtze River catchment of Wuhan. China J Hazard Mater 166(2):1186–1194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.12.034
Reichard M, Liu HZ, Smith C (2007) The co-evolutionary relationship between bitterling fishes and freshwater mussels: insights from interspecific comparisons. Evol Ecol Res 9(2):239–259 (https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228780113)
Andres S, Ribeyre F, Tourencq JN, Boudou A (2000) Interspecific comparison of cadmium and zinc contamination in the organs of four fish species along a polymetallic pollution gradient (Lot River, France). Sci Total Environ 248(1):11–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(99)00477-5
Ali H, Khan E (2018) Assessment of potentially toxic heavy metals and health risk in water, sediments, and different fish species of River Kabul. Pakistan Hum Ecol Risk Assess 24(8):2101–2118. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1438175
Canli M, Atli G (2003) The relationships between heavy metal (Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Pb, Zn) levels and the size of six Mediterranean fish species. Environ Pollut 121(1):129–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(02)00194-X
Obaidat MM, Massadeh AM, Al-Athamneh AM, Jaradat QM (2015) Heavy metals in fish from the Red Sea, Arabian Sea, and Indian Ocean: effect of origin, fish species and size and correlation among the metals. Environ Monit Assess 187(4):218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4463-0
Barone G, Giacominelli-Stuffler R, Storelli MM (2013) Comparative study on trace metal accumulation in the liver of two fish species (Torpedinidae): Concentration–size relationship. Ecotox Environ Safe 97:73–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.07.004
Suhareva N, Aigars J, Poikane R, Jansons M (2020) Development of fish age normalization technique for pollution assessment of marine ecosystem, based on concentrations of mercury, copper, and zinc in dorsal muscles of fish. Environ Monit Assess 192(5):279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08261-x
Verdouw JJ, Macleod CK, Nowak BF, Lyle JM (2011) Implications of age, size and region on mercury contamination in estuarine fish species. Water Air Soil Poll 214(1):297–306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0424-y
Liu X, Jiang J, Yan Y, Dai Y, Deng B, Ding S, Su S, Sun W, Li Z, Gan Z (2018) Distribution and risk assessment of metals in water, sediments, and wild fish from Jinjiang River in Chengdu, China. Chemosphere 196:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.135
Harangi S, Baranyai E, Fehér M, Tóth CN, Herman P, Stündl L, Fábián I, Tóthmérész B, Simon E (2017) Accumulation of metals in juvenile carp (Cyprinus carpio) exposed to sublethal levels of iron and manganese: Survival, body weight and tissue. Biol Trace Elem Res 177(1):187–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0854-5
Lipy EP, Hakim M, Mohanta LC, Islam D, Lyzu C, Roy DC, Jahan I, Akhter S, Raknuzzaman M, Abu Sayed M (2021) Assessment of heavy metal concentration in water, sediment and common fish species of Dhaleshwari River in Bangladesh and their health implications. Biol Trace Elem Res 199(11):4295–4307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02552-7
La Colla NS, Botté SE, Simonetti P, Negrin VL, Serra AV, Marcovecchio JE (2021) Water, sediments and fishes: First multi compartment assessment of metal pollution in a coastal environment from the SW Atlantic. Chemosphere 282:131131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131131
Storelli MM (2008) Potential human health risks from metals (Hg, Cd, and Pb) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) via seafood consumption: estimation of target hazard quotients (THQs) and toxic equivalents (TEQs). Food Chem Toxicol 46(8):2782–2788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2008.05.011
Varol M, Kaçar E, Sünbül MR (2022) Toxic and essential elements in selected fish species from the Tigris River (Turkey) and assessment of their health risks and benefits. J Food Compos Anal 113:104708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2022.104708
Varol M, Kaçar E, Sünbül MR, Md Towfiqul Islam AR (2022) Levels of metals and elements in tissues of fish species in the Kızılırmak River (Turkey) and assessment of health risks and nutritional benefits. Environ Res 214:113791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113791
Varol M, Kaçar E, Sünbül MR, Towfiqul Islam ARM (2022) Species, tissue and gender-related metal and element accumulation in fish species in a large reservoir (Turkey) and health risks and nutritional benefits for consumers. Environ Toxicol Phar 94:103929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2022.103929
Mei Z, Cheng P, Wang K, Wei Q, Barlow J, Wang D (2020) A first step for the Yangtze. Science 367(6484):1314. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abb5537
Zhao L, Guo Y, Meng B, Yao H, Feng X (2017) Effects of damming on the distribution and methylation of mercury in Wujiang River, Southwest China. Chemosphere 185:780–788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.07.077
Funding
This work was supported by the Education Department of Guizhou Province (No. QJJ [2022]067), and the talent base for environmental protection and mountain agricultural in Chishui River Basin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shenwen Cai organized this study, conducted the study design, and drafted the manuscript. Ziwei Shen assisted in sample tests, data analysis and edited the manuscript. The sampling and experiments were performed by Qinghe Wang, Junwei Cheng, and Xiong Yan. Boping Zeng contributed to the study design. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. No experiment was conducted with alive fish samples in this study. Only caught fish and mussel by local fishermen were used.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, S., Shen, Z., Wang, Q. et al. Bioaccumulation and Health Risk Assessment of Metals in Small-Sized Fish (Rhodeus sinensis, Ctenogobius giurinus) and Mussel (Cristaria plicata) from a River Reservoir, Southwest China. Biol Trace Elem Res 201, 5401–5414 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-023-03590-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-023-03590-7