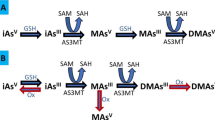
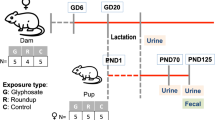
Abstract
Co-contamination of arsenic (As) and fluoride (F) is widely distributed in groundwater, which are known risk factors for the nephrotoxicity. Emerging evidence has linked environmentally associated nephrotoxicity with the disturbance of gut microbiota and blood metabolites. In this study, we generated gut microbiota and blood metabolomic profile and identified multiple serum metabolites and gut bacteria species, which were associated with kidney injury on rat model exposed to As and F alone or combined. Combined As and F exposure significantly increased creatinine level. Abnormal autophagosomes and lysosome were observed, and the autophagic genes were enhanced in kidney tissue after single and combined As and F exposure. The metabolome data showed that single and combined As and F exposure remarkably altered the serum metabolites associated with the proximal tubule reabsorption function pathway, with glutamine and alpha-ketoglutarate level decreased in all exposed group. Furthermore, phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), the key contributor of autophagosomes, was decreased significantly in As and F + As exposed groups during the screen of autophagy-animal pathway. Multiple altered gut bacterial microbiota at phylum and species levels post As and F exposure were associated with targeted kidney injury, including p_Bacteroidetes, s_Chromohalobacter_unclassified, s_Halomonas_unclassified, s_Ignatzschineria_unclassified, s_Bacillus_subtilis, and s_Brevundimonas_sp._NA6. Meanwhile, our analysis indicated that As and F co-exposure possessed an interactive influence on gut microbiota. In conclusion, single or combined As and F exposure leads to the disruption of serum metabolic and gut microbiota profiles. Multiple metabolites and bacterial species are identified and associated with nephrotoxicity, which have potential to be developed as biomarkers of As and/or F-induced kidney damage.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data available on request from the authors. The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, [niuruiyan2000@163.com], upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- As:
-
Arsenic
- F:
-
Fluoride
- PE:
-
Phosphatidylethanolamine
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
References
Pi K, Wang Y, Xie X, Su C, Ma T, Li J, Liu Y (2015) Hydrogeochemistry of co-occurring geogenic arsenic, fluoride and iodine in groundwater at Datong Basin, northern China. J Hazard Mater 300:652–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.07.080
Rahaman MS, Rahman MM, Mise N, Sikder MT, Ichihara G, Uddin MK, Kurasaki M, Ichihara S (2021) Environmental arsenic exposure and its contribution to human diseases, toxicity mechanism and management. Environ Pollut 289:117940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117940
Nagendra AH, Bose B, Shenoy PS (2021) Recent advances in cellular effects of fluoride: an update on its signalling pathway and targeted therapeutic approaches. Mol Biol Rep 48(7):5661–5673. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06523-6
Levin-Schwartz Y, Politis M, Gennings C, Tamayo-Ortiz M, Flores D, Amarasiriwardena C, Pantic I, Tolentino M, Estrada-Gutierrez G, Lamadrid-Figueroa H, Tellez-Rojo M, Baccarelli A, Wright R, Sanders A (2021) Nephrotoxic metal mixtures and preadolescent kidney function. Children (Basel) 8(8):673. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8080673
Khan KM, Chakraborty R, Bundschuh J, Bhattacharya P, Parvez F (2020) Health effects of arsenic exposure in Latin America: an overview of the past eight years of research. Sci Total Environ 710:136071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136071
Dharmaratne RW (2019) Exploring the role of excess fluoride in chronic kidney disease: a review. Hum Exp Toxicol 38(3):269–279. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327118814161
Lu K, Abo RP, Schlieper KA, Graffam ME, Levine S, Wishnok JS, Swenberg JA, Tannenbaum SR, Fox JG (2014) Arsenic exposure perturbs the gut microbiome and its metabolic profile in mice: an integrated metagenomics and metabolomics analysis. Environ Health Perspect 122(3):284–291. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1307429
Xue J, Lai Y, Chi L, Tu P, Leng J, Liu CW, Ru H, Lu K (2019) Serum metabolomics reveals that gut microbiome perturbation mediates metabolic disruption induced by arsenic exposure in mice. J Proteome Res 18(3):1006–1018. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00697
Coryell M, McAlpine M, Pinkham NV, McDermott TR, Walk ST (2018) The gut microbiome is required for full protection against acute arsenic toxicity in mouse models. Nat Commun 9(1):5424. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07803-9
Wang HW, Miao CY, Liu J, Zhang Y, Zhu SQ, Zhou BH (2020) Fluoride-induced rectal barrier damage and microflora disorder in mice. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27(7):7596–7607. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07201-8
Liu J, Wang HW, Lin L, Miao CY, Zhang Y, Zhou BH (2019) Intestinal barrier damage involved in intestinal microflora changes in fluoride-induced mice. Chemosphere 234:409–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.06.080
Yan X, Chen X, Tian X, Qiu Y, Wang J, Yu G, Dong N, Feng J, Xie J, Nalesnik M, Niu R, Xiao B, Song G, Quinones S, Ren X (2021) Co-exposure to inorganic arsenic and fluoride prominently disrupts gut microbiota equilibrium and induces adverse cardiovascular effects in offspring rats. Sci Total Environ 767:144924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144924
Qiu Y, Chen X, Yan X, Wang J, Yu G, Ma W, Xiao B, Quinones S, Tian X, Ren X (2020) Gut microbiota perturbations and neurodevelopmental impacts in offspring rats concurrently exposure to inorganic arsenic and fluoride. Environ Int 140:105763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105763
Knauf F, Brewer JR, Flavell RA (2019) Immunity, microbiota and kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 15(5):263–274. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41581-019-0118-7
Meijers B, Evenepoel P, Anders HJ (2019) Intestinal microbiome and fitness in kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 15(9):531–545. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41581-019-0172-1
Ticinesi A, Milani C, Guerra A, Allegri F, Lauretani F, Nouvenne A, Mancabelli L, Lugli GA, Turroni F, Duranti S, Mangifesta M, Viappiani A, Ferrario C, Dodi R, Dall’Asta M, Del Rio D, Ventura M, Meschi T (2018) Understanding the gut-kidney axis in nephrolithiasis: an analysis of the gut microbiota composition and functionality of stone formers. Gut 67(12):2097–2106. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2017-315734
Margiotta E, Caldiroli L, Callegari ML, Miragoli F, Zanoni F, Armelloni S, Rizzo V, Messa P, Vettoretti S (2021) Association of sarcopenia and gut microbiota composition in older patients with advanced chronic kidney disease, investigation of the interactions with uremic toxins, inflammation and oxidative stress. Toxins (Basel) 13(7):472. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13070472
Wang X, Yang S, Li S, Zhao L, Hao Y, Qin J, Zhang L, Zhang C, Bian W, Zuo L, Gao X, Zhu B, Lei XG, Gu Z, Cui W, Xu X, Li Z, Zhu B, Li Y, Chen S, Guo H, Zhang H, Sun J, Zhang M, Hui Y, Zhang X, Liu X, Sun B, Wang L, Qiu Q, Zhang Y, Li X, Liu W, Xue R, Wu H, Shao D, Li J, Zhou Y, Li S, Yang R, Pedersen OB, Yu Z, Ehrlich SD, Ren F (2020) Aberrant gut microbiota alters host metabolome and impacts renal failure in humans and rodents. Gut 69(12):2131–2142. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319766
Huang Y, Zhou J, Wang S, Xiong J, Chen Y, Liu Y, Xiao T, Li Y, He T, Li Y, Bi X, Yang K, Han W, Qiao Y, Yu Y, Zhao J (2020) Indoxyl sulfate induces intestinal barrier injury through IRF1-DRP1 axis-mediated mitophagy impairment. Theranostics 10(16):7384–7400. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.45455
Bundschuh J, Farias B, Martin R, Storniolo A, Bhattacharya P, Cortes J, Bonorino G, Albouy R (2004) Groundwater arsenic in the Chaco-Pampean Plain, Argentina: case study from Robles county, Santiago del Estero Province. Appl Geochem19(2):231–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2003.09.009
Sivasankar V, Darchen A, Omine K, Sakthivel R (2016) Fluoride: a world ubiquitous compound, its chemistry, and ways of contamination. In: Surface Modified Carbons as Scavengers for Fluoride from Water pp 5–32. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-40686-2_2
Tian X, Feng J, Dong N, Lyu Y, Wei C, Li B, Ma Y, Xie J, Qiu Y, Song G, Ren X, Yan X (2019) Subchronic exposure to arsenite and fluoride from gestation to puberty induces oxidative stress and disrupts ultrastructure in the kidneys of rat offspring. Sci Total Environ 686:1229–1237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.409
Calzada E, Onguka O, Claypool SM (2016) Phosphatidylethanolamine metabolism in health and disease. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 321:29–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.ircmb.2015.10.001
Rajapakse S, Shivanthan MC, Selvarajah M (2016) Chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology in Sri Lanka. Int J Occup Environ Health 22(3):259–264. https://doi.org/10.1080/10773525.2016.1203097
Chouhan S, Flora SJ (2010) Arsenic and fluoride: two major ground water pollutants. Indian J Exp Biol 48(7):666–678
Tian X, Xie J, Chen X, Dong N, Feng J, Gao Y, Tian F, Zhang W, Qiu Y, Niu R, Ren X, Yan X (2020) Deregulation of autophagy is involved in nephrotoxicity of arsenite and fluoride exposure during gestation to puberty in rat offspring. Arch Toxicol 94(3):749–760. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02651-y
Wu M, Lao YZ, Tan HS, Lu G, Ren Y, Zheng ZQ, Yi J, Fu WW, Shen HM, Xu HX (2019) Oblongifolin C suppresses lysosomal function independently of TFEB nuclear translocation. Acta Pharmacol Sin 40(7):929–937. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-018-0167-7
Boya P, Reggiori F, Codogno P (2013) Emerging regulation and functions of autophagy. Nat Cell Biol 15(7):713–720. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2788
Zhang X, Wei M, Fan J, Yan W, Zha X, Song H, Wan R, Yin Y, Wang W (2021) Ischemia-induced upregulation of autophagy preludes dysfunctional lysosomal storage and associated synaptic impairments in neurons. Autophagy 17(6):1519–1542. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2020.1840796
Liu P, Xue Y, Zheng B, Liang Y, Zhang J, Shi J, Chu X, Han X, Chu L (2020) Crocetin attenuates the oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosisin arsenic trioxide-induced nephrotoxic rats: Implication of PI3K/AKT pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 88:106959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106959
Li H, Fan J, Zhao Y, Yang J, Xu H, Manthari RK, Cheng X, Wang J, Wang J (2021) Calcium alleviates fluoride-induced kidney damage via FAS/FASL, TNFR/TNF, DR5/TRAIL pathways in rats. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 226:112851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112851
Zhan F, Wang X, Zhang J, Yi S, He P (2022) Glutamine alleviates the renal dysfunction associated with gentamicin-induced acute kidney injury in Sprague-Dawley rats. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 69(1):323–329. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.2111
Guo L, Chen S, Ou L, Li S, Ye ZN, Liu HF (2022) Disrupted alpha-ketoglutarate homeostasis: understanding kidney diseases from the view of metabolism and beyond. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 15:1961–1974. https://doi.org/10.2147/dmso.s369090
Gatica D, Chiong M, Lavandero S, Klionsky DJ (2015) Molecular mechanisms of autophagy in the cardiovascular system. Circ Res 116(3):456–467. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.114.303788
Zhao Y, Li Y, Wang J, Manthari RK, Wang J (2018) Fluoride induces apoptosis and autophagy through the IL-17 signaling pathway in mice hepatocytes. Arch Toxicol 92(11):3277–3289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-018-2305-x
Patel D, Witt SN (2017) Ethanolamine and phosphatidylethanolamine: partners in health and disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017:4829180. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4829180
Runwal G, Stamatakou E, Siddiqi FH, Puri C, Zhu Y, Rubinsztein DC (2019) LC3-positive structures are prominent in autophagy-deficient cells. Sci Rep 9(1):10147. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-46657-z
Guan ZZ, Xiao KQ, Zeng XY, Long YG, Cheng YH, Jiang SF, Wang YN (2000) Changed cellular membrane lipid composition and lipid peroxidation of kidney in rats with chronic fluorosis. Arch Toxicol 74(10):602–608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040000177
Wang YN, Xiao KQ, Liu JL, Dallner G, Guan ZZ (2000) Effect of long term fluoride exposure on lipid composition in rat liver. Toxicology 146(2–3):161–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0300-483x(00)00167-0
Li Y, Liu Y, Yi J, Li Y, Yang B, Shang P, Mehmood K, Bilal RM, Zhang H, Chang YF, Tang Z, Wang Y, Li Y (2021) The potential risks of chronic fluoride exposure on nephrotoxic via altering glucolipid metabolism and activating autophagy and apoptosis in ducks. Toxicology 461:152906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2021.152906
Kim C, Ashrap P, Watkins DJ, Mukherjee B, Rosario-Pabón ZY, Vélez-Vega CM, Alshawabkeh AN, Cordero JF, Meeker JD (2021) Maternal metals/metalloid blood levels are associated with lipidomic profiles among pregnant women in Puerto Rico. Front Public Health 9:754706. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2021.754706
Du X, Zhang J, Zhang X, Schramm KW, Nan B, Huang Q, Tian M, Shen H (2021) Persistence and reversibility of arsenic-induced gut microbiome and metabolome shifts in male rats after 30-days recovery duration. Sci Total Environ 776:145972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145972
Kahrstrom CT, Pariente N, Weiss U (2016) Intestinal microbiota in health and disease. Nature 535(7610):47
Colombo I, Aiello-Battan F, Elena R, Ruiz A, Petraglia L, Musso CG (2021) Kidney-gut crosstalk in renal disease. Ir J Med Sci 190(3):1205–1212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-020-02437-7
Sun N, Zhu B, Xin J, Li L, Gan B, Cao X, Fang J, Pan K, Jing B, Zeng Y, Lv C, Zhao L, Zeng D, Xu P, Wang H, Ni X (2022) Psychoactive effects of Lactobacillus johnsonii BS15 on preventing memory dysfunction induced by acute ethanol exposure through modulating intestinal microenvironment and improving alcohol metabolic level. Front Microbiol 13:847468. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.847468
Fu R, Niu R, Zhao F, Wang J, Cao Q, Yu Y, Liu C, Zhang D, Sun Z (2022) Exercise alleviated intestinal damage and microbial disturbances in mice exposed to fluoride. Chemosphere 288(Pt 3):132658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132658
Niu S, Zhu X, Zhang J, Ma Y, Lang X, Luo L, Li W, Zhao Y, Zhang Z (2022) Arsenic trioxide modulates the composition and metabolic function of the gut microbiota in a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol 111:109159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109159
Chen F, Luo Y, Li C, Wang J, Chen L, Zhong X, Zhang B, Zhu Q, Zou R, Guo X, Zhou Y, Guo L (2021) Sub-chronic low-dose arsenic in rice exposure induces gut microbiome perturbations in mice. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 227:112934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112934
Zhao M, Chen C, Yuan Z, Li W, Zhang M, Cui N, Duan Y, Zhang X, Zhang P (2021) Dietary Bacillus subtilis supplementation alleviates alcohol-induced liver injury by maintaining intestinal integrity and gut microbiota homeostasis in mice. Exp Ther Med 22(5):1312. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2021.10747
Liu Y, Yin F, Huang L, Teng H, Shen T, Qin H (2021) Long-term and continuous administration of Bacillus subtilis during remission effectively maintains the remission of inflammatory bowel disease by protecting intestinal integrity, regulating epithelial proliferation, and reshaping microbial structure and function. Food Funct 12(5):2201–2210. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0fo02786c
Choi J, Kwon H, Kim YK, Han PL (2022) Extracellular vesicles from gram-positive and gram-negative probiotics remediate stress-induced depressive behavior in mice. Mol Neurobiol 59(5):2715–2728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-021-02655-9
Wang R, Lin F, Ye C, Aihemaitijiang S, Halimulati M, Huang X, Jiang Z, Li L, Zhang Z (2023) Multi-omics analysis reveals therapeutic effects of Bacillus subtilis-fermented Astragalus membranaceus in hyperuricemia via modulation of gut microbiota. Food Chem 399:133993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133993
Chan KC, Kok KE, Huang KF, Weng YL, Chung YC (2020) Effects of fermented red bean extract on nephropathy in streptozocin-induced diabetic rats. Food Nutr Res 64:4272. https://doi.org/10.29219/fnr.v64.4272
Zhu A, Yang X, Bai L, Hou Y, Guo C, Zhao D, Wen M, Jiang P, Liu Y, Huang Y, Li C, Meng H (2020) Analysis of microbial changes in the tonsillar formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue of Chinese patients with IgA nephropathy. Pathol Res Pract 216(11):153174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2020.153174
Ryan MP, Pembroke JT (2018) Brevundimonas spp: Emerging global opportunistic pathogens. Virulence 9(1):480–493. https://doi.org/10.1080/21505594.2017.1419116
Paramasivam V, Paez A, Verma A, Landry D, Braden GL (2021) Brevundimonas vesicularis peritonitis in a chronic peritoneal dialysis patient. Case Rep Nephrol Dial 11(3):314–320. https://doi.org/10.1159/000517140
Mondal P, Chattopadhyay A (2020) Environmental exposure of arsenic and fluoride and their combined toxicity: A recent update. J Appl Toxicol 40(5):552–566. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.3931
Flora SJ, Mittal M, Mishra D (2009) Co-exposure to arsenic and fluoride on oxidative stress, glutathione linked enzymes, biogenic amines and DNA damage in mouse brain. J Neurol Sci 285(1–2):198–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2009.07.001
Ma Y, Ma Z, Yin S, Yan X, Wang J (2017) Arsenic and fluoride induce apoptosis, inflammation and oxidative stress in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Chemosphere 167:454–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.10.025
Ma Y, Niu R, Sun Z, Wang J, Luo G, Zhang J, Wang J (2012) Inflammatory responses induced by fluoride and arsenic at toxic concentration in rabbit aorta. Arch Toxicol 86(6):849–856. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-012-0803-9
Flora SJ, Pachauri V, Mittal M, Kumar D (2011) Interactive effect of arsenic and fluoride on cardio-respiratory disorders in male rats: possible role of reactive oxygen species. Biometals 24(4):615–628. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-011-9412-y
Liu P, Li R, Tian X, Zhao Y, Li M, Wang M, Ying X, Yuan J, Xie J, Yan X, Lyu Y, Wei C, Qiu Y, Tian F, Zhao Q, Yan X (2021) Co-exposure to fluoride and arsenic disrupts intestinal flora balance and induces testicular autophagy in offspring rats. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 222:112506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112506
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82173644) and the Shanxi Graduate Education Innovation Program (2020BY051).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiaolin Tian: Writing-original draft, writing-review and editing, conceptualization, formal analysis, data curation. Xiaoyan Yan: conceptualization, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition. Xushen Chen: data curation. Penghui Liu: validation, formal analysis. Zilong Sun: conceptualization, supervision. Ruiyan Niu: writing-review and editing, conceptualization, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, X., Yan, X., Chen, X. et al. Identifying Serum Metabolites and Gut Bacterial Species Associated with Nephrotoxicity Caused by Arsenic and Fluoride Exposure. Biol Trace Elem Res 201, 4870–4881 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-023-03568-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-023-03568-5