Abstract
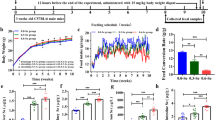
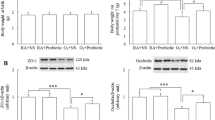
Exposure to hypobaric hypoxia at high altitude will cause different tissue and organ damage over a long period of time. Studies have shown that hypobaric hypoxia can cause severe primary intestinal barrier dysfunction, and then cause multiple organ dysfunction. Our previous research showed that selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) synthesized by Lactobacillus casei ATCC 393 (L. casei ATCC 393) can effectively alleviate intestinal barrier dysfunction caused by oxidative stress and inflammation in mice. This study was conducted to investigate the protective effect of biological SeNPs synthesized by L. casei ATCC 393 on intestinal barrier function in acute hypobaric hypoxic stress mice. The results showed that compared with the hypobaric hypoxic, the SeNPs synthesized by L. casei ATCC 393 by oral administration could effectively alleviate the shortening of intestinal villi, which decreased the level of diamine oxidase (DAO) and myeloperoxidase (MPO), and the expression level of tight junction protein in ileum was increased. In addition, SeNPs significantly increased the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), cyclooxygenase (COX-1) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and decreased the level of malondialdehyde (MDA), and inhibit the increase of hypoxia related factor. SeNPs effectively regulate the intestinal microecology disorder caused by hypobaric hypoxia stress, and maintain the intestinal microecology balance. In addition, oral administration of SeNPs had better protective effect on intestinal barrier function of mice under hypobaric hypoxia stress. These results suggested that SeNPs synthesized by L. casei ATCC 393 can effectively alleviate the damage of intestinal barrier function under acute hypobaric hypoxic stress, which may be closely related to the antioxidant activity of SeNPs.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data are available from the corresponding author.
References
Wu WM, Zhang FX, Zhang P (2010) Influence of plateau hypoxia on the tissue injury and expression of HIF-la and iNOS in intestinal mucosa of rats. Med J Chin PLA 35:592–594
Koury J, Deitch EA, Homma H, Abungu B, Gangurde P, Condon MR, Lu Q, Xu DZ, Feinman R (2004) Persistent HIF-Iα activation in gut is chemia/reperfusion injury: potential role of bacteria and lipopolysaccharide. Shock 22(3):270–277
Fairweather-Tait SJ, Bao Y, Broadley MR, Collings R, Ford D, Hesketh JE, Hurst R (2011) Selenium in human health and disease. Antioxid Redox Sign 14(7):1337–1383
Taylor CT, Colgan SP (2007) Hypoxia and gastrointestinal disease. J Mol Med (Berl) 85(12):1295–1300
Colgan SP, Taylor CT (2010) Hypoxia: an alarm signal during intestinal inflammation. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 7(5):281–287
Shah YM (2016) The role of hypoxia in intestinal inflammation. Mol Cell Pediatr 3(1):1
Rivera-Chávez F, Lopez CA, Bäumler AJ (2017) Oxygen as a driver of gut dysbiosis. Free Radic Biol Med 105:93–101
Glover LE, Colgan SP (2011) Hypoxia and metabolic factors that influence inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis. Gastroenterol 140(6):1748–1755
Schindele S, Pouokam E, Diener M (2016) Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Effects on Ion Transport across Rat Colonic Epithelium. Front Physiol 7:247
McElroy GS, Chandel NS (2017) Mitochondria control acute and chronic responses to hypoxia. Exp Cell Res 356(2):217–222
Zheng L, Kelly CJ, Colgan SP (2015) Physiologic hypoxia and oxygen homeostasis in the healthy intestine. A Review in the Theme: Cellular Responses to Hypoxia. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 309(6):C350–C360
Luan F, Li M, Han K, Ma Q, Wang J, Qiu Y, Yu L, He X, Liu D, Lv H (2019) Phenylethanoid glycosides of Phlomis younghusbandii Mukerjee ameliorate acute hypobaric hypoxia-induced brain impairment in rats. MolImmunol 108(4):81–88
Fukudome I, Kobayashi M, Dabanaka K, Maeda H, Okamoto K, Okabayashi T, Baba R, Kumagai N, Oba K, Fujita M, Hanazaki K (2014) Diamine oxidase as a marker of intestinal mucosal inj ury and the effect of soluble dietary fiber on gastrointestinal tract toxicity after intravenous 5-fluorouracil treatment in rats. Med Mol Morphol 47(2):100–107
Crapser J, Ritzel R, Verma R, Venna VR, Liu F, Chauhan A, Koellhoffer E, Patel A, Ricker A, Maas K, Graf J, McCullough LD (2016) Ischemic stroke induces gut permeability and enhances bacterial translocation leading to sepsis in aged mice. Aging(Albany NY) 8(5):1049–1060
Karhausen J, Ibla JC, Colgan SP (2003) Implications of hypoxia on mucosal barrier function. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 49(1):77–87
Rayman MP (2000) The importance ofselenium to human health. The Lancet 356(9225):233–241
Cardoso BR, Cominetti C, Seale LA (2022) Editorial: Selenium, Human Health and Chronic Disease. Front Nutr 8:827759
Nozari S, Mohammadzadeh M, Faridvand Y, Tockmechi A, Movassaghpour A, Abdolalizadeh J (2016) The Study of Extracellular Protein Fractions of Probiotic Candidate Bacteria on Cancerous Cell Line. Arch Iran Med 19(11):779–785
Lu J, Holmgren A (2014) The thioredoxin antioxidant system. Free Radical Bio Med 66(8):75–87
Hawkes WC, Alkan Z (2010) Regulation ofredox signaling by Selenoproteins. Biol Trace Elem Res 134(3):235–251
Hosnedlova B, Kepinska M, Skalickova S, Fernandez C, Ruttkay-Nedecky B, Peng Q, Baron M, Melcova M, Opatrilova R, Zidkova J, Bjørklund G, Sochor J, Kizek R (2018) Nano-selenium and its nanomedicine applications: a critical review. Int J Nanomedicine 13:2107–2128
Skalickova S, Milosavljevic V, Cihalova K, Horky P, Richtera L, Adam V (2017) Selenium nanoparticles as a nutritional supplement. Nutr 33:83–90
Dkhil MA, Zrieq R, Al-Quraishy S, Abdel Moneim AE (2016) Selenium Nanoparticles Attenuate Oxidative Stress and Tesficular Damage in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Mol 21(11):1517
Xu C, Qiao L, Guo Y, Ma L, Cheng Y (2018) Preparation, characteristics and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides and proteins-capped selenium nanoparticles synthesized by Lactobacillus casei ATCC 393. Carbohydr Polym 195:576–585
Xu C, Guo Y, Qiao L, Ma L, Cheng Y, Roman A (2018) Biogenic Synthesis of Novel Functionalized Selenium Nanoparticles by Lactobacillus casei ATCC 393 and Its Protective Effects on Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction Caused by Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88. Front Microbiol 9:1129
Barhwal K, Hota SK, Jain V, Prasad D, Singh SB, Ilavazhagan G (2009) Acetyl-1-carnitine (ALCAR) prevents hypobaric hypoxia-induced spatial memory impairment through extracellular related kinase-mediated nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 phosphorylation. Neuro-sci 161(2):501–514
Vaishnavi C (2013) Translocation of gut flora and its role in sepsis. Indian J Med Microbiol 31(4):334–342
Madara JL (2005) Intestinal absorptive cell tight junctions are linked to cytoskeleton. Am J Physiol 253(1):C171–C175
Doklandy K, Zuhl MN, Moseley PL (2016) Intestinal epithelial barrier function and tight junction proteins with heat and exercise. J Appl Physiol 120(6):692–701
González-Mariscal L, Miranda J, Raya-Sandino A, Domínguez-Calderón A, Cuellar-Perez F (2017) ZO-2, a tight junction protein involved in gene expression, proliferation, apoptosis, and cell size regulation. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1397(1):35–53
Barbara G, Barbaro MR, Fuschi D, Palombo M, Falangone F, Cremon C, Marasco G, Stanghellini V (2021) Inflammatory and Microbiota-Related Regulation of the Intestinal Epithelial Barrier. Front Nutr 8:718356
Vaziri ND, Yuan J, Norris K (2013) Role of urea in intestinal barrier dysfunction and disruption of epithelial tightjunction in chronic kidney disease. Am J Nephrol 37(1):1–6
Sánchez de Medina F, Romero-Calvo I, Mascaraque C, Martínez-Augustin O (2014) Intestinal inflammation and mucosal barrier function. Inflamm Bowel Dis 20(12):2394–2404
Palamidi I, Mountzouris KC (2018) Diet supplementation with an organic acids-based formulation affects gut microbiota and expression of gut barrier genes in broilers. Anim Nutr 4:367–377
Gong Y, Li H, Li Y (2016) Effects of Bacillus subtilis on epithelial tight junctions of mice with inflammatory bowel disease. J Interferon Cytokine Res 36(2):75–85
Glover LE, Colgan SP (2017) Epithelial Barrier Regulation by Hypoxia-Inducible Factor. Ann Am Thorac Soc 14(3):S233–S236
Furuta GT, Turner JR, Taylor CT, Hershberg RM, Comerford K, Narravula S, Podolsky DK, Colgan SP (2001) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-dependent induction of intestinal trefoil factor protects barrier function during hypoxia. J Exp Med 193(9):1027–1034
Glover LE, Lee JS, Colgan SP (2016) Oxygen metabolism and barrier regulation in the intestinal mucosa. J Clin Invest 126(10):3680–3688
Rios-Arce ND, Collins FL, Schepper JD, Steury MD, Raehtz S, Mallin H, Schoenherr DT, Parameswaran N, McCabe LR (2017) Epithelial Barrier Function in Gut-Bone Signaling. Adv Exp Med Biol 1033:151–183
Tanida S, Mizoshita T, Mizushima T, Sasaki M, Shimura T, Kamiya T, Kataoka H, Joh T (2011) Involvement of Oxidative Stress and Mucosal Addressin Cell Adhesion Molecule-1(MADCAM-1) in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Clin Biochem Nutr 48(2):112–116
Alteheld B, Evans ME, Gu LH, Ganapathy V, Leibach FH, Jones DP, Ziegler TR (2005) Alanylglutamine Dipeptide and Growth Hormone Maintain Peptl-Mediated Transport in Oxidatively Stressed Caco-2 Cells. J Nutr 135(1):19–26
Zhang F, Wu W, Deng Z, Zheng X, Zhang J, Deng S, Chen J, Ma Q, Wang Y, Yu X, Kang S, Wang X (2015) High altitude increases the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α and inducible nitric oxide synthase with intest-inal mucosal barrier failure in rats. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8(5):5189–5195
Zhang F, Deng Z, Li W, Zheng X, Zhang J, Deng S, Chen J, Ma Q, Wang Y, Yu X, Wang X (2015) Activation of autophagy in rats with plateau stress-induced intestinal failure. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8(2):1816–1821
Xu C, Sun R, Qiao X, Xu C, Shang X, Niu W, Chao Y (2014) Effect of vitamin e supplementation on intestinal barrier function in rats exposed to high altitude hypoxia environment. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 18(4):313–320
Luo H, Guo P, Zhou Q (2012) Role of TLR4/NF-κB in damage to intestinal mucosa barrier function and bacterial translocation in rats exposed to hypoxia. PLoS ONE 7(10):e46291
Karl JP, Berryman CE, Young AJ, Radcliffe PN, Branck TA, Pantoja-Feliciano IG, Rood JC, Pasiakos SM (2018) Associations between the gut microbiota and host responses to high altitude. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 315(6):G1003–G1015
Singh M, Thomas P, Shukla D, Tulsawani R, Saxena S, Bansal A (2013) Effect of subchronic hypobaric hypoxia on oxidative stress in rat heart. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 169(8):2405–2419
Zhou QQ, Yang DZ, Luo YJ, Li SZ, Liu FY, Wang GS (2011) Over-starvation aggravates intestinal injury and promotes bacterial and endotoxin translocation under high-altitude hypoxic environment. World J Gastroenterol 17(12):1584–1593
Xu CL, Sun R, Qiao XJ, Xu CC, Shang XY, Niu WN (2014) Protective effect of glutamine on intestinal injury and bacterial community in rats exposed to hypobaric hypoxia environment. World J Gastroenterol 20(16):4662–4674
Safa S, Moghaddam G, Jozani RJ, Daghigh Kia H, Janmohammadi H (2016) Effect of vitamin E and selenium nanoparticles on post-thaw variables and oxidative status of rooster semen. Anim Reprod Sci 174:100–106
Huang B, Zhang J, Hou J, Chen C (2003) Free radical scavenging efficiency of Nano-Se in vitro. Free Radic Biol Med 35(7):805–813
Chen W, Li Y, Yang S, Yue L, Jiang Q, Xia W (2015) Synthesis and antioxidant properties of chitosan and carboxymethyl chitosan-stabilized selenium nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym 132:574–581
Ullah A, Yin X, Wang F, Xu B, Mirani ZA, Xu B, Chan MWH, Ali A, Usman M, Ali N, Naveed M (2021) Biosynthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles (via Bacillus subtilis BSN313), and Their Isolation, Characterization, and Bioactivities. Mol 26(18):5559
Qiu Y, Chen X, Chen Z, Zeng X, Yue T, Yuan Y (2022) Effects of Selenium Nanoparticles on Preventing Patulin-Induced Liver. Kidney Gastrointest Damage Foods 11(5):749
Chen Y, Qiao L, Song X, Ma L, Dou X, Xu C (2021) Protective Effects of Selenium Nanoparticle-Enriched Lactococcus lactis NZ9000 against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88-Induced Intestinal Barrier Damage in Mice. Appl Environ Microbiol 87(23):e0163621
Qiao L, Zhang X, Pi S, Chang J, Dou X, Yan S, Song X, Chen Y, Zeng X, Zhu L, Xu C (2022) Dietary supplementation with biogenic selenium nanoparticles alleviate oxidative stress-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction. NPJ Sci Food 6(1):30
Sarathchandra SU, watkinson JH (1981) Oxidation of elemental selenium to selenite by Bacillus megaterium. Science 211(4482):600–601
Shoeibi S, Mashreghi M (2016) Biosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles using Enterococcus faecalis and evaluation of their antibacterial activities. J Trace Elem Med Biol 39:135–139
Soliman MM, Aldhahrani A, Althobaiti F, Ahmed MM, Sayed S, Alotaibi S, Shukry M, El-Shehawi AM (2022) Characterization of the Impacts of Living at High Altitude in Taif: Oxidative Stress Biomarker Alterations and Immunohistochemical Changes. Curr Issues Mol Biol 44(4):1610–1625
Jiang P, Mizushima N (2014) Autophagy and human diseases. Cell Res 1:69–79
Šket R, Treichel N, Debevec T, Eiken O, Mekjavic I, Schloter M, Vital M, Chandler J, Tiedje JM, Murovec B, Prevoršek Z, Stres B (2017) Hypoxia and Inactivity Related Physiological Changes (Constipation, Inflammation) Are Not Reflected at the Level of Gut Metabolites and Butyrate Producing Microbial Community: The PlanHab Study. Front Physiol 8:250
Kleessen B, Schroedl W, Stueck M, Richter A, Rieck O, Krueger M (2005) Microbial and immunological responses relative to high-altitude exposure in mountaineers. Med Sci Sports Exerc 37(8):1313–1318
Wu Z, Pan D, Jiang M, Sang L, Chang B (2021) Selenium-Enriched Lactobacillus acidophilus Ameliorates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Chronic Colitis in Mice by Regulating Inflammatory Cytokines and Intestinal Microbiota. Front Med (Lausanne) 8:716816
Funding
This study received the following funding sources and grant support: National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 32072746), and the Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi Province (No. 2021NY-004), and the Innovation Foundation for Doctor Dissertation of Northwestern Polytechnical University (No. CX2021029), and the Innovation Foundation for Doctor Dissertation of Northwestern Polytechnical University (No. CX2022062).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Chunlan Xu, Xina Dou, and Baohua Zhang contributed to the study conception and design. Xina Dou, Baohua Zhang, and Lei Qiao collected and analyzed the data. Jiajing Chang, Xiaofan Song, and Xinyi Zhang provided technical support. Xina Dou and Shanyao Pi drafted the manuscript. Chunlan Xu, Xiaofan Song, Xiaonan Zeng, and Lixu Zhu critically revised the manuscript to its final version. All authors contributed critically to the drafts and gave final approval for submission. Chunlan Xu is the guarantor.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dou, X., Zhang, B., Qiao, L. et al. Biogenic Selenium Nanoparticles Synthesized by Lactobacillus casei ATCC 393 Alleviate Acute Hypobaric Hypoxia-Induced Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction in C57BL/6 Mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 201, 4484–4496 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03513-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03513-y