Abstract
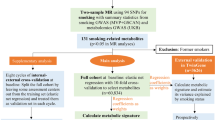
Previous research has investigated the association between individual metal exposure and overweight/obesity (OW/OB). However, there is limited data about metal mixture exposure and OW/OB. This study aimed to explore the individual and joint effects of 21 metals on OW/OB and its metabolic phenotypes. A total of 4042 participants were enrolled in our study, and 51.0% of them were overweight/obese. We quantified 21 metal levels in the urine sample. OW/OB was defined as BMI ≥ 24 kg/m2, while the metabolic phenotypes, including metabolic unhealthy overweight/obesity (MUOW/OB) and metabolic health overweight/obesity (MHOW/OB), were determined by BMI and metabolic state. We used logistic regression to analyze the effect of individual metal exposure on OW/OB and its metabolic phenotypes. Quantile g-computation was applied to evaluate the joint effect of metal exposure on OW/OB and its metabolic phenotypes. In logistic regression, zinc (Zn) was positively associated with OW/OB, with the odds ratio (OR) in the highest quartiles of 2.19 (95% confidence interval (CI), 1.74, 2.77; P trend < 0.001), while arsenic (As) and cadmium (Cd) were negatively associated with OW/OB (OR = 0.70 (0.56, 0.87) and 0.61 (0.48, 0.78), respectively). After adjustment for age, gender, education, cigarette smoking, alcohol drinking, physical activity, meat intake, and vegetable intake, Zn was positively associated with MUOW/OB, while As, Cd, nickel (Ni), and strontium (Sr) were negatively associated with MUOW/OB (all P trend < 0.05). Quantile g-computation showed a significantly negative association between metal mixture exposure and MUOW/OB. Our study suggested that metal mixture exposure might be negatively associated with OW/OB, particularly with MUOW/OB. Zn, As and Cd contributed most to the effect of the mixture. More prospective studies are warranted to confirm these findings and reveal the underlying mechanisms.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Pan XF, Wang L, Pan A (2021) Epidemiology and determinants of obesity in China. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 9(6):373–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00045-0
Ding WQ, Yan YK, Zhang MX, Cheng H, Zhao XY, Hou DQ, Mi J (2015) Hypertension outcomes in metabolically unhealthy normal-weight and metabolically healthy obese children and adolescents. J Hum Hypertens 29(9):548–554. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2014.124
Bragg F, Tang K, Guo Y, Iona A, Du H, Holmes MV, Bian Z, Kartsonaki C, Chen Y, Yang L, Sun Q, Dong C, Chen J, Collins R, Peto R, Li L, Chen Z (2018) Associations of general and central adiposity with incident diabetes in Chinese men and women. Diabetes Care 41(3):494–502. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc17-1852
Chen Z, Iona A, Parish S, Chen Y, Guo Y, Bragg F, Yang L, Bian Z, Holmes MV, Lewington S, Lacey B, Gao R, Liu F, Zhang Z, Chen J, Walters RG, Collins R, Clarke R, Peto R, Li L (2018) Adiposity and risk of ischaemic and haemorrhagic stroke in 0·5 million Chinese men and women: a prospective cohort study. Lancet Glob Health 6(6):e630–e640. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2214-109X(18)30216-X
Pang Y, Holmes MV, Kartsonaki C, Guo Y, Yang L, Bian Z, Chen Y, Bragg F, Iona A, Millwood IY, Chen J, Li L, Chen Z (2017) Young adulthood and adulthood adiposity in relation to incidence of pancreatic cancer: a prospective study of 0.5 million Chinese adults and a meta-analysis. J Epidemiol Community Health 71(11):1059–1067. https://doi.org/10.1136/jech-2017-208895
Pang Y, Kartsonaki C, Guo Y, Chen Y, Yang L, Bian Z, Bragg F, Millwood IY, Mao E, Li Y, Shi L, Chen J, Li L, Holmes MV, Chen Z (2018) Adiposity and risks of colorectal and small intestine cancer in Chinese adults: a prospective study of 0.5 million people. Br J Cancer 119(2):248–250. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-018-0124-8
Arnlöv J, Ingelsson E, Sundström J, Lind L (2010) Impact of body mass index and the metabolic syndrome on the risk of cardiovascular disease and death in middle-aged men. Circulation 121(2):230–236. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.887521
Phillips CM (2013) Metabolically healthy obesity: definitions, determinants and clinical implications. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 14(3):219–227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11154-013-9252-x
Iacobini C, Pugliese G, Blasetti FC, Federici M, Menini S (2019) Metabolically healthy versus metabolically unhealthy obesity. Metabolism 92:51–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2018.11.009
Qi Q, Li Y, Chomistek AK, Kang JH, Curhan GC, Pasquale LR, Willett WC, Rimm EB, Hu FB, Qi L (2012) Television watching, leisure time physical activity, and the genetic predisposition in relation to body mass index in women and men. Circulation 126(15):1821–1827. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.098061
Tinkov AA, Filippini T, Ajsuvakova OP, Aaseth J, Gluhcheva YG, Ivanova JM, Bjørklund G, Skalnaya MG, Gatiatulina ER, Popova EV, Nemereshina ON, Vinceti M, Skalny AV (2017) The role of cadmium in obesity and diabetes. Sci Total Environ 601–602:741–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.224
Scinicariello F, Buser MC, Mevissen M, Portier CJ (2013) Blood lead level association with lower body weight in NHANES 1999–2006. Toxicol Appl Pharm 273(3):516–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2013.09.022
Rothenberg SE, Korrick SA, Fayad R (2015) The influence of obesity on blood mercury levels for U.S. non-pregnant adults and children: NHANES 2007–2010. Environ Res 138:173–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2015.01.018
Grashow R, Zhang J, Fang SC, Weisskopf MG, Christiani DC, Kile ML, Cavallari JM (2014) Inverse association between toenail arsenic and body mass index in a population of welders. Environ Res 131:131–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2014.03.010
Park JS, Ha KH, He K, Kim DJ (2017) Association between blood mercury level and visceral adiposity in adults. Diabetes Metab J 41(2):113–120. https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.2.113
Padilla MA, Elobeid M, Ruden DM, Allison DB (2010) An examination of the association of selected toxic metals with total and central obesity indices: NHANES 99–02. Int J Environ Res Public Health 7(9):3332–3347. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7093332
Bulka CM, Persky VW, Daviglus ML, Durazo-Arvizu RA, Argos M (2019) Multiple metal exposures and metabolic syndrome: a cross-sectional analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011–2014. Environ Res 168:397–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2018.10.022
Ngu YJ, Skalny AV, Tinkov AA, Tsai CS, Chang CC, Chuang YK, Nikolenko VN, Zotkin DA, Chiu CF, Chang JS (2022) Association between essential and non-essential metals, body composition, and metabolic syndrome in adults. Biol Trace Elem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-03077-3
Shahid M, Natasha DC, Niazi NK, Xiong TT, Farooq A, Khalid S (2021) Ecotoxicology of heavy metal(loid)-enriched particulate matter: foliar accumulation by plants and health impacts. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 253:65–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/398_2019_38
Carrico C, Gennings C, Wheeler DC, Factor-Litvak P (2015) Characterization of weighted quantile sum regression for highly correlated data in a risk analysis setting. J Agric Biol Environ Stat 20(1):100–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13253-014-0180-3
Keil AP, Buckley JP, O’Brien KM, Ferguson KK, Zhao S, White AJ (2020) a quantile-based g-computation approach to addressing the effects of exposure mixtures. Environ Health Perspect 128(4):47004. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP5838
Bobb JF, Valeri L, Claus HB, Christiani DC, Wright RO, Mazumdar M, Godleski JJ, Coull BA (2015) Bayesian kernel machine regression for estimating the health effects of multi-pollutant mixtures. Biostatistics 16(3):493–508. https://doi.org/10.1093/biostatistics/kxu058
Lazarevic N, Barnett AG, Sly PD, Knibbs LD (2019) Statistical methodology in studies of prenatal exposure to mixtures of endocrine-disrupting chemicals: a review of existing approaches and new alternatives. Environ Health Perspect 127(2):26001. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP2207
Zhou BF (2002) Predictive values of body mass index and waist circumference for risk factors of certain related diseases in Chinese adults–study on optimal cut-off points of body mass index and waist circumference in Chinese adults. Biomed Environ Sci 15(1):83–96
Alberti KG, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA, Fruchart JC, James WP, Loria CM, Smith SJ (2009) Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 120(16):1640–1645. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.192644
Wang X, Mukherjee B, Park SK (2018) Associations of cumulative exposure to heavy metal mixtures with obesity and its comorbidities among U.S. adults in NHANES 2003–2014. Environ Int 121(Pt 1):683–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.09.035
Zhong Q, Qin QR, Yang WJ, He JL, Zhu JL, Zhu ZY, Huang F (2021) Multiple metal exposure and obesity: a prospective cohort study of adults living along the Yangtze River. China Environ Pollut 285:117150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117150
Duc HN, Oh H, Kim MS (2021) The effect of mixture of heavy metals on obesity in individuals ≥50 years of age. Biol Trace Elem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02972-z
Ainsworth BE, Haskell WL, Herrmann SD, Meckes N, Bassett DJ, Tudor-Locke C, Greer JL, Vezina J, Whitt-Glover MC, Leon AS (2011) 2011 compendium of physical activities: a second update of codes and MET values. Med Sci Sports Exerc 43(8):1575–1581. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e31821ece12
Su CT, Lin HC, Choy CS, Huang YK, Huang SR, Hsueh YM (2012) The relationship between obesity, insulin and arsenic methylation capability in Taiwan adolescents. Sci Total Environ 414:152–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.10.023
Farkhondeh T, Samarghandian S, Azimi-Nezhad M (2019) The role of arsenic in obesity and diabetes. J Cell Physiol 234(8):12516–12529. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28112
Ercal N, Gurer-Orhan H, Aykin-Burns N (2001) Toxic metals and oxidative stress part I: mechanisms involved in metal-induced oxidative damage. Curr Top Med Chem 1(6):529–539. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026013394831
Kawakami T, Nishiyama K, Kadota Y, Sato M, Inoue M, Suzuki S (2013) Cadmium modulates adipocyte functions in metallothionein-null mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 272(3):625–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2013.07.015
Miao X, Sun W, Fu Y, Miao L, Cai L (2013) Zinc homeostasis in the metabolic syndrome and diabetes. Front Med-Prc 7(1):31–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-013-0251-9
Nasab H, Rajabi S, Eghbalian M, Malakootian M, Hashemi M, Mahmoudi-Moghaddam H (2022) Association of As, Pb, Cr, and Zn urinary heavy metals levels with predictive indicators of cardiovascular disease and obesity in children and adolescents. Chemosphere 294:133664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133664
Błażewicz A, Klatka M, Astel A, Partyka M, Kocjan R (2013) Differences in trace metal concentrations (Co, Cu, Fe, Mn, Zn, Cd, And Ni) in whole blood, plasma, and urine of obese and nonobese children. Biol Trace Elem Res 155(2):190–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-013-9783-8
Marreiro DN, Fisberg M, Cozzolino SM (2002) Zinc nutritional status in obese children and adolescents. Biol Trace Elem Res 86(2):107–122. https://doi.org/10.1385/bter:86:2:107
Olechnowicz J, Tinkov A, Skalny A, Suliburska J (2018) Zinc status is associated with inflammation, oxidative stress, lipid, and glucose metabolism. J Physiol Sci 68(1):19–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12576-017-0571-7
Iavicoli I, Fontana L, Bergamaschi A (2009) The effects of metals as endocrine disruptors. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev 12(3):206–223. https://doi.org/10.1080/10937400902902062
Niehoff NM, Keil AP, O’Brien KM, Jackson BP, Karagas MR, Weinberg CR, White AJ (2020) Metals and trace elements in relation to body mass index in a prospective study of US women. Environ Res 184:109396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109396
Eckel N, Meidtner K, Kalle-Uhlmann T, Stefan N, Schulze MB (2016) Metabolically healthy obesity and cardiovascular events: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Prev Cardiol 23(9):956–966. https://doi.org/10.1177/2047487315623884
Gao M, Lv J, Yu C, Guo Y, Bian Z, Yang R, Du H, Yang L, Chen Y, Li Z, Zhang X, Chen J, Qi L, Chen Z, Huang T, Li L (2020) Metabolically healthy obesity, transition to unhealthy metabolic status, and vascular disease in Chinese adults: a cohort study. Plos Med 17(10):e1003351. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1003351
Liu L, Li X, Wu M, Yu M, Wang L, Hu L, Li Y, Song L, Wang Y, Mei S (2022) Individual and joint effects of metal exposure on metabolic syndrome among Chinese adults. Chemosphere 287(Pt 3):132295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132295
Hendrych M, Olejnickova V, Novakova M (2016) Calcium versus strontium handling by the heart muscle. Gen Physiol Biophys 35(1):13–23. https://doi.org/10.4149/gpb_2015026
Acknowledgements
We thank all the study participants in this study and the staffs of the Wuhan Tongji Hospital.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82073660, 82003479) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019M662646, 2020T130220).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Youjie Wang and Lulu Song designed the study and reviewed the manuscript. Gaojie Fan, Lulu Song, Qing Liu, Mingyang Wu, Jianing Bi, Xiya Qin, Qing Fang, Zhengce Wan, and Yongman Lv conducted the study. Gaojie Fan analyzed the data and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. All authors provided important intellectual contributions, edited the manuscript, and ensured its final contents.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
The study protocol was approved by the ethics committees of Wuhan Tongji Hospital and Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology.
Consent to Participate
Written informed consent was provided by all participants.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, G., Liu, Q., Wu, M. et al. Exposure to Metal Mixtures and Overweight or Obesity Among Chinese Adults. Biol Trace Elem Res 201, 3697–3705 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03484-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03484-0