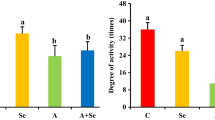
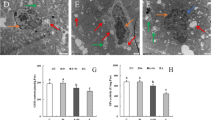
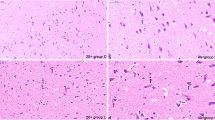
Abstract
Ammonia is a significant pollutant in the livestock houses and the atmospheric environment, and excessive ammonia would harm the health of livestock and breeders. Previous studies have shown that ammonia exposure could damage the tissue structure of the nervous system, but the molecular mechanism of ammonia-induced hypothalamus damage was still unclear. The purpose of this study was to determine the role of excessive ammonia in abnormal autophagy of pig hypothalamus and whether selenomethionine would have a mitigating effect on ammonia toxicity. Twenty-four 18-week pigs were randomly divided into four groups: the control group (C group), the selenium group (Se group), the ammonia + selenium group (A + Se group), and the ammonia group (A group). In our study, the expression levels of NF-κB, IL-1β, iNOS, TNF-α, IKK-α, p-IKK-α, Nrf2, ATG5, ATG 10, ATG 12, LC3 I/II, HSP60, HSP70, and HSP90 were increased after ammonia exposure; meanwhile, IFN-γ, IKB-α, p-IKB-α, Keap1, P62, mTOR, AKT, p-AKT, PI3K, SQSTM, and Beclin1 showed decreasing trends. The results indicated that excessive ammonia inhalation inhibited the AKT/mTOR pathway to acclerated autophagy through oxidative stress-mediated inflammation in the porcine hypothalamus. L-selenomethionine could alleviate hypothalamus injury induced by ammonia exposure.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Original data used and generated in this study are available from the corresponding authors on request with a completed Data Transfer Agreement. The raw sequencing files can be obtained through the National Center for Biotechnology Information website (Accession No. PRJNA741846).
References
Wang H, Zeng X, Zhang X, Liu H, Xing H (2021) Ammonia exposure induces oxidative stress and inflammation by destroying the microtubule structures and the balance of solute carriers in the trachea of pigs. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 212:111974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.111974
Zhang X, Wang A, Wang X, Zhao Q, Xing H, (2022) Evaluation of L-selenomethionine on ameliorating cardiac injury induced by environmental ammonia. Biol Trace Elem Res 200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-03071-9.514
Wang H, Zhang Y, Han Q, Xu Y, Hu G, Xing H (2020) The inflammatory injury of heart caused by ammonia is realized by oxidative stress and abnormal energy metabolism activating inflammatory pathway. Sci Total Environ 742:140532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140532
Zeng X, Liu R, Li Y, Li J, Zhao Q, Li X, Bao J (2021) Excessive ammonia inhalation causes liver damage and dysfunction by altering gene networks associated with oxidative stress and immune function. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 217:112203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112203
Kearney G, Shaw R, Prentice M, Tutor-Marcom R (2014) Evaluation of respiratory symptoms and respiratory protection behavior among poultry workers in small farming operations. J Agromedicine 19(2):162–170. https://doi.org/10.1080/1059924X.2014.886536
Zhang H, Ji W, Li X, Feng Y, Wang J, Liu H, Bao J (2021) Immunosuppression, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in pig kidney caused by ammonia: application of transcriptome analysis in risk assessment of ammonia exposure. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 428:115675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2021.115675
Li Y, Pan L, Zeng X, Zhang R, Li X, Li J, Xing H, Bao J (2021) Ammonia exposure causes the imbalance of the gut-brain axis by altering gene networks associated with oxidative metabolism, inflammation and apoptosis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 224:112668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112668
Xu Y, Li Z, Zhang S, Zhang H, Teng X (2020) MiR-187-5p/apaf-1 axis was involved in oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis caused by ammonia via mitochondrial pathway in chicken livers. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 388:114869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2019.114869
Benli A, Köksal G, Özkul A (2008) Sublethal ammonia exposure of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.): effects on gill, liver and kidney histology. Chemosphere 72(9):1355–1358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.04.037
Qian B (2017) Inflammation fires up cancer metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol 47:170–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.08.006
Pickering R, Bryant C (2020) Preventing pores and inflammation. Science 369(6511):1564–1565. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abe0917
Shah S, Chen D, Zhang J, Liu Y, Ishfaq M, Tang Y, Teng X (2020) The effect of ammonia exposure on energy metabolism and mitochondrial dynamic proteins in chicken thymus: through oxidative stress, apoptosis, and autophagy. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 206:111413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111413
Hseu Y, Wu F, Wu J, Chen J, Chang W, Lu F, Lai Y, Yang H (2005) Anti-inflammatory potential of Antrodia Camphorata through inhibition of iNOS, Cox-2 and cytokines via the NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 5(13–14):1914–1925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2005.06.013
Balzano T, Dadsetan S, Forteza J, Cabrera-Pastor A, Taoro-Gonzalez L, Malaguarnera M, Gil-Perotin S, Cubas-Nuñez L, Casanova B, Castro-Quintas A, Ponce-Mora A, Arenas YM, Leone P, Erceg S, Llansola M, Felipo V (2020) Chronic hyperammonemia induces peripheral inflammation that leads to cognitive impairment in rats: reversed by anti-TNF-α treatment. J Hepatol 73(3):582–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2019.01.008
Salter-Cid L, Wang E, O’Rourke A, Miller A, Gao H, Huang L, Garcia A, Linnik MD (2005) Anti-inflammatory effects of inhibiting the amine oxidase activity of semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 315(2):553–562. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.105.089649
Weeks B, Hanna M, Cooperstein D (2012) Dietary selenium and selenoprotein function. Med Sci Monitor 18(8):RA127–RA132. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.883258
Chu J, Yan Y, Gao P, Chen X, Fan R (2020) Response of selenoproteins gene expression profile to mercuric chloride exposure in chicken kidney. Res Vet Sci 133:4–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rvsc.2020.08.020
Cheng Z, Shu YF, Li X, Li YT, Zhou ST, Liu HG (2022) Evaluation of potential cardiotoxicity of ammonia: L-selenomethionine inhibits ammonia-induced cardiac autophagy by activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 233:113304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113304
Raisbeck MF (2020) Selenosis in ruminants. Vet Clin N Am Food Anim Pract 36(3):775–789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cvfa.2020.08.013
DeMartino GN (2018) Introduction to the thematic minireview series: autophagy. J Biol Chem 293(15):5384–5385. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.TM118.002429
Doherty J, Baehrecke EH (2018) Life, death and autophagy. Nat Cell Biol 20(10):1110–1117. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0201-5
Wang Y, Wang S, Jing H, Zhang T, Song N, Xu S (2022) CircRNA-IGLL1/miR-15a/RNF43 axis mediates ammonia-induced autophagy in broilers jejunum via Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Environ Pollut 292:118332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118332
Bolt A, Klimecki W (2012) Autophagy in toxicology: self-consumption in times of stress and plenty: autophagy in toxicology. J Appl Toxicol 32(7):465–479. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.1787
Li Y, Zhang R, Li X, Li J, Ji W, Zeng X, Bao J (2021) Exposure to the environmental pollutant ammonia causes changes in gut microbiota and inflammatory markers in fattening pigs. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 208:111564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111564
Wang H, Han Q, Chen Y, Hu G, Xing H (2021) Novel insights into cytochrome P450 enzyme and solute carrier families in cadmium-induced liver injury of pigs. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 211:111910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.111910
Hunt J, Zaretsky D, Sarkar S, DiMicco JA (2010) Dorsomedial hypothalamus mediates autonomic, neuroendocrine, and locomotor responses evoked from the medial preoptic area. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 298(1):R130–R140. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00574.2009
Porter R (1952) Alterations in electrical activity of the hypothalamus induced by stress stimuli. Amer J Physiolt 169(3):629–637. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplegacy.1952.169.3.629
Rodrigues Siqueira I, Fochesatto C, da Silva Torres I, Dalmaz C, Alexandre Netto C (2005) Aging affects oxidative state in hippocampus, hypothalamus and adrenal glands of Wistar rats. Life Sci 78(3):271–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2005.04.044
Reichlin S (1960) Thyroid function, body temperature regulation and growth in rats with hypothalamic lesions. Endocrinology 66(3):340–354. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo-66-3-340
Yang C, Gao J, Wang H, Liu Q, Xu M, Wang Z, Jiang J (2011) Effects of hypothalamus destruction on the level of plasma corticosterone after blast injury and its relation to interleukin-6 in rats. Cytokine 54(1):29–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2010.12.011
Xia C, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Li J, Xing H (2021) Ammonia exposure causes the disruption of the solute carrier family gene network in pigs. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 210:111870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111870
Fan R, Liu J, Yan Y, Wang L, Wang Z (2020) Selenium relieves oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis within spleen of chicken exposed to mercuric chloride. Poult Sci 99:5430–5439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psj.2020.08.031
Hu X, Chi Q, Wang D, Chi X, Teng X, Li S (2018) Hydrogen sulfide inhalation-induced immune damage is involved in oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis and the Th1/Th2 imbalance in broiler bursa of Fabricius. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 164:201–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.08.029
Shi Q, Wang W, Chen M, Zhang H, Xu S (2019) Ammonia induces Treg/Th1 imbalance with triggered NF-κB pathway leading to chicken respiratory inflammation response. Sci Total Environ 659:354–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.375
Zheng S, Zhao J, Xing H, Xu S (2019) Oxidative stress, inflammation, and glycometabolism disorder-induced erythrocyte hemolysis in selenium-deficient exudative diathesis broilers. J Cell Physiol 234(9):16328–16337. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28298
Xing H, Peng M, Li Z, Chen J, Zhang H, Teng X (2019) Ammonia inhalation-mediated mir-202-5p leads to cardiac autophagy through PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway. Chemosphere 235:858–866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.06.235
Bellezza I, Giambanco I, Minelli A, Donato R (2018) Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in oxidative and reductive stress. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1865(5):721–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.02.010
Wang AQ, Zhang XX, Wang H, Xing HJ (2022) Recent evidence for toxic effects of NH3 exposure on lung injury: protective effects of L-selenomethionine. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 242:113937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113937
Higarza S, Arboleya S, Gueimonde M, Gómez-Lázaro E, Arias JL, Arias N (2019) Neurobehavioral dysfunction in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis is associated with hyperammonemia, gut dysbiosis, and metabolic and functional brain regional deficits. PLoS ONE 14(9):e0223019. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0223019
Shah S, Chen J, Han Q, Xu Y, Ishfaq M, Teng X (2020) Ammonia inhalation impaired immune function and mitochondrial integrity in the broilers bursa of fabricius: implication of oxidative stress and apoptosis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 190:110078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110078
Han Q, Tong J, Sun Q, Teng X, Zhang H, Teng X (2020) The involvement of miR-6615-5p/Smad7 axis and immune imbalance in ammonia-caused inflammatory injury via NF-κB pathway in broiler kidneys. Poult Sci 99(11):5378–5388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psj.2020.08.005
Zhao F, Qu J, Wang W, Li S, Xu S (2020) The imbalance of Th1/Th2 triggers an inflammatory response in chicken spleens after ammonia exposure. Poult Sci 99(8):3817–3822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psj.2020.04.029
Li R, Kou X, Tian J, Meng Z, Cai Z, Cheng F, Dong C (2014) Effect of sulfur dioxide on inflammatory and immune regulation in asthmatic rats. Chemosphere 112:296–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.04.065
Wang W, Chen M, Jin X, Li X, Yang Z, Lin H, Xu S (2018) H2S induces Th1/Th2 imbalance with triggered NF-κB pathway to exacerbate LPS-induce chicken pneumonia response. Chemosphere 208:241–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.152
Zhao H, Wang Y, Shao Y, Liu J, Wang S, Xing M (2018) Oxidative stress-induced skeletal muscle injury involves in NF-κB/p53-activated immunosuppression and apoptosis response in copper (II) or/and arsenite-exposed chicken. Chemosphere 210:76–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.06.165
Yang L, Liu G, Zhu X, Luo Y, Shang Y, Gu X (2019) The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of leonurine hydrochloride after lipopolysaccharide challenge in broiler chicks. Poult Sci 98(4):1648–1657. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pey532
Napetschnig J, Wu H (2013) Molecular basis of NF-κB signaling. Annu Rev Biophys 42(1):443–468. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biophys-083012-130338
Aggarwal B, Shishodia S, Sandur S, Pandey M, Sethi G (2006) Inflammation and cancer: how hot is the link? Biochem Pharmacol 72(11):1605–1621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2006.06.029
Xie W, Lv A, Li R, Tang Z, Ma D, Huang X, Zhang R, Ge M (2018) Agaricus blazei Murill polysaccharides protect against cadmium-induced oxidative stress and inflammatory damage in chicken spleens. Biol Trace Elem Res 184(1):247–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1189-6
Wang Y, Wang K, Huang H, Gu X, Teng X (2017) Alleviative effect of selenium on inflammatory damage caused by lead via inhibiting inflammatory factors and heat shock proteins in chicken testes. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24(15):13405–13413. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8785-z
Jarosz Ł, Marek A, Grądzki Z, Kwiecień M, Żylińska B, Kaczmarek B (2017) Effect of feed supplementation with zinc glycine chelate and zinc sulfate on cytokine and immunoglobulin gene expression profiles in chicken intestinal tissue. Poult Sci 96(12):4224–4235. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pex253
Huang W, Cao Z, Zhang J, Ji Q, Li Y (2019) Aflatoxin B1 promotes autophagy associated with oxidative stress-related PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in mice testis. Environ Pollut 255:113317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113317
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by the Earmarked Fund for the China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA (Project No. CARS-35-05B). The authors would thank Lian Chuan-Biotechnology Co., Ltd (Hangzhou, China) for their assistance during transcriptome sequencing. The experiment also got support from the animal welfare and healthy breeding team of Northeast Agriculture University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jianxing Wang: writing—original draft, methodology, investigation, formal analysis, data curation. Jing Wang and Yutao Li: writing—review and editing, investigation, formal analysis, animal breeding, conceptualization. Qi Han and Yulai Wang: methodology, investigation, language revision. Honggui Liu and Jun Bao: supervision, writing—review and editing, project administration, funding acquisition. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Wang, J., Li, Y. et al. Organic Selenium Alleviates Ammonia-Mediated Abnormal Autophagy by Regulating Inflammatory Pathways and the Keap1/Nrf2 Axis in the Hypothalamus of Finishing Pigs. Biol Trace Elem Res 201, 3812–3824 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03452-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03452-8