Abstract
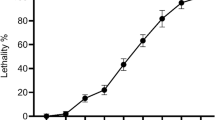
Arsenic is currently ranked as the most toxicant on the ATSDR 2015 substance priority list and is categorised as a Group 1 human carcinogen. Biota that are subjected to inorganic arsenicals through food, water, occupational or medical exposure pose a risk to the environment and to human health. The present study was carried out to investigate the toxicity caused by inorganic arsenic. After fertilisation, zebrafish embryos were exposed to sodium arsenite at several concentrations (100 nM to 600 nM) for 24 to 96 hpf. The indicators of teratogenicity (hatchability, morphological abnormalities, mortality), behavioural modifications (touch induced escape response (TIER), startle response (SR) and turning behaviour (TB)), biochemical testing (superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPX), and glutathione S transferase (GST)) and the expressions of tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) were investigated. The aforementioned parameters were found to be altered in embryos exposed to sodium arsenite. According to the findings of the current study, even a low dose of inorganic arsenic compound caused teratogenicity, behavioural abnormalities, altered enzyme activities and the expression of proinflammatory cytokines in zebrafish embryos.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings are all included in the article.
References
Palamuleni LG (2019) Heavy metal pollution in soil and plants from a mining area in the Northwest Province, South Africa (Doctoral dissertation, North-West University (South Africa))
Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) (2017) Summary data for 2015 priority list of hazardous substances, Agency for Toxic Substances and disease registry. U.S. Division of Toxicology and Human Health Sciences, Atlanta
Naujokas MF, Anderson B, Ahsan H, Aposhian HV, Graziano JH, Thompson C, Suk WA (2013) The broad scope of health effects from chronic arsenic exposure: update on a worldwide public health problem. Environ Health Perspect 121(3):295–302
Thomas DJ, Waters SB, Styblo M (2004) Elucidating the pathway for arsenic methylation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 198(3):319–326
Lansdown AB (1995) Physiological and toxicological changes in the skin resulting from the action and interaction of metal ions. Crit Rev Toxicol 25(5):397–462
Jha PK, Tripathi P (2021) Arsenic and fluoride contamination in groundwater: a review of global scenarios with special reference to India. Groundw Sustain Dev 13:100576
Rehman K, Naranmandura H (2012) Arsenic metabolism and thioarsenicals Metallomics 4(9):881–892
Banerjee M, Banerjee N, Bhattacharjee P, Mondal D, Lythgoe PR, Martínez M, Pan J, Polya DA, Giri AK (2013) High arsenic in rice is associated with elevated genotoxic effects in humans. Sci Rep 3(1):1–8
Abdul KSM, Jayasinghe SS, Chandana EP, Jayasumana C, De Silva PMC (2015) Arsenic and human health effects: a review. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 40(3):828–846
Eddins D, Cerutti D, Williams P, Linney E, Levin ED (2010) Zebrafish provide a sensitive model of persisting neurobehavioral effects of developmental chlorpyrifos exposure: comparison with nicotine and pilocarpine effects and relationship to dopamine deficits. Neurotoxicol Teratol 32(1):99–108
Zanandrea R, Bonan CD and Campos MM (2020) Zebrafish as a model for inflammation and drug discovery, Drug Discovery Today. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2020.09.036
Busquet F, Strecker R, Rawlings JM, Belanger SE, Braunbeck T, Carr GJ, Cenijn P, Fochtman P, Gourmelon A, Hübler N, Kleensang A (2014) OECD validation study to assess intra-and inter-laboratory reproducibility of the zebrafish embryo toxicity test for acute aquatic toxicity testing. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 69(3):496–511
Truong L, Tanguay RL (2017) Evaluation of embryotoxicity using the zebrafish model. Methods Mol Biol 1641:325–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7172-5_18
Lahnsteiner F (2008) The sensitivity and reproducibility of the zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryo test for the screening of wastewater quality and for testing the toxicity of chemicals. ATLA Altern Lab Anim 36(3):299–311. https://doi.org/10.1177/026119290803600308
Embry MR, Belanger SE, Braunbeck TA, Galay-Burgos M, Halder M, Hinton DE, Léonard MA, Lillicrap A, Norberg-King T, Whale G (2010) The fish embryo toxicity test as an animal alternative method in hazard and risk assessment and scientific research. Aquat Toxicol 97(2):79–87
Del Razo LM, Quintanilla-Vega B, Brambila-Colombres E, Calderón-Aranda ES, Manno M, Albores A (2001) Stress proteins induced by arsenic. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 177(2):132–148
Xing P, Zhang Y, Chi Q, Li S (2022) Zinc alleviates arsenic-induced inflammation and apoptosis in the head kidney of common carp by inhibiting oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Biol Trace Elem Res 200(5):2380–2390
Milan FS, Maleki BRS, Moosavy MH, Mousavi S, Sheikhzadeh N, Khatibi SA (2021) Ameliorating effects of dietary Haematococcus pluvialis on arsenic-induced oxidative stress in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fillet. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 207:111559
Allen T, Rana SVS (2004) Effect of arsenic (AsIII) on glutathione-dependent enzymes in liver and kidney of the freshwater fish Channa punctatus. Biol Trace Elem Res 100(1):39–48
González Núñez AA, Ferro JP, Campos LB, Eissa BL, Mastrángelo MM, Ferrari L, Ossana NA (2022) Evaluation of the acute effects of arsenic on adults of the neotropical native fish Cnesterodon decemmaculatus using a set of biomarkers. Environ Toxicol Chem 41(5):1246–1259
Barone G, Storelli A, Garofalo R, Mallamaci R, Storelli MM (2022) Residual levels of mercury, cadmium, lead and arsenic in some commercially key species from Italian Coasts (Adriatic Sea): Focus on Human Health. Toxics 10(5):223
Wang T, Secombes CJ (2009) Identification and expression analysis of two fish-specific IL-6 cytokine family members, the ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF)-like and M17 genes, in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Mol Immunol 46(11–12):2290–2298
Secombes CJ, Zou J, Bird S (2009) Fish cytokines: discovery, activities and potential applications. Fish Defenses 1:1–36
Laing KJ, Secombes CJ (2004) Chemokines. Dev Comp Immunol 28(5):443–460
Aleström P, D’Angelo L, Midtlyng PJ, Schorderet DF, Schulte-Merker S, Sohm F, Warner S (2020) Zebrafish: housing and husbandry recommendations. Lab Anim 54(3):213–224
Ali S, Van Mil HG, Richardson MK (2011) Large-scale assessment of the zebrafish embryo as a possible predictive model in toxicity testing. PLoS ONE 6(6):e21076
Gilbert BM, Avenant-Oldewage A (2016) Hatchability and survival of oncomiracidia of Paradiplozoon ichthyoxanthon (Monogenea: Diplozoidae) exposed to aqueous aluminium. Parasit Vectors 9(1):1–11
Kong X, Jiang H, Wang S, Wu X, Fei W, Li L, Nie G, Li X (2013) Effects of copper exposure on the hatching status and antioxidant defense at different developmental stages of embryos and larvae of goldfish Carassius auratus. Chemosphere 92(11):1458–1464
Aksakal FI, Ciltas A (2019) Impact of copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO NPs) exposure on embryo development and expression of genes related to the innate immune system of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Comp Biochem Physiol C: Toxicol Pharmacol 223:78–87a
Coral JA, Heaps S, Glaholt SP, Karty JA, Jacobson SC, Shaw JR, Bondesson M (2021) Arsenic exposure induces a bimodal toxicity response in zebrafish. Environ Pollut 287:117637
Misra HP, Fridovich I (1972) The generation of superoxide radical during the autoxidation of hemoglobin. J Biol Chem 247(21):6960–6962
Sinha AK (1972) Colorimetric assay of catalase. Anal Biochem 47(2):389–394
Rotruck JT, Pope AL, Ganther HE, Swanson AB, Hafeman DG, Hoekstra W (1973) Selenium: biochemical role as a component of glutathione peroxidase. Science 179(4073):588–590
Habig WH and Jakoby WB (1981) [51]Assays for differentiation of glutathione S-transferases. In Methods in enzymology 77:398–405. Academic press
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Laemmli UK, Beguin F, Gujer-Kellenberger G (1970) A factor preventing the major head protein of bacteriophage T4 from random aggregation. J Mol Biol 47(1):69–85
Kabir T, Anwar S, Mourosi JT, Hossain J, Rabbane MG, Rahman MM, Tahsin T, Hasan MN, Shill MC, Hosen MJ (2020) Arsenic hampered embryonic development: an in vivo study using local Bangladeshi Danio rerio model. Toxicol Rep 7:155–161
Li D, Lu C, Wang J, Hu W, Cao Z, Sun D, Xia H, Ma X (2009) Developmental mechanisms of arsenite toxicity in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Aquat Toxicol 91(3):229–237
Fuse Y, Nguyen VT, Kobayashi M (2016) Nrf2-dependent protection against acute sodium arsenite toxicity in zebrafish. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 305:136–142
Olivares CI, Field JA, Simonich M, Tanguay RL, Sierra-Alvarez R (2016) Arsenic (III, V), indium (III), and gallium (III) toxicity to zebrafish embryos using a high-throughput multi-endpoint in vivo developmental and behavioral assay. Chemosphere 148:361–368
Sun HJ, Xiang P, Tang MH, Sun L, Ma LQ (2016) Arsenic impacted the development, thyroid hormone and gene transcription of thyroid hormone receptors in bighead carp larvae (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis). J Hazard Mater 303:76–82
Zikic V, Stajn AS, Ognjanovic BI, Pavlovic SZ, Saicic ZS (1997) Activities of superoxide dismutase and catalase in erythrocytes and transaminases in the plasma of carps (Cyprinus carpio L.) expose to cadmium. Physiol Res 46:391–396
Farombi EO, Adelowo OA, Ajimoko YR (2007) Biomarkers of oxidative stress and heavy metal levels as indicators of environmental pollution in African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) from Nigeria Ogun River. Int J Environ Res Public Health 4(2):158–165
Di Giulio RT, Washburn PC, Wenning RJ, Winston GW, Jewell CS (1989) Biochemical responses in aquatic animals: a review of determinants of oxidative stress. Environ Toxicol Chem: An Int J 8(12):1103–1123
Sun HJ, Zhao WJ, Teng XQ, Shu SP, Li SW, Hong HC, Guan DX (2020) Antioxidant responses and pathological changes in the gill of zebrafish (Danio rerio) after chronic exposure to arsenite at its reference dose. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 200:110743
Kim JH, Kang JC (2015) The arsenic accumulation and its effect on oxidative stress responses in juvenile rockfish, Sebastes schlegelii, exposed to waterborne arsenic (As3+). Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 39(2):668–676
Flora SJ (2011) Arsenic-induced oxidative stress and its reversibility. Free Radical Biol Med 51(2):257–281
Thompson JA, White CC, Cox DP, Chan JY, Kavanagh TJ, Fausto N, Franklin CC (2009) Distinct Nrf1/2-independent mechanisms mediate As3+-induced glutamate-cysteine ligase subunit gene expression in murine hepatocytes. Free Radical Biol Med 46(12):1614–1625
Aruljothi B and Samipillai SS (2014) Effect of arsenic on lipid peroxidation and antioxidants system in freshwater fish. Labeo roh Greani S, Lourkisti R, Berti L, Marchand B, Giannettini J, Santini J and Quilichini Y (2017) Effect of chronic arsenic exposure under environmental conditions on bioaccumulation, oxidative stress, and antioxidant enzymatic defenses in wild trout Salmo trutta (Pisces, Teleostei). Ecotoxicology 26(7):930–941
Greani S, Lourkisti R, Berti L, Marchand B, Giannettini J, Santini J, Quilichini Y (2017) Effect of chronic arsenic exposure under environmental conditions on bioaccumulation, oxidative stress, and antioxidant enzymatic defenses in wild trout Salmo trutta (Pisces, Teleostei). Ecotoxicology 26(7):930–941
Leite CE (2013) Caracterização de um modelo de inflamação em larvas de zebrafish: o papel do sistema purinérgico
Kozul CD, Hampton TH, Davey JC, Gosse JA, Nomikos AP, Eisenhauer PL, Weiss DJ, Thorpe JE, Ihnat MA, Hamilton JW (2009) Chronic exposure to arsenic in the drinking water alters the expression of immune response genes in mouse lung. Environ Health Perspect 117(7):1108–1115
Funding
Tamil Nadu Dr. J. Jayalalithaa Fisheries University – Institute of Fisheries Postgraduate Studies provided the funds and all the necessary facilities to carry out this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Modi Kiran — performed experiment and drafted the article, prepared the figures and tables.
Ambika Binesh — designed the experiment and reviewed the manuscript.
S. A. Shanmugam — reviewed the manuscript.
Kaliyamurthi Venkatachalam — designed the experiment, drafted and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical Statement
Zebrafish were maintained as per Institutional Animal Ethical Care (IAEC) and committee for the purpose of control and supervision of experiments on animals (CPCSEA).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Piyushbhai, M.K., Binesh, A., Shanmugam, S.A. et al. Exposure to low-dose arsenic caused teratogenicity and upregulation of proinflammatory cytokines in zebrafish embryos. Biol Trace Elem Res 201, 3487–3496 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03418-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03418-w