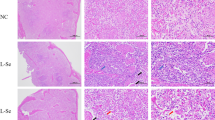
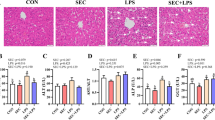
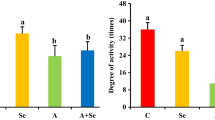
Abstract
Ammonia (NH3) is a harmful gas in livestock houses. So far, many researchers have demonstrated that NH3 is detrimental to animal and human organs. Selenium (Se) is one of the essential trace elements in the body and has a good antioxidant effect. However, there was little conclusive evidence that Se alleviated NH3 poisoning. To investigate the toxic mechanism of NH3 on pig spleen and the antagonistic effect of L-selenomethionine, a porcine NH3-poisoning model and an L-selenomethionine intervention model were established in this study. Our results showed that NH3 exposure increased the apoptosis rate, while L-selenomethionine supplementation alleviated the process of excessive apoptosis. Immunofluorescence staining, real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), and western blot results confirmed that exposure to NH3 changed the expression levels of interleukin family factors, apoptosis, death receptor, and oxidative stress factors. Our study further confirmed that excessive NH3 induced inflammatory response and mediated necroptosis leading to cell apoptosis by activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Excessive NH3 could mediate spleen injury through oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial dynamics disorder. L-Selenomethionine could alleviate inflammation and abnormal apoptosis by inhibiting the IL-17/TNF-α/FADD axis. Our study would pave the way for comparative medicine and environmental toxicology.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All original data (including the raw sequencing files) used in the current manuscript could be available to access from the corresponding author (jbao@neau.edu.cn). You can find supplementary files related to this article online.
References
Li Y, Zhang R, Li X, Li J, Ji W, Zeng X, Bao J 2020. Exposure to the environmental pollutant ammonia causes changes in gut microbiota and inflammatory markers in fattening pigs. Ecotox. Environ.Safe. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111564
Carlile F (1984) Ammonia in poultry houses: a literature review. Worlds Poult Sci J 40:99–113. https://doi.org/10.1079/WPS19840008
Philippe F, Cabaraux J, Nicks B 2011. Ammonia emissions from pig houses: influencing factors and mitigation techniques [J]. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 2011, 141(3–4): 245–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2011.03.012
Bauer S, Tsigaridis K, Miller R (2016) Significant atmospheric aerosol pollution caused by world food cultivation. Geophys Res Lett 43:5394–5400. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016GL068354
Tao Z, Xu W, Zhu C, Zhang S, Shi Z, Song W, Liu H, Li H (2019) Effects of ammonia on intestinal microflora and productive performance of laying ducks. Poult Sci 98:1947–1959. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pey578
Rangroo V, Thrane A, Wang F, Cotrina M, Smith N, Chen M, Xu Q, Kang N, Fujita T, Nagelhus E, Nedergaard M (2013) Ammonia triggers neuronal disinhibition and seizures by impairing astrocyte potassium buffering. Nat Med 19:1643–1648. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3400
Whitaker C, Paigen B, Beamer W, Bronson R, Churchill G, Schweitzer I, Myers D (2001) The impact of reduced frequency of cage changes on the health of mice housed in ventilated cages. Lab Anim 35:58–73. https://doi.org/10.1258/0023677011911381
Xing H, Peng M, Li Z, Chen J, Zhang H, Teng X (2019) Ammonia inhalation mediated mir-202-5p leads to cardiac autophagy through PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway. Chemosphere 235:858–866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.06.235
Morisse J, Morisse 1979 Action of an irritant (NH3) on the pathogeny of a respiratory disease induced experimentally by Pasteurella multocida in the rabbit. Annales de zootechnie, INRA/EDP Sciences, 1979, 28 (1), pp.139–139. Hal-00887861
Soudani N, Sefi M, Ben Amara I, Boudawara T, Zeghal N (2010) Protective effects of selenium (Se) on chromium (VI) induced nephrotoxicity in adult rats. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:671–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2009.10.002
Zhang J, Liu Y, Tian L, Yang H, Liang G, Xu D (2012) Effects of dietary mannan oligosaccharide on growth performance, gut morphology and stress tolerance of juvenile Pacific white shrimp. Litopenaeus vannamei Fish Shellfish Immunol 33:1027–1032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2012.05.001
Gao J, Zhu Y, Guo Z, Xu G, Xu P 2020. Transcriptomic analysis reveals different responses to ammonia stress and subsequent recovery between Coilia nasus larvae and juveniles. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 230, 108710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2020.108710
Mellert’, W., Deckardt, K., Gembardt, C., Zwirner-Baier, I., Jickh, R., van Ravenzwaay, B., (2004) Aniline: early indicators of toxicity in male rats and their relevance to spleen carcinogenicity. Hum Exp Toxicol 23:379–389. https://doi.org/10.1191/0960327104ht466oa
Xie W, Lv A, Li R, Tang Z, Ma D, Huang X, Zhang R, Ge M (2018) Agaricus blazei Murill polysaccharides protect against cadmium-induced oxidative stress and inflammatory damage in chicken spleens. Biol Trace Elem Res 184:247–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1189-6
Guo Y, Zhao P, Guo G, Hu Z, Tian L, Zhang K, Sun Y, Zhang X, Zhang W, Xing M (2016) Effects of arsenic trioxide exposure on heat shock protein response in the immune organs of chickens. Biol Trace Elem Res 169:134–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0389-1
Li J, Li S, Tang Z S, Xu W 2010. Oxidative stress-mediated cytotoxicity of cadmium in chicken splenic lymphocytes. 196(Supp-S). https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2010.03.429
An Y, Xing H, Zhang Y, Jia P, Gu X, Teng X (2019) The evaluation of potential immunotoxicity induced by environmental pollutant ammonia in broilers. Poult Sci 98:3165–3175. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pez135
Halliwell B (1999) Antioxidant defense mechanisms: from the beginning to the end (of the beginning). Free Radic Res 31:261–272. https://doi.org/10.1080/10715769900300841
G Farrugia R Balzan 2012 Oxidative stress and programmed cell death in yeast Front Oncol 2https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2012.00064
Liang Z, Liu R, Zhao D, Wang L, Sun M, Wang M, Song L (2016) Ammonia exposure induces oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in hepatopancreas of pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Fish Shellfish Immunol 54:523–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2016.05.009
Wang H, Wang A, Wang X, Zeng X, Xing H (2022) AMPK/PPAR-γ/NF-κB axis participates in ROS-mediated apoptosis and autophagy caused by cadmium in pig liver. Environ Pollut 294:118659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118659
Cabiscol E, Piulats E, Echave P, Herrero E (2000) Oxidative stress promotes specific protein damage in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 275:27393–27398. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m003140200
Del Rio D, Stewart A, Pellegrini N (2005) A review of recent studies on malondialdehyde as toxic molecule and biological marker of oxidative stress. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 15:316–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2005.05.003
Avery S (2011) Molecular targets of oxidative stress. Biochem J 434:201–210. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20101695
Jeon B, Kim K, Chang S, Kim H (2002) Phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase/protein kinase B inhibits apoptotic cell death induced by reactive oxygen species in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biochem (Tokyo) 131:693–699. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a003153
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35:495–516. https://doi.org/10.1080/01926230701320337
X Jin Z Xu X Zhao M Chen S Xu 2017 The antagonistic effect of selenium on lead-induced apoptosis via mitochondrial dynamics pathway in the chicken kidney Chemospherehttps://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.03.130
Seo Y, Shin J, Ko K, Cha J, Park J, Lee B, Yun C, Kim Y, Seol D, Kim D, Yin X, Kim T (2003) The molecular mechanism of noxa-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in p53-mediated cell death. J Biol Chem 278:48292–48299. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M308785200
Bellosillo B, Villamor N, López-Guillermo A, Marcé S, Bosch F, Campo E, Montserrat E, Colomer D (2002) Spontaneous and drug-induced apoptosis is mediated by conformational changes of Bax and Bak in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 100:1810–1816. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2001-12-0327
Chen Q, Gong B, Almasan A (2000) Distinct stages of cytochrome c release from mitochondria: evidence for a feedback amplification loop linking caspase activation to mitochondrial dysfunction in genotoxic stress induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 7:227–233. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4400629
Li Y, Zhou F, Huang J, Yang L, Jiang S, Yang Q, He J, Jiang S (2018) Transcriptome reveals involvement of immune defense, oxidative imbalance, and apoptosis in ammonia-stress response of the black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon). Fish Shellfish Immunol 83:162–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.09.026
Li, X., Xing, M., Chen, M., Zhao, J., Fan, R., Zhao, X., Cao, C., Jie Yang, Zhang, Z., Xu, S.,2017. Effects of selenium-lead interaction on the gene expression of inflammatory factors and selenoproteins in chicken neutrophils. Ecotox Environ Safe.139, 447–453. https:// doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.02.017
Han Q, Liu H, Zhang R, Yang X, Bao J, Xing H (2021) Selenomethionine protects against ammonia-induced apoptosis through inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress in pig kidneys. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 223:112596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112596
Li Y, Pan L, Zeng X, Zhang R, Li X, Li J, Xing H, Bao J (2021) Ammonia exposure causes the imbalance of the gut-brain axis by altering gene networks associated with oxidative metabolism, inflammation and apoptosis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 224:112668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112668
H Wang Q Han Y Chen G Hu H Xing 2021 Novel insights into cytochrome P450 enzyme and solute carrier families in cadmium-induced liver injury of pigs Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 211https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.111910
Wang H, Zhang Y, Han Q, Xu Y, Hu G, Xing H (2020) The inflammatory injury of heart caused by ammonia is realized by oxidative stress and abnormal energy metabolism activating inflammatory pathway. Sci Total Environ 742:140532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140532
Wang S, Li X, Zhang M, Jiang H, Wang R, Qian Y, Li M (2021) Ammonia stress disrupts intestinal microbial community and amino acid metabolism of juvenile yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 227:112932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112932
Cheng Z, Shu Y, Li X, Li Y, Liu H 2022. Evaluation of potential cardiotoxicity of ammonia: L-selenomethionine plays a protective role by inhibiting autophagy mediated by PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2022, 233 (113304). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113304
Kim J, Kang Y, Kim K, Kim S, Kim J (2019) Toxic effects of nitrogenous compounds (ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate) on acute toxicity and antioxidant responses of juvenile olive flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 67:73–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2019.02.001
Kır M, Sunar MC, Gök MG (2019) Acute ammonia toxicity and the interactive effects of ammonia and salinity on the standard metabolism of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Aquaculture 511:734273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734273
Mihina Š, Sauter M, Palkovičová Z, Karandušovská I, Brouček J (2012) Concentration of harmful gases in poultry and pig houses. Anim Sci Pap Rep 30:395–406
Duan Y, Xiong D, Wang Y, Li H, Dong H, Zhang J (2021) Toxic effects of ammonia and thermal stress on the intestinal microbiota and transcriptomic and metabolomic responses of Litopenaeus vannamei. Sci Total Environ 754:141867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141867
Wang H, Zeng X, Zhang X, Liu H, Xing H (2021) Ammonia exposure induces oxidative stress and inflammation by destroying the microtubule structures and the balance of solute carriers in the trachea of pigs. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 212:111974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.111974
Shi Q, Jin X, Fan R, Xing M, Guo J, Zhang Z, Zhang J, Xu S (2019) Cadmium-mediated miR-30a-GRP78 leads to JNK-dependent autophagy in chicken kidney. Chemosphere 215:710–715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.019
Zhang J, Li C, Tang X, Lu Q, Sa R, Zhang H (2015) High concentrations of atmospheric ammonia induce alterations in the hepatic proteome of broilers (Gallus gallus): an iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomic analysis. PLoS ONE 10:e0123596. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0123596
Cao Y, Lv G, Wang Y, Fan Z, Bi Y, Zhao L, Guo Z 2013. Mitochondrial fusion and fission after spinal sacord injury in rats[J]. Brain Research,2013,15–22. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2013.05.033.
Liu L, Gong L, Zhang Y, Li N 2013. Glycolysis in Panc-1 human pancreatic cancer cells is inhibited by everolimus. Exp Ther Med 5: 338–342, 2. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2012.787
Duan Y, Yao X, Zhu J, Li Y, Zhang J, Zhou X, Qiao Y, Yang M, Li X 2017. Effects of yak‑activated protein on hematopoiesis and related cytokines in radiation‑induced injury in mice. Exp. Ther. Med. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.5256
Hu X, Chi Q, Wang D, Chi X, Teng X, Li S (2018) Hydrogen sulfide inhalation-induced immune damage is involved in oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis and the Th1/Th2 imbalance in broiler bursa of Fabricius. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 164:201–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.08.029
Marquez R, Xu L (2015) Bcl-2: Beclin 1 complex: multiple, mechanisms regulating autophagy/apoptosis toggle switch. Am J Cancer Res 2:214–221
Wang Y, Zhao H, Shao Y, Liu J, Li J, Luo L, Xing M (2018) Copper (II) and/or arsenite-induced oxidative stress cascades apoptosis and autophagy in the skeletal muscles of chicken. Chemosphere 206:597–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.013
Zhang H, Ji W, Li X, Feng Y, Wang J, Liu H, Bao J (2021) Immunosuppression, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in pig kidney caused by ammonia: application of transcriptome analysis in risk assessment of ammonia exposure. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 428:115–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2021.115675
Hot A, Miossec P (2011) Effects of interleukin (IL)-17A and IL-17F in human rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes. Ann Rheum Dis 70:727–732. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2010.143768
Patel N, Chatterjee P, Di Paola R, Mazzon E, Britti D, De Sarro A, Cuzzocrea S, Thiemermann C (2005) Endogenous Interleukin-6 enhances the renal injury, dysfunction, and inflammation caused by ischemia/reperfusion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 312:1170–1178. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.104.078659
Kan X, Liu B, Guo W, Wei L, Lin Y, Guo Y, Gong Q, Li Y, Xu D, Cao Y, Huang B, Dong A, Ma H, Fu S, Liu J (2019) Myricetin relieves LPS-induced mastitis by inhibiting inflammatory response and repairing the blood–milk barrier. J Cell Physiol 234:16252–16262. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28288
Lv L, Zhang H, Liu Z, Lei L, Feng Z, Zhang D, Ren Y, Zhao S (2020) Comparative study of yeast selenium vs. sodium selenite on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative activity in weaned piglets challenged by Salmonella typhimurium. Innate Immun 26:248–258. https://doi.org/10.1177/1753425919888566
L Liu C Wu D Chen B Yu Z Huang Y Luo P Zheng X Mao J Yu J Luo H Yan J He 2020 Selenium-enriched yeast alleviates oxidative stress-induced intestinal mucosa disruption in weaned pigs Oxid Med Cell Longev 1–11https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5490743
Acknowledgements
Thanks are given to the Animal Welfare Team of Northeast Agricultural University for supporting this study. All authors thank Lian Chuan-Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Hangzhou, China) for their help in transcriptome sequencing.
Funding
This study was supported by the China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA (Project No. CARS-35-05B).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jun Bao, Honggui Liu, and Jing Wang: conceived and designed the current experiments plans. Jing Wang: wrote the manuscript and completed the experiments. Yutao Li: analyzed these data. Jianxing Wang and Yulai Wang: provided help during animal breeding. Jun Bao and Honggui Liu: revised the whole manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The Animal Ethics Committee approved all procedures in this experiment of Northeast Agricultural University (No. SRM-06).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Li, Y., Wang, J. et al. Selenium Alleviates Ammonia-Induced Splenic Cell Apoptosis and Inflammation by Regulating the Interleukin Family/Death Receptor Axis and Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res 201, 1748–1760 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03279-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03279-3