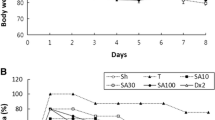
Abstract
Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) are two chronic relapsing inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). Although there are several treatment options available to improve the symptoms of IBD patients, there is no effective treatment that provides a definitive solution. In the present study, we aim to investigate the antioxidative/anti-inflammatory effects of oral administration of boric acid and Bacillus clausii in a rat trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced colitis model. The effects of boric acid and B. clausii were examined in serum and colon tissues with the help of some biochemical and histological analyses. Elevated inflammation and oxidative damage were found in the blood and colon tissue samples in the TNBS-induced group according to the complete blood count (CBC), tumor necrosis factor (TNF) alpha, interleukin-35 (IL-35), malondialdehyde (MDA), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), myeloperoxidase (MPO), nitric oxide (NO), and histological findings. Particularly, the highest IL-35 level (70.09 ± 12.62 ng/mL) in the combined treatment group, highest catalase activity (5322 ± 668.1 U/mg protein) in the TNBS-induced group, and lower relative expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in the TNBS-induced group than the control group were striking findings. According to our results, it can be concluded that boric acid showed more curative effects, even if B. clausii probiotics was partially ameliorative.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Abad C, Martinez C, Juarranz MG, Arranz A, Leceta J, Delgado M, Gomariz RP (2003) Therapeutic effects of vasoactive intestinal peptide in the trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid mice model of Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology 124(4):961–971. https://doi.org/10.1053/gast.2003.50141
Head KA, Jurenka JS (2003) Inflammatory bowel disease part I: ulcerative colitis—pathophysiology and conventional and alternative treatment options. Altern Med Rev 8(3):247–283
Torres J, Mehandru S, Colombel JF, Peyrin-Biroulet L (2017) Crohn’s disease. Lancet 389:1741–1755. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31711-1
de Mattos BRR, Garcia MPG, Nogueira JB, Paiatto LN, Albuguerque CG, Souza C L, Fernandes LGR, Tamashiro WM, Simioni PU (2015) Inflammatory bowel disease: an overview immun mechanisms and biological treatments. Mediators of Inflamm 1-11.https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/493012
Rezaie A, Parker RD, Abdollahi M (2007) Oxidative stress and pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease: an epiphenomenon or the cause? Dig Dis Sci 52(9):2015–2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9622-2
Davies MJ (2011) Myeloperoxidase-derived oxidation: mechanisms of biological damage and its prevention. J Clin Biochem Nutr 48(1):8–19. https://doi.org/10.3164/jcbn.11-006FR
Knowles RG, Moncada S (1994) Nitric oxide synthases in mammals. Biochem J 298:249–258. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj2980249
Nathan C, Xie QW (1994) Nitric oxide synthase: roles, tolls, and controls. Cell 78(6):915–918. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(94)90266-6
Bruckdorfer R (2005) The basics about nitric oxide. Mol Aspects Med 26:3–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2004.09.002
Cross RK, Wilson KT (2003) Nitric oxide in ınflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 9(3):179–189. https://doi.org/10.1097/00054725-200305000-00006
Neurath MF (2014) (2014) Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Immunol 14(5):329–342. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3661]
Catalan-Diebne J, Mclntyre LL, Zlotnik A (2018) Interleukin 30 to interleukin 40. J Interferon Cytokine Res 38(10):423–439. https://doi.org/10.1089/jir.2018.0089
Wirtz S, Billmeier U, Mchedlidze T, Blumberg RS, Neurath MF (2011) Interleukin-35 mediates mucosal immune responses that protect against T-cell–dependent colitis. Gastroentergology 141(5):1875–1886. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2011.07.040
Ardite E, Sans M, Panes J, Romero FJ, Pique JM, Fernandez-Checa JC (2000) Replenishment of glutathione levels improves mucosal function in experimental acute colitis. Lab Invest 80(5):735–744. https://doi.org/10.1038/labinvest.3780077
Tham DM, Whitin JC, Cohen HJ (2002) Increased expression of extracellular glutathione peroxidase in mice with dextran sodium sulfate-ınduced experimental colitis. Pediatr Res 51(5):641–646. https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-200205000-00016
Nieto N, Torres MI, Fernandez MI, Giron MD, Rios A, Suarez MD, Gil A (2000) Experimental ulcerative colitis ımpairs antioxidant defense system in rat intestine. Dig Dis Sci 45(9):1820–1827. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1005565708038
Ghafar H, Yasa N, Mohammadirad A, Dehghan G, Zamani MJ, Nikfar S, Khorasani R, Minaie B, Abdollahi M (2006) Protection by Ziziphora clinopoides of acetic acid-induced toxic bowel inflammation through reduction of cellular lipid peroxidation and myeloperoxidase activity. Hum Exp Toxicol 25(6):325–332. https://doi.org/10.1191/0960327105ht626oa
Kolias G, Valatas V, Ward SG (2004) Nitric oxide in inflammatory bowel disease: a universal messenger in an unsolved puzzle. Immunology 113(4):427–437. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2567.2004.01984.x
Murray FJ (1998) A comparative review of the pharrnacokinetics of boric acid in rodents and humans. Biol Trace Elem Res 66:331–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02783146
Ince S, Kucukkurt I, Cigerci IH, Fidan F, Eryavuz A (2010) The effects of dietary boric acid and borax supplementation on lipid peroxidation, antioxidant activity, and DNA damage in rats. J Trace Elem Med Biol 24(3):161–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2010.01.003
Türkez H, Geyikoğlu F, Tatar A, Keleş S, Özkan A (2007) Effects of some boron compounds on peripheral human blood. Z Naturforsch C J Biosci 62:889–896. https://doi.org/10.1515/znc-2007-11-1218
Kar F, Hacıoğlu C, Özkoç M, Üstünışık N, Bütün A, Uslu S, Kanbak G (2018) The new perspective neuroprotective effect of boric acid against ethanol-induced oxidative damage on synaptosome. J Appl Biol Sci 12(2):28–33
Kar F, Hacioglu C, Senturk H, Donmez Burukoglu D, Kanbak G (2020) The role of oxidative stress, renal inflammation, and apoptosis in post ischemic reperfusion injury of kidney tissue: the protective effect of dose-dependent boric acid administration. Biol Trace Elem Res 195(1):150–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01824-1
Mack DR (2005) Probiotics. Can Fam Physician 51(11):1455–1457
Cutting SM (2011) Bacillus probiotics. Food Microbiol 28(2):214–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2010.03.007
Patel C, Patel P, Acharya S (2020) Therapeutic prospective of a spore-forming probiotic—Bacillus clausii UBBC07 against acetaminophen-induced uremia in rats. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 12(1):253–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-019-09540-x]
Di Caro S, Tao H, Grillo A, Franceschi F, Elia C, Zocco MA, Gasbarrini G, Sepulveda AR, Gasbarrini A (2005) Bacillus clausii effect on gene expression pattern in small bowel mucosa using DNA microarray analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 17(9):951–960. https://doi.org/10.1097/00042737-200509000-00011
Kankuri E, Asmawi MZ, Korpela R, Vapaatalo H, Moilanen E (1991) Induction of iNOS ın a rat model of acute colitis. Inflammation 23(2):141–152. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1020241028723
Ataizi Z, Ozkoc M, Kanbak G, Karimkhani H, Burukoglu Donmez D, Ustunisik N, Ozturk B (2019) Evaluation of the neuroprotective role of boric acid in preventing traumatic brain injury-mediated oxidative stress. Turk Neurosur 1-7.https://doi.org/10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.25692-18.5
Karimkhani H, Özkoç M, Shojaolsadati P, Uzuner K, Burukoglu Donmez D, Kanbak G (2021) Protective effect of boric acid and omega-3 on myocardial infarction in an experimental rat model. Biol Trace Elem Res 199:2612–2620. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02360-z
Can B, Kar F, Kar E, Özkoç M, Şentürk H, Dönmez Burukoğlu D, Kanbak G, Alataş İÖ (2021) Conivaptan and boric acid treatments in acute kidney ınjury: ıs this combination effective and safe? Biol Trace Elem Res 1-15.https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02977-8
Suzuki K, Ota H, Sasagawa S, Sakatani T, Fujikura T (1983) Assay meethod for myeloperoxidase in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Anal Biochem 132(2):345–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(83)90019-2
Cortas NK, Wakid NW (1990) Determination of inorganic nitrate in serum and urine by a kinetic cadmium-reduction method. Clin Chem 36:1440–1443
Ohkawa H, Ohisi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95(2):351–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0076-6879(84)05016-3
Gornall AG, Bardawill CJ, David MM (1949) Determination of serum proteins by means of the biuret reaction. J Biol Chem 177(2):751–766
Cengiz M, Altuner Y, Sahinturk V, Ozden H, Senturk H, Bayramoglu G, Burukoglu Donmez D, Sahin I, Ayhanci A (2012) Lycopene protects liver against ulcerative colitis. Current Drug Therapy 7(1):24–29. https://doi.org/10.2174/157488512800389227
Mateus V, Rocha J, Mota-Filipe H, Sepodes B, Pinto R (2018) Hemin reduces inflammation associated with TNBS-induced colitis. Clin Exp Gastroenterol 11:325–334. https://doi.org/10.2147/CEG.S166197
Fawley J, Gourlay D (2016) Intestinal alkaline phosphatase: a summary of its role in clinical disease. J Sur Res 202(1):225–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2015.12.008
Malo MS, Alam SN, Mostafa G, Zeller SJ, Johnson PV, Mohammad N, Chen KT, Moss AK, Ramasamy S, Faruqui A, Hodin S, Malo PS, Ebrahimi F, Narisawa S, Millan JL, Warren HS, Kaplan JB, Kitts CL, Hohmann EL, Hodin RA (2010) Intestinal alkaline phosphatase preserves the normal homeostasis of gut microbiota. Gut 59(11):1476–1484. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2010.211706
Hoa TH, Duc LH, Isticato R, Baccigalupi L, Ricca E, Van PH, Cutting SM (2011) Fate and sissemination of Bacillus subtilis spores in a murine model. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(9):3819–3823. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.67.9.3819-3823.2001
Togawa JI, Nagase H, Tanaka K, Inamori M, Nakajima A, Ueno N, Saito T, Sekihara H (2002) Oral administration of lactoferrin reduces colitis in rats via modulation of the immune system and correction of cytokine imbalance. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 17(12):1291–1298. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-1746.2002.02868.x
Liu L, Yuan S, Sun Y, Long Y, Li Y, Niu Y, Li C, Gan H, Cao S, Mei Q (2009) The possible mechanisms of Fructus Mume pill in the treatment of colitis induced by 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 126(2):557–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2009.08.013
Larrosa M, Yanez-Gascon M, Selma M, Gonzalez-Sarrisa A, Toti S, Ceron J, Tomas-Barberan F, Dolara P, Espin JC (2009) Effect of a low dose of dietary resveratrol on colon microbiota, inflammation and tissue damage in a DSS-induced colitis rat model. J Agric Food Chem 57(6):2211–2220. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf803638d
Celikbilek M, Dogan S, Ozbakır O, Zararsız G, Kücük H, Gürsoy S, Yurci A, Güven K, Yücesoy M (2013) Neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of disease severity in ulcerative colitis. J Clin Lab Anal 27(1):72–76. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.21564
Idiz UO, Aysan E, Firat D, Ercan C, Demirci S, Sahin F (2019) Effects of boric acid-linked ampicillin on the rat intra-abdominal sepsis model. Pak J Pharm Sci 32(2):477–481
Herias MV, Koninkx J, Vos J, Huis in’t Veld J, van Dijk J, (2005) Probiotic effects of Lactobacillus casei on DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in mice. Int J Food Microbiol 103(2):143–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2004.11.032
Garside P (1991) Cytokines in experimental colitis. Clin Exp Immunol 118(3):337–339. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.01088.x
Xu C-L, Guo Y, Qiao L, Ma L, Cheng Y-Y (2018) Recombinant expressed vasoactive intestinal peptide analogue ameliorates TNBS-induced colitis in rats. World J Gastroenterol 24(6):706–715. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i6.706
Collison LW, Workman CJ, Kuo TT, Boyd K, Wang Y, Vignali KM, Cross R, Sehy D, Blumberg RS, Vignali DAA (2007) The inhibitory cytokine IL-35 contributes to regulatory T-cell function. Nature 450:566–569. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06306
Zhang B, Liu Y, Lan X, Zhang X, Li X, Zhao Y, Li G, Du C, Lu S, Wang H (2018) Oral Escherichia coli expressing IL-35 meliorates experimental colitis in mice. J Transl Med 16(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-018-1441-7
Nan Z, Fan H, Tang Q, Zhang M, Xu M, Chen Q, Liu Y, Dong Y, Wu H, Deng S (2018) Dual expression of CXCR4 and IL-35 enhances the therapeutic effects of BMSCs on TNBS-induced colitis in rats through expansion of Tregs and suppression of Th17 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 499(4):727–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.03.043
Cao J, Jiang L, Zhang X, Yao X, Geng C, Xue X, Zhong L (2008) Boric acid inhibits LPS-induced TNF-a formation through a thiol-dependent mechanism in THP-1 cells. J Trace Elem Med Biol 22(3):189–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2008.03.005
Dargahi N, Johnson J, Donkor O, Vasiljevic T, Apostolopoulos V (2019) Immunomodulatory effects of probiotics: can they be used to treat allergiesand autoimmune diseases? Maturitas 119:25–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2018.11.002
Dar HY, Pal S, Shukla P, Mishra PK, Tomar GB, Chattopadhyay N, Srivastava RK (2018) Bacillus clausii inhibits bone loss by skewing Treg-Th17 cell equilibrium in postmenopausal osteoporotic mice model. Nutrition 54:118–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2018.02.013
Ancha HR, Kurella RR, McKimmey CC, Lightfoot S, Harty RF (2009) Effects of n-acetylcysteine plus mesalamine on prostaglandin synthesis and nitric oxide generation in TNBS-induced colitis in rats. Dig Dis Sci 54(Suppl 4):758–766. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-008-0438-0
Avdagić N, Zaćiragić A, Babić N, Hukić M, Šeremet M, Lepara O, Nakaš-Ićindić E (2013) Nitric oxide as a potential biomarker in inflammatory bowel disease. Bosn J Basic Med Sci 13(1):5–9. https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2013.2402
Urdaci MC, Bressollier P, Pinchuk I (2004) Bacillus clausii probiotic strains: antimicrobial and immunomodulatory activities. J Clin Gastroenterol 38(3):86–90. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mcg.0000128925.06662.69
Li XL, Cai YQ, Qin H, Wu YJ (2008) Therapeutic effect and mechanism of proanthocyanidins from grape seeds in rats with TNBS-induced ulcerative colitis. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 86(12):841–849. https://doi.org/10.1139/Y08-089
Liu X, Wang J (2011) Anti-inflammatory effects of iridoid glycosides fraction of Folium syringae leaves on TNBS-induced colitis in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 133(2):780–787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2010.11.010
Tabari MV, Moein S, Qujeq D, Kashifard M, Shirvani JS, Tilaki KH, Farshidfar G (2017) Evaluation of the potential antioxidant role of high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-c) in patients with ulcerative colitis. Ann Colorectal Res 1-6.https://doi.org/10.5812/acr.13699
Xu M, Tao J, Yang Y, Tan S, Liu H, Jiang J, Zheng F, Wu B (2020) Ferroptosis involves in intestinal epithelial cell death in ulcerative colitis. Cell Death Dis 11:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2299-1
Cengiz M (2018) Boric acid protects against cyclophosphamide-induced oxidative stress and renal damage in rats. Cell Mol Biol 64(12):11–14
Ince S, Keles H, Erdogan M, Hazman O, Kucukkurt I (2012) Protective effect of boric acid against carbon tetrachloride–induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Drug Chem Toxicol 35(3):285–292. https://doi.org/10.3109/01480545.2011.607825
Sogut I, Oglakci A, Kartkaya K, Kusat Ol K, Savasan Sogut M, Kanbak G, Erden Inal M (2015) Effect of boric acid on oxidative stress in rats with fetal alcohol syndrome. Exp Ther Med 9(3):1023–1027. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2014.2164
Catinean A, Neag MA, Krishnan K, Muntean DM, Bocsan CI, Pop RM, Mitre AO, Melincovici CS, Buzoianu AD (2020) Probiotic Bacillus spores together with amino acids and immunoglobulins exert protective effects on a rat model of ulcerative colitis. Nutrients 12(12):1–18. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12123607
Izawa S, Inoue Y, Kimura A (1996) Importance of catalase in the adaptive response to hydrogen peroxide: analysis of acatalasaemic Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem J 320:61–67. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj3200061
Tehrani SH, Moosavi-Movahedi AA (2018) Catalase and its mysteries. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 140:5–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2018.03.001
Esworthy RS, Binder SW, Doroshow JH, Chu FF (2003) Microflora trigger colitis in mice deficient in selenium gene expression. Biol Chem 384(4):597–607. https://doi.org/10.1515/BC.2003.067
Häuser F, Rossmann H, Laubert-Reh D, Wild PS, Zeller T, Müller C, Neuwirth S, Blankenberg S, Lackner KJ (2015) Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) locus 12: is glutathione peroxidase-1 (GPX1) the relevant gene? Genes Immun 16(8):571–575. https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2015.35
Lee IA, Hyun YJ, Kim DH (2010) Berberine ameliorates TNBS-induced colitis by inhibiting lipid peroxidation, enterobacterial growth and NF-κB activation. Eur J Pharmacol 648:162–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.08.046
Yildiz G, Yildiz Y, Ulutas PA, Yaylali A, Ural M (2015) Resveratrol pretreatment ameliorates TNBS colitis in rats. Recent Pat Endocr Metab Immune Drug Discov 9(2):134–140. https://doi.org/10.2174/1872214809666150806105737
Colares JR, Schemitt EG, Hartmann RM, Moura RM, Morgan-Martins MI, Fillmann HS, Fillmann L, Marroni NP (2016) Effect of lecithin on oxidative stress in an experimental model of colitis rats induced by acetic acid. J Coloproctol 36(2):97–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcol.2016.03.002
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Director and workers of the Medical and Surgical Experimental Research Centre of the University for their kind cooperation throughout the animal care.
Funding
This project was financially supported by the Scientific Research Projects Commission of the Eskisehir Osmangazi University (Eskişehir, Turkey) (Project #202011D03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Özkoç M. and Kanbak G. designed the study; Özkoç M., Can B., and Şentürk H. performed surgical operations; Özkoç M. and Can B. performed the biochemical experiments, acquired and analyzed data; Özkoç M. and Kanbak G. interpreted the biochemical data; Dönmez Burukoğlu D. carried out the histological experiments and interpreted the histologic data; Özkoç M. wrote the manuscript; all authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
All animal research protocols in this study were approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee (HADYEK, Protocol # 778/2019).
Consent for Publication
All authors have given consent for the manuscript to be published by the corresponding author.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Özkoç, M., Can, B., Şentürk, H. et al. Possible Curative Effects of Boric Acid and Bacillus clausii Treatments on TNBS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 201, 1237–1251 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03215-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03215-5