Abstract
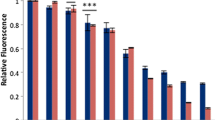
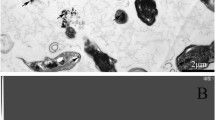
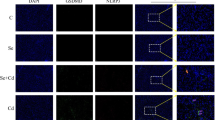
Hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)] is one of the most common environmental contaminants caused by its broad industrial applications. Importantly, exposure to Cr(VI) induces oxidative damage and apoptosis in animal cells. Studies have shown that selenium (Se) can alleviate the toxic effects of Cr(VI) by functioning as an antioxidant and/or by chelating Cr(VI) into biologically inert complexes, but the underlying mechanism remains unknown. Here, we evaluated whether Se can ameliorate ileum damage and cecal microbial disturbances induced by Cr(VI) in vivo. Mice administered Cr(VI) for 30 days presented histopathological damage, reduced responses to oxidative stress, and increased expression of apoptosis-related genes in the ileum compared with those in the control (non-exposed) group. Se alleviated the histopathological damage and decreased the oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by Cr(VI) in the ileum. In addition, Cr(VI) disturbed cecal microflora, and it was partially reversed by Se treatment. These findings demonstrate that the damaging and potentially pathological effects of Cr(VI) on the ileum and cecal microflora can be effectively alleviated with Se treatment.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wakeel A, Xu M, Gan Y (2020) Chromium-induced reactive oxygen species accumulation by altering the enzymatic antioxidant system and associated cytotoxic, genotoxic, ultrastructural, and photosynthetic changes in plants. Int J Mol Sci 21(3):728
Bza B, Gd A, Yfb C, Xuan DA, Yybc D, Kh A (2020) Selenium(VI) alleviates chromium-induced toxicity in the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Environ Pollut 272: 116407
Kafilzadeh F, Saberifard S (2016) Isolation and identification of chromium (VI)-resistant bacteria from Soltan Abad River sediments (Shiraz-Iran). Jundishapur J Health Sci 8(1):e33576
Bagchi D, Stohs SJ, Downs BW, Bagchi M, Preuss HG (2002) Cytotoxicity and oxidative mechanisms of different forms of chromium. Toxicology 180(1):5–22
Zhu Y, Wang L, Yu X, Jiang S, Liu J (2021) Cr(VI) promotes tight joint and oxidative damage by activating the Nrf2/ROS/Notch1 axis. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 85:103640
Son YO, Hitron JA, Shi X (2013) Chromium(VI), oxidative cell damage. Springer, New York
Marouani N, Tebourbi O, Hallègue D, Mokni M, Yacoubi MT, Sakly M, Benkhalifa M, Rhouma KB (2017) Mechanisms of chromium hexavalent-induced apoptosis in rat testes. Toxicol Ind Health 33(2):97–106
Zhang S, Zhao X, Hao J, Zhu Y, Wang Y, Wang L, Guo S, Yi H, Liu Y, Liu J (2020) The role of ATF6 in Cr(VI)-induced apoptosis in DF-1 cells. J Hazard Mater 410:124607
Ge H, Li Z, Jiang L, Li Q, Geng C, Yao X, Shi X, Liu Y, Cao J (2018) Cr (VI) induces crosstalk between apoptosis and autophagy through endoplasmic reticulum stress in A549 cells. Chemico Biological Interactions 298:35–42
Tang S, Ye S, Ma Y, Liang Y, Xiao F (2020) Clusterin alleviates Cr(VI)-induced mitochondrial apoptosis in L02 hepatocytes via inhibition of Ca2+-ROS-Drp1-mitochondrial fission axis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 205:111326
Weiss GA, Hennet T (2017) Mechanisms and consequences of intestinal dysbiosis. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS 74(16):2959–2977
Zhang W, Guo R, Yang Y, Ding J, Zhang Y (2016) Long-term effect of heavy-metal pollution on diversity of gastrointestinal microbial community of Bufo raddei. Toxicol Lett 258:192–197
Liu Y, Li Y, Liu K, Shen J (2014) Exposing to cadmium stress cause profound toxic effect on microbiota of the mice intestinal tract. Plos One 9(2):e85323
Zwolak I, Zaporowska H (2011) Selenium interactions and toxicity: a review. Cell Biol Toxicol 28(1):31–46
Zwolak I (2019) The role of selenium in arsenic and cadmium toxicity: an updated review of scientific literature. Biol Trace Elem Res 193(1):44–63
Elwej A, Ghorbel I, Chaabane M, Soudani N, Marrekchi R, Jamoussi K, Mnif H, Boudawara T, Zeghal N, Sefi M (2017) Protective effects of dietary selenium and vitamin C in barium-induced cardiotoxicity. Hum Exp Toxicol 36(11):1146–1157
Freitas A, Funck VR, Rotta M, Bohrer D, Mörschbächer V, Puntel RL, Nogueira CW, Farina M, Aschner M, Rocha JB (2009) Diphenyl diselenide, a simple organoselenium compound, decreases methylmercury-induced cerebral, hepatic and renal oxidative stress and mercury deposition in adult mice. Brain Res Bull 79(1):77–84
Li X, Xing M, Chen M, Zhao J, Xu S (2017) Effects of selenium-lead interaction on the gene expression of inflammatory factors and selenoproteins in chicken neutrophils. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 139:447–453
Hao P, Zhu Y, Wang S, Wan H, Chen P, Wang Y, Cheng Z, Liu Y, Liu J (2017) Selenium administration alleviates toxicity of chromium(VI) in the chicken brain. Biol Trace Elem Res 178(1):127–135
Kubachka KM, Hanley T, Mantha M, Wilson RA, Caruso J (2017) Evaluation of selenium in dietary supplements using elemental speciation. Food Chem 218:313–320
Boşgelmez Iİ, Güvendik G (2017) N-Acetyl-L-cysteine protects liver and kidney against chromium(VI)-Induced oxidative stress in mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 178(1):44–53
Ueno S, Susa N, Furukawa Y, Sugiyama M (1995) Formation of paramagnetic chromium in liver of mice treated with dichromate (VI). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 135(2):165–171
Luo J, Li X, Li X, He Y, Zhang M, Cao C, Wang K (2018) Selenium-rich yeast protects against aluminum-induced peroxidation of lipide and inflammation in mice liver. Biometals 31(6):1051–1059
Krohn RM, Lemaire M, Silva L, Lemarié C, Smits JE (2016) High-selenium lentil diet protects against arsenic-induced atherosclerosis in a mouse model. J Nutr Biochem 27:9–15
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Liu L, Lin L, Zheng L, Tang H, Fan X, Xue N, Min L, Min L, Li X (2018) Cecal microbiome profile altered by Salmonella enterica, serovar Enteritidis inoculation in chicken. Gut Pathogens 10:34
Sakaki T, Takeshima T, Tominaga M, Hashimoto H, Kawaguchi S (1994) Recurrence of ICA-PCoA aneurysms after neck clipping. J Neurosurg 80(1):58–63
Liu X, Zou Y, Ruan M, Chang L, Chen X, Wang S, Yang W, Zhang L, Guo Y, Chen Y, Zhang Y, He H, Gan Y, Wang K, Zhu X (2020) Pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients exhibit distinctive alterations in the gut microbiota. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 10:558799
Segata N, Izard J, Waldron L, Gevers D, Miropolsky L, Garrett WS, Huttenhower C (2011) Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol 12(6):R60
Parks DH, Tyson GW, Philip H, Beiko RG (2014) STAMP: statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 30(21):3123–3124
Zhang Z, Cao H, Song N, Zhang L, Tai J (2020) Long-term hexavalent chromium exposure facilitates colorectal cancer in mice associated with changes in gut microbiota composition. Food Chem Toxicol 138:111237
Bagchi D, Bagchi M, Stohs SJ (2001) Chromium (vi)-induced oxidative stress, apoptotic Cell death and modulation of p53 tumor suppressor Gene. Springer US 222(1–2):149–158
Wang XF, Xing ML, Shen Y, Zhu X, Xu LH (2006) Oral administration of Cr(VI) induced oxidative stress, DNA damage and apoptotic cell death in mice. Toxicology 228(1):16–23
Wang Y, Liu Y,Wan H, Zhu Y, Chen P, Hao P, Cheng Z, Liu J (2017) Moderate selenium dosing inhibited chromium (VI) toxicity in chicken liver. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 31(8):1–8
Son YO, Hitron JA, Wang X, Chang Q, Pan J, Zhuo Z, Liu J, Wang S, Lee JC, Shi X (2010) Cr(VI) induces mitochondrial-mediated and caspase-dependent apoptosis through reactive oxygen species-mediated p53 activation in JB6 Cl41 cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 245(2):226–235
Lee KB, Kim KR, Huh TL, Lee YM (2008) Proton induces apoptosis of hypoxic tumor cells by the p53-dependent and p38/JNK MAPK signaling pathways. Int J Oncol 33(6):1247–1256
Granville DJ, Gottlieb RA (2002) Mitochondria: regulators of cell death and survival. Scientific World Journal 2:1569–1578
Liang S, Sun K, Wang Y, Dong S, Wang C, Liu L, Wu Y (2016) Role of Cyt-C/caspases-9,3, Bax/Bcl-2 and the FAS death receptor pathway in apoptosis induced by zinc oxide nanoparticles in human aortic endothelial cells and the protective effect by alpha-lipoic acid. Chem Biol Interact 258:40–51
Liu G, Wang ZK, Wang ZY, Yang DB, Liu ZP, Wang L (2016) Mitochondrial permeability transition and its regulatory components are implicated in apoptosis of primary cultures of rat proximal tubular cells exposed to lead. Arch Toxicol 90(5):1193–1209
Feng M, Yin H, Peng H, Liu Z, Lu G, Dang Z (2017) Hexavalent chromium induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in Pycnoporus sanguineus. Environ Pollut 228:128–139
Yao Q, Yang H, Wang X, Wang H (2019) Effects of hexavalent chromium on intestinal histology and microbiota in Bufo gargarizans tadpoles. Chemosphere 216:313–323
Hu S, Wang J, Xu Y, Yang H, Wang J, Xue C, Yan X, Su L (2019) Anti-inflammation effects of fucosylated chondroitin sulphate from Acaudina molpadioides by altering gut microbiota in obese mice. Food Funct 10(3):1736–1746
Wu X, Pan S, Luo W, Shen Z, Meng X, Xiao M, Tan B, Nie K, Tong T, Wang X (2020) Roseburiaintestinalisderived flagellin ameliorates colitis by targeting miR-223-3p-mediated activation of NLRP3 inflammasome and pyroptosis. Mol Med Rep 22(4):2695–2704
Strati F, Cavalieri D, Albanese D, De Felice C, Donati C, Hayek J, Jousson O, Leoncini S, Renzi D, Calabrò A, De Filippo C (2017) New evidences on the altered gut microbiota in autism spectrum disorders. Microbiome 5(1):24
Goldstein EJ, Tyrrell KL, Citron DM (2015) Lactobacillus species: taxonomic complexity and controversial susceptibilities. Clin Infect Dis 60(Suppl 2):S98-107
Earle KA, Billings G, Sigal M, Lichtman JS, Hansson GC, Elias JE, Amieva MR, Huang KC, Sonnenburg JL (2015) Quantitative imaging of gut microbiota spatial organization. Cell Host Microbe 18(4):478–488
Huang H, Wang Y, An Y, Jiao W, Xu Y, Han Q, Teng X, Teng X (2019) Selenium alleviates oxidative stress and autophagy in lead-treated chicken testes. Theriogenology 131:146–152
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China(31802248), Science and Technology Innovation Project of Universities in Shanxi Province (2019L0361), fund for introducing talents and doctoral research of the Shanxi Agricultural University (2017YJ08), and the Shanxi Province Outstanding Doctor Award Fund (SXYBKY201750).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
All animal experimental procedures were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the Shanxi Agricultural University.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Zhang, H., Hao, D. et al. Selenium Alleviates Chromium(VI)-Induced Ileum Damage and Cecal Microbial Disturbances in Mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 200, 4750–4761 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-03061-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-03061-x