Abstract
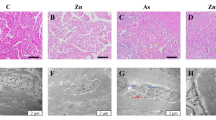
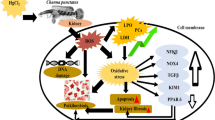
Arsenic (As) pollution is ubiquitous in water, which shows immunotoxicity to aquatic organisms. As an indispensable regulator of gene transcription and enzymatic modification, zinc (Zn) may play a preventive and therapeutic effect on As toxicity. The purpose of this study was to investigate the interactions of As and Zn on the head kidney of common carp Cyprinus carpio. Herein the carp were treated alone or in combination with waterborne As3+ (2.83 mg/L) and/or Zn2+ (1 mg/L). Results suggested a head kidney-toxic effect of As exposure, which was manifested by the histopathological damage of the head kidney, elevation of nuclear translocation of pro-inflammatory nuclear factor-kappa light chain enhancer of B cells (NF-κB), and blockage of the anti-oxidative nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway. The global activation of three endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress pathways led to the execution of programmed cell death, including ER apoptosis mediated by C/EBP-homologous protein (CHOP), death receptor–mediated exogenous cell apoptosis, and the endogenous apoptosis executed by Caspases9. The combined application of Zn can significantly improve the histopathological damage of the head kidney, the imbalance of the antioxidant system, and the apoptosis outcomes due to ER stress. In conclusion, this study indicates that Zn has an antagonistic effect on the head kidney injury of common carp induced by sub-chronic As exposure. The results of this study provide basic data for the risk assessment of As accumulation in an aquatic environment and a reference for the use of Zn preparation in aquaculture.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Anvarifar H, Amirkolaie AK, Jalali AM, Miandare HK, Sayed AH, Ucuncu SI, Ouraji H, Ceci M, Romano N (2018) Environmental pollution and toxic substances: cellular apoptosis as a key parameter in a sensible model like fish. Aquat Toxicol 204:144–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2018.09.010
Wang Y, Zhao H, Guo M, Fei D, Zhang L, Xing M (2020) Targeting the miR-122/PKM2 autophagy axis relieves arsenic stress. J Hazard Mater 383:121217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121217
Li Y, Gao Y, Zhao L, Wei Y, Feng H, Wang C, Wei W, Ding Y, Sun D (2012) Changes in serum thioredoxin among individuals chronically exposed to arsenic in drinking water. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 259(1):124–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2011.12.016
Gibb HJ, Barchowsky A, Bellinger D, Bolger PM, Carrington C, Havelaar AH, Oberoi S, Zang Y, O’Leary K, Devleesschauwer B (2019) Estimates of the 2015 global and regional disease burden from four foodborne metals - arsenic, cadmium, lead and methylmercury. Environ Res 174:188–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2018.12.062
Sambu S, Wilson R (2008) Arsenic in food and water–a brief history. Toxicol Ind Health 24(4):217–226. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233708094096
Taylor V, Goodale B, Raab A, Schwerdtle T, Reimer K, Conklin S, Karagas MR, Francesconi KA (2017) Human exposure to organic arsenic species from seafood. Sci Total Environ 580:266–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.113
Wang X, Liu L, Wang X, Ren J, Jia P, Fan W (2020) Influence of humic acid on arsenic bioaccumulation and biotransformation to zebrafish: a comparative study between As(III) and As(V) exposure. Environ Pollut 256:113459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113459
Zhao H, Wang Y, Fei D, Guo M, Yang X, Mu M, Yu H, Xing M (2019) Destruction of redox and mitochondrial dynamics co-contributes to programmed cell death in chicken kidney under arsenite or/and copper (II) exposure. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 179:167–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.04.062
Wang Y, Gu YH, Liu M, Bai Y, Liang LY, Wang HL (2017) TBHQ alleviated endoplasmic reticulum stress-apoptosis and oxidative stress by PERK-Nrf2 crosstalk in methamphetamine-induced chronic pulmonary toxicity. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017:4310475. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4310475
Zhu YF, Li XH, Yuan ZP, Li CY, Tian RB, Jia W, Xiao ZP (2015) Allicin improves endoplasmic reticulum stress-related cognitive deficits via PERK/Nrf2 antioxidative signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 762:239–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.06.002
Wang Y, Zhao H, Liu Y, Nie X, Xing M (2020) Zinc exerts its renal protection effect on arsenic-exposed common carp: a signaling network comprising Nrf2, NF-kappaB and MAPK pathways. Fish Shellfish Immunol 104:383–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2020.06.031
Arnold MG, Gokulan K, Doerge DR, Vanlandingham M, Cerniglia CE, Khare S (2019) A single or short time repeated arsenic oral exposure in mice impacts mRNA expression for signaling and immunity related genes in the gut. Food Chem Toxicol 132:110597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2019.110597
Wang Y, Zhao H, Liu Y, Li J, Nie X, Huang P, Xing M (2021) Environmentally relevant concentration of sulfamethoxazole-induced oxidative stress-cascaded damages in the intestine of grass carp and the therapeutic application of exogenous lycopene. Environ Pollut 274:116597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116597
Zhao H, Wang Y, Liu Y, Yin K, Wang D, Li B, Yu H, Xing M (2021) ROS-induced hepatotoxicity under cypermethrin: involvement of the crosstalk between Nrf2/Keap1 and NF-kappaB/ikappaB-alpha pathways regulated by proteasome. Environ Sci Technol 55(9):6171–6183. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c00515
Liu Q, Yang J, Gong Y, Cai J, Zheng Y, Zhang Y, Yu D, Zhang Z (2020) MicroRNA profiling identifies biomarkers in head kidneys of common carp exposed to cadmium. Chemosphere 247:125901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.125901
Zhang Z, Zheng Z, Cai J, Liu Q, Yang J, Gong Y, Wu M, Shen Q, Xu S (2017) Effect of cadmium on oxidative stress and immune function of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) by transcriptome analysis. Aquat Toxicol 192:171–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2017.09.022
Zhang M, Wan K, Zeng J, Lin W, Ye C, Yu X (2020) Co-selection and stability of bacterial antibiotic resistance by arsenic pollution accidents in source water. Environ Int 135:105351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.105351
Chouchene L, Pellegrini E, Gueguen MM, Hinfray N, Brion F, Piccini B, Kah O, Said K, Messaoudi I, Pakdel F (2016) Inhibitory effect of cadmium on estrogen signaling in zebrafish brain and protection by zinc. J Appl Toxicol 36(6):863–871. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.3285
Jihen EH, Fatima H, Nouha A, Baati T, Imed M, Abdelhamid K (2010) Cadmium retention increase: a probable key mechanism of the protective effect of zinc on cadmium-induced toxicity in the kidney. Toxicol Lett 196(2):104–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2010.04.006
Zhao H, Wang Y, Liu J, Guo M, Fei D, Yu H, Xing M (2019) The cardiotoxicity of the common carp (Cyprinus carpio) exposed to environmentally relevant concentrations of arsenic and subsequently relieved by zinc supplementation. Environ Pollut 253:741–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.07.065
Castaldo G, Pillet M, Slootmaekers B, Bervoets L, Town RM, Blust R, De Boeck G (2020) Investigating the effects of a sub-lethal metal mixture of Cu, Zn and Cd on bioaccumulation and ionoregulation in common carp Cyprinus carpio. Aquat Toxicol 218:105363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.105363
Vutukuru SS, Prabhath NA, Raghavender M, Yerramilli A (2007) Effect of arsenic and chromium on the serum amino-transferases activity in Indian major carp, Labeo rohita. Int J Environ Res Public Health 4(3):224–227. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph2007030005
Malekpouri P, Moshtaghie AA, Kazemian M, Soltani M (2011) Protective effect of zinc on related parameters to bone metabolism in common carp fish (Cyprinus carpio L.) intoxified with cadmium. Fish Physiol Biochem 37(1):187–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-010-9430-7
Altikat S, Uysal K, Kuru HI, Kavasoglu M, Ozturk GN, Kucuk A (2015) The effect of arsenic on some antioxidant enzyme activities and lipid peroxidation in various tissues of mirror carp (Cyprinus carpio carpio). Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22(5):3212–3218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2896-6
Venturalima J, Fattorini D, Regoli F, Monserrat JM (2009) Effects of different inorganic arsenic species in Cyprinus carpio (Cyprinidae) tissues after short-time exposure: bioaccumulation, biotransformation and biological responses. Environ Pollut 157(12):3479–3484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2009.06.023
Nie X, Wang Y, Zhao H, Guo M, Liu Y, Xing M (2020) As(3+) or/and Cu(2+) exposure triggers oxidative stress imbalance, induces inflammatory response and apoptosis in chicken brain. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 203:110993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110993
Ryan JA, Hightower LE (2010) Evaluation of heavy-metal ion toxicity in fish cells using a combined stress protein and cytotoxicity assay. Environ Toxicol Chem 13(8):1231–1240. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620130804
Saydam N, Georgiev O, Nakano MY, Greber UF, Schaffner W (2001) Nucleo-cytoplasmic trafficking of metal-regulatory transcription factor 1 is regulated by diverse stress signals. J Biol Chem 276(27):25487–25495. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M009154200
Giudice G, Sconzo G, Roccheri MC (1999) Studies on heat shock proteins in sea urchin development. Dev Growth Differ 41(4):375–380. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-169x.1999.00450.x
Wang Z, Xu Z, Wu Y, Zhang Z, Li X (2020) Impact of ketamine on the behavior and immune system of adult medaka (Oryzias latipes) at environmentally relevant concentrations and eco-risk assessment in surface water. J Hazard Mater 393:121577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121577
Verfaillie T, Rubio N, Garg AD, Bultynck G, Rizzuto R, Decuypere JP, Piette J, Linehan C, Gupta S, Samali A, Agostinis P (2012) PERK is required at the ER-mitochondrial contact sites to convey apoptosis after ROS-based ER stress. Cell Death Differ 19(11):1880–1891. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2012.74
Martucciello S, Masullo M, Cerulli A, Piacente S (2020) Natural products targeting ER stress, and the functional link to mitochondria. Int J Mol Sci 21(6) https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21061905
Zhao H, Wang Y, Guo M, Mu M, Yu H, Xing M (2020) Grass carps co-exposed to environmentally relevant concentrations of cypermethrin and sulfamethoxazole bear immunodeficiency and are vulnerable to subsequent Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Environ Pollut 266(Pt 3):115156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115156
Varol S, Kose I (2018) Effect on human health of the arsenic pollution and hydrogeochemistry of the Yazir Lake wetland (Cavdir-Burdur/Turkey). Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25(16):16217–16235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1815-7
Biswas S, Banna HU, Jahan M, Anjum A, Siddique AE, Roy A, Nikkon F, Salam KA, Haque A, Himeno S, Hossain K, Saud ZA (2020) In vivo evaluation of arsenic-associated behavioral and biochemical alterations in F0 and F1 mice. Chemosphere 245:125619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125619
Cai Z, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Miao X, Li S, Yang H, Ling Q, Hoffmann PR, Huang Z (2019) Use of a mouse model and human umbilical vein endothelial cells to investigate the effect of arsenic exposure on vascular endothelial function and the associated role of calpains. Environ Health Perspect 127(7):77003. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP4538
Wang Y, Zhao H, Shao Y, Liu J, Li J, Xing M (2017) Copper or/and arsenic induce oxidative stress-cascaded, nuclear factor kappa B-dependent inflammation and immune imbalance, trigging heat shock response in the kidney of chicken. Oncotarget 8(58):98103–98116. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.21463
Liu J, Kadiiska MB, Liu Y, Lu T, Qu W, Waalkes MP (2001) Stress-related gene expression in mice treated with inorganic arsenicals. Toxicol Sci 61(2):314–320. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/61.2.314
Zhou P, Kalakonda N, Comenzo RL (2005) Changes in gene expression profiles of multiple myeloma cells induced by arsenic trioxide (ATO): possible mechanisms to explain ATO resistance in vivo. Br J Haematol 128(5):636–644. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.2005.05369.x
Rahman MA, Hasegawa H, Lim RP (2012) Bioaccumulation, biotransformation and trophic transfer of arsenic in the aquatic food chain. Environ Res 116:118–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2012.03.014
Zhao H, Wang Y, Yang X, Fei D, Mu M, Guo M, Yu H, Xing M (2019) Zinc alleviates arsenism in common carp: varied change profiles of cytokines and tight junction proteins among two intestinal segments. Fish Shellfish Immunol 94:761–768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2019.09.069
Zhang Q, Zheng S, Wang S, Wang W, Xing H, Xu S (2019) Chlorpyrifos induced oxidative stress to promote apoptosis and autophagy through the regulation of miR-19a-AMPK axis in common carp. Fish Shellfish Immunol 93:1093–1099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2019.07.022
Ghosh D, Datta S, Bhattacharya S, Mazumder S (2007) Long-term exposure to arsenic affects head kidney and impairs humoral immune responses of Clarias batrachus. Aquat Toxicol 81(1):79–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2006.11.004
Freitas R, Fraga C (2018) NF-kappaB-IKKbeta pathway as a target for drug development: realities, challenges and perspectives. Curr Drug Targets 19(16):1933–1942. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389450119666180219120534
Hunto ST, Kim HG, Baek KS, Jeong D, Kim E, Kim JH, Cho JY (2020) Loratadine, an antihistamine drug, exhibits anti-inflammatory activity through suppression of the NF-kB pathway. Biochem Pharmacol 177:113949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2020.113949
van Eden W, van der Zee R, Prakken B (2005) Heat-shock proteins induce T-cell regulation of chronic inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 5(4):318–330. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri1593
Patni H, Mathew JT, Luan L, Franki N, Chander PN, Singhal PC (2007) Aldosterone promotes proximal tubular cell apoptosis: role of oxidative stress. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 293(4):F1065–F1071. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00147.2007
Chen H, Liu G, Qiao N, Kang Z, Hu L, Liao J, Yang F, Pang C, Liu B, Zeng Q, Li Y, Li Y (2020) Toxic effects of arsenic trioxide on spermatogonia are associated with oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, autophagy and metabolomic alterations. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 190:110063. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110063
Song YF, Hogstrand C, Wei CC, Wu K, Pan YX, Luo Z (2017) Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and cAMP/PKA pathway mediated Zn-induced hepatic lipolysis. Environ Pollut 228:256–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.05.046
Delaney P, Ramdas NA, Palmer C, Khan N, Sadler KC (2020) Arsenic induced redox imbalance triggers the unfolded protein response in the liver of zebrafish. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 409:115307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2020.115307
Wang Y, Zhao H, Mu M, Guo M, Xing M (2021) Zinc offers splenic protection through suppressing PERK/IRE1-driven apoptosis pathway in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) under arsenic stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 208:111473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111473
Delaunay-Moisan A, Appenzeller-Herzog C (2015) The antioxidant machinery of the endoplasmic reticulum: protection and signaling. Free Radic Biol Med 83:341–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.02.019
Zhao H, Wang Y, Guo M, Liu Y, Yu H, Xing M (2021) Environmentally relevant concentration of cypermethrin or/and sulfamethoxazole induce neurotoxicity of grass carp: involvement of blood-brain barrier, oxidative stress and apoptosis. Sci Total Environ 762:143054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143054
Zhang Y, Wei Z, Liu W, Wang J, He X, Huang H, Zhang J, Yang Z (2017) Melatonin protects against arsenic trioxide-induced liver injury by the upregulation of Nrf2 expression through the activation of PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncotarget 8(3):3773–3780. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.13931
Ikeyama S, Kusumoto K, Miyake H, Rokutan K, Tashiro S (2001) A non-toxic heat shock protein 70 inducer, geranylgeranylacetone, suppresses apoptosis of cultured rat hepatocytes caused by hydrogen peroxide and ethanol. J Hepatol 35(1):53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-8278(01)00053-8
Shin MK, Jeong KH, Choi H, Ahn HJ, Lee MH (2018) Heat shock protein 90 inhibitor enhances apoptosis by inhibiting the AKT pathway in thermal-stimulated SK-MEL-2 human melanoma cell line. J Dermatol Sci 90(3):357–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2018.02.004
Del RL, Quintanilla-Vega B, Brambila-Colombres E, Calderon-Aranda ES, Manno M, Albores A (2001) Stress proteins induced by arsenic. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 177(2):132–148. https://doi.org/10.1006/taap.2001.9291
Lau AT, He QY, Chiu JF (2004) A proteome analysis of the arsenite response in cultured lung cells: evidence for in vitro oxidative stress-induced apoptosis. Biochem J 382(Pt 2):641–650. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20040224
Jia R, Du J, Cao L, Feng W, He Q, Xu P, Yin G (2020) Chronic exposure of hydrogen peroxide alters redox state, apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquat Toxicol 229:105657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2020.105657
Wang X, Zhuang Y, Fang Y, Cao H, Zhang C, Xing C, Guo X, Li G, Liu P, Hu G, Yang F (2021) Endoplasmic reticulum stress aggravates copper-induced apoptosis via the PERK/ATF4/CHOP signaling pathway in duck renal tubular epithelial cells. Environ Pollut 272:115981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115981
Ron D, Walter P (2007) Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8(7):519–529. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2199
Verfaillie T, Garg AD, Agostinis P (2013) Targeting ER stress induced apoptosis and inflammation in cancer. Cancer Lett 332(2):249–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2010.07.016
Gao D, Xu Z, Zhang X, Wang H, Wang Y, Min W (2013) Molecular cloning, immunohistochemical localization, characterization and expression analysis of caspase-9 from the purse red common carp (Cyprinus carpio) exposed to cadmium. Aquat Toxicol 142–143:53–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2013.07.017
Oyadomari S, Mori M (2004) Roles of CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ 11(4):381–389. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401373
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 30471278) for the financial support of the study.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 30471278).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Pengcheng Xing: conceptualization, data curation, software, formal analysis, writing — original draft, writing — review and editing. Yiming Zhang: conceptualization, software, formal analysis, investigation, visualization. Qianru Chi: investigation, data Curation. Shu Li: data curation, validation, resources, funding acquisition, project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
The Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Northeast Agricultural University (SRM-11).
Consent for Publication
The manuscript is approved by all authors for publication.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, P., Zhang, Y., Chi, Q. et al. Zinc Alleviates Arsenic-Induced Inflammation and Apoptosis in the Head Kidney of Common Carp by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Biol Trace Elem Res 200, 2380–2390 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02837-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02837-5