Abstract
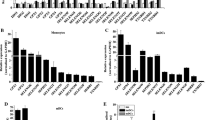
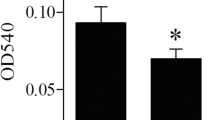
Selenium levels can regulate the function of T cells, macrophages, B cells, natural killer cells and other immune cells. However, the effect of selenium on the immune function of dendritic cells (DCs) isolated from selenium-supplemented mice is unknown. In this study, C57BL/6J mice were randomly divided into three groups and fed diets containing low (0.08 ppm), medium (0.25 ppm) or high (1 ppm) selenium levels for 8 weeks. Immature (imDCs) and mature (mDCs) dendritic cells were then isolated from the bone marrow. Next, the migration, phagocytic capacity and mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR) for imDCs and mDCs were detected by transwell and flow cytometry. The levels of C-C chemokine receptor type 7 (CCR7), major histocompatibility complex II (MHCII) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) were assayed by flow cytometry. F-actin and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity was detected by fluorescence microscopy and SOD assay kit, respectively. In addition, the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), Akt, Ras homolog gene family member A/Rho-associated protein kinase (RhoA/ROCK) signalling, selenoprotein K (SELENOK) and glutathione peroxidase 1 (GPX1) levels were measured by western blot analysis. The results indicated that selenium deficiency enhanced the migration of imDCs by ROS and SELENOK-mediated ERK, Akt and RhoA/ROCK pathways but impaired the antigen uptake of imDCs. Although a high selenium level inhibited the migration of imDCs, it had no effect on phagocytic capacity. For mDCs, low selenium levels impaired free migration, and high levels inhibited the chemotactic migration involved in F-actin and CCR7, respectively. Low and high selenium levels impaired the MLR by inhibiting MHCII surface localisation, which might be related to ROS- and SELENOK-mediated ERK, Akt and RhoA/ROCK signalling pathways. In summary, selenium may regulate the immune function of mouse DCs through the ROS- and SELENOK-mediated ERK, Akt and RhoA/ROCK signalling.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AO:
-
Average optical
- CCR7:
-
C-C chemokine receptor type 7
- DCs:
-
Dendritic cells
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- GPX1:
-
Glutathione peroxidase 1
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- imDCs:
-
Immature dendritic cells
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharides
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinases
- mDCs:
-
Mature dendritic cells
- MHCII:
-
Major histocompatibility complex II
- MLR:
-
Mixed lymphocyte reaction
- MoDCs:
-
Monocyte-derived DCs
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- RhoA:
-
Ras homolog gene family member A
- ROCK:
-
Rho-associated protein kinases
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- rmGM-CSF:
-
Recombinant mouse granulocyte-macrophage CSF
- rmIL-4:
-
Recombinant mouse interleukin-4
- SELENOK:
-
Selenoprotein K
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
References
Eisenbarth SC (2019) Dendritic cell subsets in T cell programming: location dictates function. Nat Rev Immunol 19(2):89–103
Collin M, Bigley V (2018) Human dendritic cell subsets: an update. Immunology 154(1):3–20
Segura E, Amigorena S (2015) Cross-presentation in mouse and human dendritic cells. Adv Immunol. Academic Press 127:1–31
Perez CR, De Palma M (2019) Engineering dendritic cell vaccines to improve cancer immunotherapy. Nat Commun 10(1):1–10
Bryant CE, Sutherland S, Kong B, Papadimitrious MS, Hart DNJ, Fromm PD (2019) Dendritic cells as cancer therapeutics. Semin Cell Dev Biol 86:77–88
Rayman MP (2012) Selenium and human health. Lancet 79(9822):1256–1268
Avery JC, Hoffmann PR (2018) Selenium, selenoproteins, and immunity. Nutrients 10(9):E1203
Huang Z, Rose AH, Hoffmann PR (2012) The role of selenium in inflammation and immunity: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal 16(7):705–743
Hawkes WC, Kelley DS, Taylor PC (2001) The effects of dietary selenium on the immune system in healthy men. Biol Trace Elem Res 81:189–213
Sun Z, Liu C, Pan T, Yao H, Li S (2017) Selenium accelerates chicken dendritic cells differentiation and affects selenoproteins expression. Dev Comp Immunol 77:30–37
Sun Z, Xu Z, Wang D, Yao H, Li S (2018) Selenium deficiency inhibits dendritic cells differentiation and immune function, imbalance the Th1/Th2 of dendritic cells. Metallomics 10(5):759–767
Gostner JM, Becker K, Fuchs D, Sucher R (2013) Redox regulation of the immune response. Redox Rep 18(3):88–94
Götz A, Ty MC, Rodriguez A (2019) Oxidative stress enhances dendritic cell responses to plasmodium falciparum. Immunohorizons 3(11):511–518
Kroening PR, Barnes TW, Pease L, Limper A, Kita H, Vassallo R (2008) Cigarette smoke-induced oxidative stress suppresses generation of dendritic cell IL-12 and IL-23 through ERK-dependent pathways. J Immunol 181(2):1536–1547
Zaccagnino P, Saltarella M, Maiorano S, Gaballo A, Santoro G, Nico B, Lorusso M, Del Prete A (2012) An active mitochondrial biogenesis occurs during dendritic cell differentiation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 44(11):1962–1969
Kantengwa S, Jornot L, Devenoges C, Nicod LP (2003) Superoxide anions induce the maturation of human dendritic cells. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 167(3):431–437
Matsue H, Edelbaum D, Shalhevet D, Mizumoto N, Yang C, Mummert ME, Oeda J, Masayasu H, Takashima A (2003) Generation and function of reactive oxygen species in dendritic cells during antigen presentation. J Immunol 171(6):3010–3018
Kamide Y, Utsugi M, Dobashi K, Ono A, Ishizuka T, Hisada T, Koga Y, Uno K, Hamuro J, Mori M (2011) Intracellular glutathione redox status in human dendritic cells regulates IL-27 production and T-cell polarization. Allergy 66(9):1183–1192
Zhang Y, Liu Q, Yin H, Min Y, Li S (2020) Selenium deficiency causes immune damage by activating the DUSP1/NF-κB pathway and endoplasmic reticulum stress in chicken spleen. Food Funct 11:6467–6475
Nakahara T, Moroi Y, Uchi H, Furue M (2006) Differential role of MAPK signaling in human dendritic cell maturation and Th1/Th2 engagement. J Dermatol Sci 42(1):1–11
Kim JH, Kang TH, Noh KH, Kim SH, Lee YH, Kim KW, Bae HC, Ahn YH, Choi EY, Kim JS et al (2010) Enhancement of DC vaccine potency by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway with a small interfering RNA targeting PTEN. Immunol Lett 134(1):47–54
Bros M, Haas K, Moll L, Grabbe S (2019) RhoA as a key regulator of innate and adaptive immunity. Cells 8(7):733
Marciel MP, Hoffmann PR (2019) Molecular mechanisms by which selenoprotein K regulates immunity and cancer. Biol Trace Elem Res 192(7):60–68
Verma S, Hoffmann FKW, Kumar M, Huang Z, Roe K, Nguyen-Wu E, Hashimoto AS, Hoffmann PR (2011) Selenoprotein K knockout mice exhibit deficient calcium flux in immune cells and impaired immune responses. J Immunol 186(4):2127–2137
Zhang M, Tang H, Guo Z, An H, Zhu X, Song W, Guo J, Huang X, Chen T, Wang J, Cao X (2004) Splenic stroma drives mature dendritic cells to differentiate into regulatory dendritic cells. Nat Immunol 5(11):1124–1133
Zeng Z, Yao W, Xu X, Xu G, Long J, Wang X, Wen Z, Chien S (2009) Hepatocellular carcinoma cells deteriorate the biophysical properties of dendritic cells. Cell Biochem Biophys 55(1):33–43
Jia Y, Zhou J, Liu H, Huang K (2014) Effect of methionine sulfoxide reductase B1 (SelR) gene silencing on peroxynitrite-induced F-actin disruption in human lens epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 443(3):876–881
Jia Y, Li Y, Du S, Huang K (2012) Involvement of MsrB1 in the regulation of redox balance and inhibition of peroxynitrite-induced apoptosis in human lens epithelial cells. Exp Eye Res 100:7–16
Hoffmann FW, Hashimoto AC, Shafer LA, Dow S, Berry MJ, Hoffmann PR (2010) Dietary selenium modulates activation and differentiation of CD4+ T cells in mice through a mechanism involving cellular free thiols. J Nutr 140(6):1155–1161
Matos TJ, Duarte CB, Gonçalo M, Lopes MC (2005) Role of oxidative stress in ERK and p38 MAPK activation induced by the chemical sensitizer DNFB in a fetal skin dendritic cell line. Immunol Cell Biol 83(6):607–614
Mizuashi M, Ohtani T, Nakagawa S, Aiba S (2005) Redox imbalance induced by contact sensitizers triggers the maturation of dendritic cells. J Invest Dermatol 124(3):579–586
Pearce G, Audzevich T, Jessberger R (2011) SYK regulates B-cell migration by phosphorylation of the F-actin interacting protein SWAP-70. Blood 117(5):1574–1584
Tak H, Jang E, Kim SB, Park J, Suk J, Yoon YS, Ahn JK, Lee JH, Joe CO (2007) 14-3-3epsilon inhibits MK5-mediated cell migration by disrupting F-actin polymerization. Cell Signal 19(11):2379–2387
Wang LH, Xiang J, Yan M, Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Yue CF, Xu J, Zheng FM, Chen JN, Kang Z, Chen TS, Xing D, Liu Q (2010) The mitotic kinase Aurora-A induces mammary cell migration and breast cancer metastasis by activating the Cofilin-F-actin pathway. Cancer Res 70(22):9118–9128
Schachtner H, Weimershaus M, Stache V, Plewa N, Legler DF, Höpken UE, Maritzen T (2015) Loss of Gadkin affects dendritic cell migration in vitro. PLoS One 10(12):e0143883
Zeng Z, Liu X, Jiang Y, Wang G, Zhan J, Guo J, Yao W, Sun D, Ka W, Tang Y, Tang J, Wen Z, Chien S (2006) Biophysical studies on the differentiation of human CD14+ monocytes into dendritic cells. Cell Biochem Biophys 45(1):19–30
Ocana-Morgner C, Wahren C, Jessberger R (2009) SWAP-70 regulates RhoA/RhoB-dependent MHCII surface localization in dendritic cells. Blood 113(7):1474–1482
Seul HJ, Ahn YR, Song HM, Ha YJ, Lee JR (2012) Over-expression of a RhoA-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factor, p190RhoGEF, in mouse dendritic cells negatively regulates cellular responses to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Mol Cell 34(2):159–164
Puig-Kröger A, Relloso M, Fernández-Capetillo O, Zubiaga A, Silva A, Bernabéu C, Corbí AL (2001) Extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase signaling pathway negatively regulates the phenotypic and functional maturation of monocyte-derived human dendritic cells. Blood 98(7):2175–2182
Nakagawa S, Ohtani T, Mizuashi M, Mollah ZU, Ito Y, Tagami H, Aiba S (2004) p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase mediates dual role of ultraviolet B radiation in induction of maturation and apoptosis of monocyte-derived dendritic cells. J Invest Dermatol 123(2):361–370
Aiba S, Manome H, Nakagawa S, Mollah ZU, Mizuashi M, Ohtani T, Yoshino Y, Tagami H (2003) p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinases play distinct roles in the activation of dendritic cells by two representative haptens, NiCl2 and 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene. J Invest Dermatol 120(3):390–399
Rajalingam K, Wunder C, Brinkmann V, Churin Y, Hekman M, Sievers C, Rapp UR, Rudel T (2005) Prohibitin is required for Ras-induced Raf–MEK–ERK activation and epithelial cell migration. Nat Cell Biol 7(8):837–843
Bąbolewska E, Pietrzak A, Brzezińska-Błaszczyk E (2014) Cathelicidin rCRAMP stimulates rat mast cells to generate cysteinyl leukotrienes, synthesize TNF and migrate: involvement of PLC/A2, PI3K and MAPK signaling pathways. Int Immunol 26(11):637–646
Katagiri A, Nakayama K, Rahman MT, Rahman M, Yeasmin S, Ishikawa M, Iida K, Nakayama N, Miyazaki K (2010) MEK inhibition suppresses cell invasion and migration in ovarian cancers with activation of ERK1/2. Exp Ther Med 1(4):591–596
Liao YC, Shih YW, Chao CH, Lee XY, Chiang TA (2009) Involvement of the ERK signaling pathway in fisetin reduces invasion and migration in the human lung cancer cell line A549. J Agric Food Chem 57(19):8933–8941
Filippi I, Morena E, Aldinucci C, Carraro F, Sozzani S, Naldini A (2014) Short-term hypoxia enhances the migratory capability of dendritic cell through HIF-1α and PI3K/Akt pathway. J Cell Physiol 229(12):2067–2076
Bhattacharyya S, Sen P, Wallet M, Long B, Baldwin AS Jr, Tisch R (2004) Immunoregulation of dendritic cells by IL-10 is mediated through suppression of the PI3K/Akt pathway and of IkappaB kinase activity. Blood 104(4):1100–1109
Meng XL, Chen CL, Liu YY, Su SJ, Gou JM, Huan FN, Wang D, Liu HS, Ben SB, Lu J (2019) Selenoprotein SELENOK enhances the migration and phagocytosis of microglial cells by increasing the cytosolic free Ca2+ level resulted from the up-regulation of IP3R. Neuroscience 406:38–49
Li M, Cheng W, Nie T, Lai H, Hu X, Luo J, Li F, Li H (2018) Selenoprotein K mediates the proliferation, migration, and invasion of human choriocarcinoma cells by negatively regulating human chorionic gonadotropin expression via ERK, p38 MAPK, and Akt signaling pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res 184(1):47–59
Ben SB, Peng B, Wang GC, Li C, Gu HF, Jiang H, Meng XL, Lee BJ, Chen CL (2015) Overexpression of selenoprotein SelK in BGC-823 cells inhibits cell adhesion and migration. Biochemistry (Mosc) 80(10):1344–1353
Norton RL, Fredericks GJ, Huang Z, Fay JD, Hoffmann FW, Hoffmann PR (2017) Selenoprotein K regulation of palmitoylation and calpain cleavage of ASAP2 is required for efficient FcγR-mediated phagocytosis. J Leukoc Biol 101(2):439–448
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21561006 and No. 21867007), Guizhou Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. [2019]1258 and No. LH[2016]7372) and Opening fund of Hubei Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic Chemistry & Materia Medica (No. BCMM202002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Liangliang Zhang and Huan Xia contributed to the work equally and should be regarded as co-first authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 22 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Xia, H., Xia, K. et al. Selenium Regulation of the Immune Function of Dendritic Cells in Mice Through the ERK, Akt and RhoA/ROCK Pathways. Biol Trace Elem Res 199, 3360–3370 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02449-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02449-5