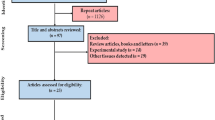
Abstract
In this work, articles regarding the concentration on potentially harmful elements (PHEs) in fillet trout (rainbow and brown) fishes were retrieved from Cochrane, Scopus, and PubMed databases between 1 January 1983 and 30 April 2020. The pooled concentration of PHEs in fillet trout fishes was meta-analyzed using a random-effect model (REM) and following the non-carcinogenic and carcinogenic risks was calculated using the Monte Carlo simulation (MCS) method. The meta-analysis of 42 articles (43 data report) revealed that a sort of PHEs in fillet trout was 19,996.64 μg/kg ww for Fe; 1834.75 μg/kg ww for Co; 772.21 μg/kg ww for Cu; 335.78 μg/kg ww for Ni; 290.46 μg/kg ww for Se; 226.20for Cr; 178.11 μg/kg ww for Pb; 77.40 μg/kg ww for Hg; 19.40 μg/kg ww for Cd; and 3.66 μg/kg ww for inorganic As. The non-carcinogenic risk assessment indicated that the lowest and highest hazard index (HI) in the adults was Pakistan (0.0012) and Turkey (0.2388), respectively, and in children was Pakistan (0.0057) and Turkey (1.114), respectively. The non-carcinogenic risk was acceptable for adult consumers in all countries (HI > 1 value) but non-carcinogenic risk for children was not acceptable in Turkey. The sort of countries based on carcinogenic risk in the adults due to inorganic As was China (1.44E−06) > Iran (9.14E−08) > Turkey (4.45E−08) > Portugal (9.04E−10). The carcinogenic risk was threshold for adult consumers in China (CR < 10–6). Consumption of fillet trout (rainbow and brown) content of PHEs in many countries cannot endanger the health of consumers.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
McEneff G, Quinn B, Bennion M, Dolan S, O'Rourke K, Morrison L (2017) Bioaccumulation of metals in juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) via dietary exposure to blue mussels. Chemosphere 188:548–556
Cobelo-Garcı́a A, Prego R, Labandeira A (2004) Land inputs of trace metals, major elements, particulate organic carbon and suspended solids to an industrial coastal bay of the NE Atlantic. Water Res 38 (7):1753–1764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2003.12.038
Korn MGA, dos Santos GL, Rosa SM, Teixeira LSG, de Oliveira PV (2010) Determination of cadmium and lead in cetacean Dolphinidae tissue from the coast of Bahia state in Brazil by GFAAS. Microchem J 96(1):12–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2010.01.001
Saha N, Mollah MZI, Alam MF, Safiur Rahman M (2016) Seasonal investigation of heavy metals in marine fishes captured from the Bay of Bengal and the implications for human health risk assessment. Food Control 70:110–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.05.040
WFD E (2013) European union water framework directive 2013/39/EU. Offic J Eur Communities OJL226
Tudor M-I, Tudor M, David C, Teodorof L, Tudor D, Ibram O Heavy metals concentrations in aquatic environment and living organisms in the Danube Delta, Romania. In: Simeonov L, Chirila E (eds) Chemicals as Intentional and Accidental Global Environmental Threats, Dordrecht, 2006// 2006. Springer Netherlands, pp 435–442
Fallah AA, Saei-Dehkordi SS, Nematollahi A, Jafari T (2011) Comparative study of heavy metal and trace element accumulation in edible tissues of farmed and wild rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) using ICP-OES technique. Microchem J 98(2):275–279
Varol M, Kaya GK, Alp A (2017) Heavy metal and arsenic concentrations in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) farmed in a dam reservoir on the Firat (Euphrates) River: risk-based consumption advisories. Sci Total Environ 599:1288–1296
Alibabić V, Vahčić N, Bajramović M (2007) Bioaccumulation of metals in fish of Salmonidae family and the impact on fish meat quality. Environ Monit Assess 131(1–3):349–364
Fisher NS, Hook SE (2002) Toxicology tests with aquatic animals need to consider the trophic transfer of metals. Toxicology 181-182:531–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0300-483X(02)00475-4
Bosch AC, O'Neill B, Sigge GO, Kerwath SE, Hoffman LC (2016) Heavy metals in marine fish meat and consumer health: a review. J Sci Food Agric 96(1):32–48. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.7360
Kalantzi I, Pergantis SA, Black KD, Shimmield TM, Papageorgiou N, Tsapakis M, Karakassis I (2016) Metals in tissues of seabass and seabream reared in sites with oxic and anoxic substrata and risk assessment for consumers. Food Chem 194:659–670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.08.072
Agency UUSEP (2000) Guidance for assessing chemical contaminant data for use in fish advisories, volume II. Risk Assessment and fish con-sumption limits. (EPA 823-B-00-008). . United States Environmental Protection Agen-cy, Washington, DC
Ahmed MK, Shaheen N, Islam MS, Habibullah-al-Mamun M, Islam S, Mohiduzzaman M, Bhattacharjee L (2015) Dietary intake of trace elements from highly consumed cultured fish (Labeo rohita, Pangasius pangasius and Oreochromis mossambicus) and human health risk implications in Bangladesh. Chemosphere 128:284–292
Tao Y, Yuan Z, Xiaona H, Wei M (2012) Distribution and bioaccumulation of heavy metals in aquatic organisms of different trophic levels and potential health risk assessment from Taihu lake, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 81:55–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.04.014
Al-Busaidi M, Yesudhason P, Al-Mughairi S, Al-Rahbi WAK, Al-Harthy KS, Al-Mazrooei NA, Al-Habsi SH (2011) Toxic metals in commercial marine fish in Oman with reference to national and international standards. Chemosphere 85(1):67–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.05.057
Solgi E, Beigzadeh-Shahraki F (2019) Accumulation and human health risk of heavy metals in cultured rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) form different fish farms of eight cities of Chaharmahal and Bakhtiari province, Iran. Thalassas: Int J Mar Sci 35(1):305–317
Kelly BC, Ikonomou MG, Higgs DA, Oakes J, Dubetz C (2008) Mercury and other trace elements in farmed and wild salmon from British Columbia, Canada. Environ Toxicol Chem 27(6):1361–1370. https://doi.org/10.1897/07-527.1
Heshmati A, Sadati R, Ghavami M, Mousavi Khaneghah A (2019) The concentration of potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in muscle tissue of farmed Iranian rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss), feed, and water samples collected from the west of Iran: a risk assessment study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(33):34584–34593. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06593-x
Undercurrent (2020) Global rainbow trout consumption to hit 950,000t by end of 2019. https://www.undercurrentnews.com/2019/07/09/global-rainbow-trout-consumption-to-hit-950000t-by-end-of-2019/
Dvorak P, Roy K, Andreji J, Liskova ZD, Mraz J (2020) Vulnerability assessment of wild fish population to heavy metals in military training area: synthesis of a framework with example from Czech Republic. Ecol Indic 110:105920
Majid M, Janmohammad M, Enayat B, Akbartabar TM (2019) Heavy metal content in farmed rainbow trout in relation to aquaculture area and feed pellets. Foods Raw Mater 7(2)
Varol M, Kaya GK, Sünbül MR (2019) Evaluation of health risks from exposure to arsenic and heavy metals through consumption of ten fish species. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(32):33311–33320
Yeltekin AÇ, Sağlamer E (2019) Toxic and trace element levels in Salmo trutta macrostigma and Oncorhynchus mykiss trout raised in different environments. Membranes 5:6
Dvořák P, Andreji J, Leitmanová IF, Petrách F, Mráz J (2018) Accumulation of selected metals pollution in aquatic ecosystems in the Smeda river (Czech Republic). Neuroendocrinol Lett 39(5)
Andreji J, Dvořák P (2018) Levels of selected contaminants in fish muscle from upper Nitra River. Neuroendocrinol Lett 39(4)
Jiang H, Qin D, Mou Z, Zhao J, Tang S, Wu S, Gao L (2016) Trace elements in farmed fish (Cyprinus carpio, Ctenopharyngodon idella and Oncorhynchus mykiss) from Beijing: implication from feed. Food Addit Contam: Part B 9(2):132–141
Yabanlı M, Yozukmaz A, Alparslan Y, Acar Ü (2014) Evaluation of heavy metals and selenium contents in the muscle tissues of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum, 1792) in Western Anatolia. J Food Agric Environ 12(2):165–168
Higgins JP, Green S (2011) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions, vol 4. John Wiley & Sons
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, Clarke M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J, Moher D (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med 6(7):15–25
Quan H, Zhang J (2003) Estimate of standard deviation for a log-transformed variable using arithmetic means and standard deviations. Stat Med 22(17):2723–2736
Higgins J, White IR, Anzures-Cabrera J (2008) Meta-analysis of skewed data: combining results reported on log-transformed or raw scales. Stat Med 27(29):6072–6092
Higgins., Thompson S (2002) Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 21 (11):1539–1558
Kuroki T, Watanabe Y, Teranishi H, Izumiyama S, Amemura-Maekawa J, Kura F (2017) Legionella prevalence and risk of legionellosis in Japanese households. Epidemiol Infect 145(7):1398–1408
Khaneghah AM, Fakhri Y, Sant'Ana AS (2018) Impact of unit operations during processing of cereal-based products on the levels of deoxynivalenol, total aflatoxin, ochratoxin A, and zearalenone: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Food Chem 268:611–624
Firestone M, Fenner-Crisp P, Barry T, Bennett D, Chang S, Callahan M, Burke A, Michaud J, Olsen M, Cirone P (1997) Guiding principles for Monte Carlo analysis, vol 5. US Environmental Protection Agency. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
Varol M, Kaya GK, Alp SA, Sünbül MR (2018) Trace metal levels in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) cultured in net cages in a reservoir and evaluation of human health risks from consumption. Biol Trace Elem Res 184(1):268–278
Cilingir-Yeltekin A (2018) Comparison of toxic metal, trace element and macro element levels in trout cultivated in Latvia and Turkey. FEB-FRESENIUS ENVIRONMENTAL BULLETIN:7039
Heshmati A, Sadati R, Ghavami M, Khaneghah AM (2019) The concentration of potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in muscle tissue of farmed Iranian rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss), feed, and water samples collected from the west of Iran: a risk assessment study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(33):34584–34593
Woelfl S, Mages M, Torres P (2008) Trace metal concentrations in single specimens of the intestinal broad flatworm (Diphyllobothrium latum), compared to their fish host (Oncorhynchus mykiss) measured by total reflection X-ray fluorescence spectrometry. Spectrochim Acta B At Spectrosc 63(12):1450–1454
Barrientos C, Tapia J, Bertrán C, Peña-Cortés F, Hauenstein E, Fierro P, Vargas-Chacoff L (2019) Is eating wild rainbow trout safe? The effects of different land-uses on heavy metals content in Chile. Environ Pollut 254:112995
Bat L, Oztekin A, Yardim O (2018) Metal levels in large sea trout from Sinop fish market. Fresenius Environ Bull 27(12):8505–8508
Dizman S, Görür FK, Keser R (2017) Assessment of human health risk from heavy metals levels in water and tissues of two trout species (Oncorhynchus mykiss and Salmo coruhensis) from the Fırtına and Güneysu Rivers in Turkey. Toxin Rev 36(4):306–312
Bilandžić N, Sedak M, Čalopek B, Đokić M, Varenina I, Kolanović BS, Luburić ĐB, Varga I, Benić M, Roncarati A (2018) Element contents in commercial fish species from the Croatian market. J Food Compos Anal 71:77–86
Dadar M, Adel M, Ferrante M, Nasrollahzadeh Saravi H, Copat C, Oliveri Conti G (2016) Potential risk assessment of trace metals accumulation in food, water and edible tissue of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) farmed in Haraz River, northern Iran. Toxin Rev 35(3–4):141–146
Majlesi M, Malekzadeh J, Berizi E, Akbartabar Toori M (2019) Heavy metal content in farmed rainbow trout in relation to aquaculture area and feed pellets. Foods Raw Mater 7(2)
Varol M, Sünbül MR (2017) Comparison of heavy metal levels of farmed and escaped farmed rainbow trout and health risk assessment associated with their consumption. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(29):23114–23124
Mendil D, Ünal ÖF, Tüzen M, Soylak M (2010) Determination of trace metals in different fish species and sediments from the River Yeşilırmak in Tokat, Turkey. Food Chem Toxicol 48(5):1383–1392
Ahmed M, Ahmad T, Liaquat M, Abbasi KS, Farid IBA, Jahangir M (2016) Tissue specific metal characterization of selected fish species in Pakistan. Environ Monit Assess 188(4):212
Djedjibegovic J, Larssen T, Skrbo A, Marjanović A, Sober M (2012) Contents of cadmium, copper, mercury and lead in fish from the Neretva river (Bosnia and Herzegovina) determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Food Chem 131(2):469–476
Reyahi-Khoram M, Setayesh-Shiri F, Cheraghi M (2016) Study of the heavy metals (Cd and Pb) content in the tissues of rainbow trouts from Hamedan coldwater fish farms. Iran J Fish Sci 15(2):858–869
Özparlak H, Arslan G, Arslan E (2012) Determination of some metal levels in muscle tissue of nine fish species from Beyşehir Lake, Turkey. Turk J Fish Aquat Sci 12(4):761–770
Can E, Yabanli M, Kehayias G, Aksu Ö, Kocabaş M, Demir V, Kayim M, Kutluyer F, Şeker S (2012) Determination of bioaccumulation of heavy metals and selenium in tissues of brown trout Salmo trutta macrostigma (Duméril, 1858) from Munzur Stream, Tunceli, Turkey. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 89(6):1186–1189
Sobhanardakani S, Tayebi L, Farmany A, Cheraghi M (2012) Analysis of trace elements (Cu, Cd, and Zn) in the muscle, gill, and liver tissues of some fish species using anodic stripping voltammetry. Environ Monit Assess 184(11):6607–6611
Topuz OK, Yerlikaya P, Yatmaz HA, Kaya A, Alp AC, Kilic M (2017) Comparison of essential trace element profiles of rainbow trout fish (Oncorhynchus mykiss) meat and egg. Sci Pap Ser D Anim Sci 60:316–319
Mol S (2011) Determination of trace metals in canned anchovies and canned rainbow trouts. Food Chem Toxicol 49(2):348–351
Yasmeen K, Mirza MA, Khan NA, Kausar N, A-u R, Hanif M (2016) Trace metals health risk appraisal in fish species of Arabian Sea. SpringerPlus 5(1):859
Nauen CE (1983) Compilation of legal limits for hazardous substances in fish and fishery products. FAO Fisheries Circular (FAO) no 764
FAO/WHO J (1972) Evaluation of certain food additives and the contaminants mercury, lead, and cadmium: sixteenth report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives
Alimentarius C (2015) General standard for contaminants and toxins in food and feed (Codex STAN 193-1995). URL: https://www.dokipediaru/document/5197124
Topal A, Atamanalp M, Oruç E, Erol HS (2017) Physiological and biochemical effects of nickel on rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) tissues: assessment of nuclear factor kappa B activation, oxidative stress and histopathological changes. Chemosphere 166:445–452
Strapáč I, Sokol J, Žatko D, Baranová M (2012) Mercury and selenium concentrations in muscle tissue of different species of predatory freshwater fish and correlation between these elements. Food Addit Contam: Part B 5(3):194–199
Arribére M, Guevara SR, Bubach D, Vigliano P (2006) Trace elements as fingerprint of lake of provenance and of species of some native and exotic fish of northern Patagonian lakes. Biol Trace Elem Res 111(1–3):71–95
Linde A, Sanchez-Galan S, Garcia-Vazquez E (2004) Heavy metal contamination of European eel (Anguilla anguilla) and brown trout (Salmo trutta) caught in wild ecosystems in Spain. J Food Prot 67(10):2332–2336
EPA (2012) Quantitative risk assessment calculations. Sustainable futures / P2 framework manual 2012 EPA-748-B12–001 13. Quantitative Risk Assessment Calculations 13.:1–11
Gholami Z, Abtahi M, Golbini M, Parseh I, Alinejad A, Avazpour M, Moradi S, Fakhri Y, Mousavi Khaneghah A (2019) The concentration and probabilistic health risk assessment of nitrate in Iranian drinking water: a case study of Ilam city. Toxin Rev:1–10
Pirsaheb M, Fakhri Y, Karami M, Akbarzadeh R, Safaei Z, Fatahi N, Sillanpää M, Asadi A (2019) Measurement of permethrin, deltamethrin and malathion pesticide residues in the wheat flour and breads and probabilistic health risk assessment: a case study in Kermanshah, Iran. Int J Environ Anal Chem:1–12
Rezaei H, Jafari A, Kamarehie B, Fakhri Y, Ghaderpoury A, Karami MA, Ghaderpoori M, Shams M, Bidarpoor F, Salimi M (2019) Health-risk assessment related to the fluoride, nitrate, and nitrite in the drinking water in the Sanandaj, Kurdistan County, Iran. Human Ecolog Risk Assess: Int J 25(5):1242–1250
Atamaleki A, Yazdanbakhsh A, Fakhri Y, Mahdipour F, Khodakarim S, Mousavi Khaneghah A (2019) The concentration of potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in the onion and tomato irrigated by wastewater: A systematic review; meta-analysis and health risk assessment. Food Res Int 125:108518
Fakhri Y, Rahmani J, Oliveira CAF, Franco LT, Corassin CH, Saba S, Rafique J, Khaneghah AM (2019) Aflatoxin M1 in human breast milk: a global systematic review, meta-analysis, and risk assessment study (Monte Carlo simulation). Trends in food science & technology
Fakhri Y, Saha N, Miri A, Baghaei, Mehdi, Roomiani L, Ghaderpoori M, Taghavi M, Keramati H, Bahmani Z (2018) Metal concentrations in fillet and gill of parrotfish (Scarus ghobban) from the Persian Gulf and implications for human health. Food Chem Toxicol 115 (2018):348–354
Rahmani J, Fakhri Y, Shahsavani A, Bahmani Z, A. Urbina M, Chirumbolo S, Keramati H, Moradi B, Bay A, Bjørklund G (2018) A systematic review and meta-analysis of metal concentrations in canned tuna fish in Iran and human health risk assessment. Food Chem Toxicol 118 (2018):753–765
Fakhri Y, Sahab N, Ghanbari, Sahebe, Rasouli M, Miri A, Avazpour, Moayed, Rahimizadeh A, Riahih S-M, Ghaderpoori M, Keramati H, Moradi B, Amanidaz N (2018) Carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic health risks of metal (oid) s in tap water from Ilam city, Iran Food Chem Toxicol 118 (2018):204–211
Heshmati A, Ghadimi S, Mousavi Khaneghah A, J. Barba F, M. Lorenzo J, Nazemi F, Fakhri Y (2018) Risk assessment of benzene in food samples of Iran's market. Food Chem Toxicol 114 (2018):278–284
Rahmani J, Alipour S, Miri A, Fakhri Y, Seyed-Mohammad R, Hassan K, Moradi M, Nazak A, Rokhsane HP, Zohreh B (2018) The prevalence of aflatoxin M1 in milk of Middle East region: a systematic review, meta-analysis and probabilistic health risk assessment. Food Chem Toxicol 118 (2018):653–666
Yousefi M, Shemshadi G, Khorshidian N, Ghasemzadeh-Mohammadi V, Fakhri Y, Hosseini H, Mousavi Khaneghah A (2018) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) content of edible vegetable oils in Iran: a risk assessment study. Food Chem Toxicol 118 (2018):480–489
Fakhri Y, Mohseni-Bandpei A, Oliveri Conti G, Keramati H, Zandsalimi Y, Amanidaz N, Hosseini Pouya R, Moradi B, Bahmani Z, Rasouli Amirhajeloo L (2017) Health risk assessment induced by chloroform content of the drinking water in Iran: systematic review. Toxin Rev 36(4):322–330
Hedges LV, Gurevitch J, Curtis PS (1999) The meta-analysis of response ratios in experimental ecology 80 (4):1150–1156. https://doi.org/10.1890/0012-9658(1999)080[1150:Tmaorr]2.0.Co;2
Njuguna SM, Makokha VA, Yan X, Gituru RW, Wang Q, Wang J (2019) Health risk assessment by consumption of vegetables irrigated with reclaimed waste water: a case study in Thika (Kenya). J Environ Manag 231:576–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.10.088
Barnes DG, Dourson M, Preuss P, Bellin J, Derosa C, Engler R, Erdreich L, Farber T, Fenner-Crisp P, Francis E (1988) Reference dose (RfD): description and use in health risk assessments. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 8(4):471–486
EPA (2000) Risk-based concentration table. J Philadelphia PA, United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington DC
EPA (2011) Exposure factors handbook: 2011 edition. EPA/600/R-09,
FAO (2018) Fish and seafood consumption per capita. https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/fish-and-seafood-consumption-per-capita
Lourenço HM, Afonso C, Anacleto P, Martins MF, Nunes ML, Lino AR (2012) Elemental composition of four farmed fish produced in Portugal. Int J Food Sci Nutr 63(7):853–859
Makovský J, Spurný P, Mareš J, Hedbávný J, Vítek T (2014) Heavy metal pollution of ecosystem within the middle course of the Jihlava River. Acta Universitatis Agriculturae et Silviculturae Mendelianae Brunensis 58(5):255–262
Vitek T, Spurný P, Mareš J, Zikova A (2007) Heavy metal contamination of the Loučka River water ecosystem. Acta Vet Brno 76(1):149–154
Svobodova Z, Celechovska O, Kolarova J, Randak T, Zlabek V (2004) Assessment of metal contamination in the upper reaches of the Tichá Orlice River. Czech Journal of Animal Science-UZPI (Czech Republic)
Olson CI, Beaubien GB, Sims JL, Otter RR (2019) Mercury accumulation in millipedes (Narceus spp.) living adjacent to a southern Appalachian Mountain stream (USA). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 103(4):528–532
Varol M, Sünbül MR (2017) Organochlorine pesticide, antibiotic and heavy metal residues in mussel, crayfish and fish species from a reservoir on the Euphrates River, Turkey. Environ Pollut 230:311–319
Mashaii N, Mosaddegh M, Aliabad HS, Rajabipour F, Bitaraf A, Mohammadi M (2011) Determination of some minerals and heavy metals in muscle tissues of rainbow trout, Onchorhynchus mykiss, cultured in Iran. Global Veterinaria 7(2):113–122
Zapata FCC, Villanueva MC, Esquivel RAP, Payano IGU (2017) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in Oncorhynchus mykiss for export at production centers in the Peruvian Central Highlands. Revista Ambiente & Agua 12(4):527–542
Celik M, Goekce MA, BAŞUSTA N, Kuecuekguelmez A, TAŞBOZAN O, TABAKOĞLU ŞS (2008) Nutritional quality of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) caught from the Atatürk Dam Lake in Turkey. J Muscle Foods 19(1):50–61
Mariussen E, Heier LS, Teien HC, Pettersen MN, Holth TF, Salbu B, Rosseland BO (2017) Accumulation of lead (Pb) in brown trout (Salmo trutta) from a lake downstream a former shooting range. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 135:327–336
Verep B, Akin S, Mutlu C, Ertugral B, Apaydin G, Cevik U (2007) Assesment of trace elements in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) cultured in the marine aquaculture cages on the Black Sea coast. Fresenius Environ Bull 16(9A):1005
Mortazavi A, Hatamikia M, Bahmani M, Hassanzadazar H (2016) Heavy metals (mercury, lead and cadmium) determination in 17 species of fish marketed in Khorramabad city, west of Iran. J Chem Health Risks 6(1)
Funding
This study was financially supported by grants from the student research committee at Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (#21152).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fakhri, Y., Nematollahi, A., Abdi-Moghadam, Z. et al. Concentration of Potentially Harmful Elements (PHEs) in Trout Fillet (Rainbow and Brown) Fish: a Global Systematic Review and Meta-analysis and Health Risk Assessment. Biol Trace Elem Res 199, 3089–3101 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02419-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02419-x