Abstract
The role of elements in physiological and pathological metabolic processes remains an unmet challenge in biomedical research and clinical applications. Herein, a visual elemental imaging of tumor tissue platform of a laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) was developed to initially understand anti-tumor mechanisms. The relative enrichment degree and heterogeneous spatial distributions of four elements (calcium, sodium, copper, and magnesium) of tumor tissue from different treated could be easy to visualize. In particular, significant differences in the distribution of elements were observed in tumor tissue from drug-loading complex (hydrogel/DOX) treatment group. Correspondingly, the analysis of histopathological morphology showed that the morphology and density of tumor tissue in hydrogel/DOX treatment group changed obviously by using hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining assay, meanwhile cleaved caspase-3 (caspase-3) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) were expressed at high levels tumors tissue in hydrogel/DOX treatment group by using immunohistochemical (IHC) staining. These results would endow different biological elements with incredible potential to study the mechanisms of anti-tumor, which opens new direction and perspectives for the multi-elemental mapping of biological tissues, especially in clinic application.

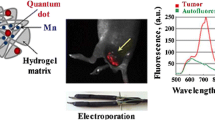
The integrated platform of DNA nanohydrogel drug carrier–based anti-tumor treatment combined with LIBS elemental imaging, via tail intravenous injection of saline, hydrogel, DOX, and hydrogel/DOX in breast cancer xenograft tumor mice. (A) The workflow is outlined starting from nanohydrogel drug carrier–based anti-tumor treatment. (B) Schematic diagram of LIBS imaging platform



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68:394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Leibowitz-Amit R, Pintilie M, Khoja L, Azad AA, Berger R, Laird AD (2016) Changes in plasma biomarkers following treatment with cabozantinib in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: a post hoc analysis of an extension cohort of a phase II trial. J Transl Med 14:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-015-0747-y
Korell M, Brassel F, Pagels J (2013) Evaluation of an in situ polymerizing hydrogel applied in tumor excision cavities during breast conservation surgery. Surg Sci 04:464–468. https://doi.org/10.4236/ss.2013.410091
Carvalho C, Santos RX, Cardoso S, Correia S, Oliveira PJ, Santos MS (2009) Doxorubicin: the good, the bad and the ugly effect. Curr Med Chem 16:3267–3285. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986709788803312
Boulaiz H, Ramos MC, Grinan-Lison C, Garcia-Rubino ME, Vicente F, Marchal JA (2017) What’s new in the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer: a patent review (2011-present). Expert Opin Ther Pat 27:1319–1328. https://doi.org/10.1080/13543776.2017.1379991
Tyanova S, Cox J (2018) Perseus: a bioinformatics platform for integrative analysis of proteomics data in cancer research. Methods Mol Biol 1711:133–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7493-1_7
Nacif LS, Rocha-Santos V, Claro LCL, Vintimilla A, Ferreira LA, Arantes RM (2018) Liver biopsy may facilitate pancreatic graft evaluation: positive association between liver steatosis and pancreatic graft adipose infiltration. Clinics 73:1–49. https://doi.org/10.6061/clinics/2018/e49
Moncayo S, Trichard F, Busser B, Sabatier-Vincent M, Pelascini F, Pinel N (2017) Multi-elemental imaging of paraffin-embedded human samples by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta B 133:40–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sab.2017.04.013
Sapkota M, Knoell DL (2018) Essential role of zinc and zinc transporters in myeloid cell function and host defense against infection. J Immunol Res 10:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/4315140
Zablocka-Slowinska K, Placzkowska S, Prescha A, Pawelczyk K, Porebska I, Kosacka M (2018) Serum and whole blood Zn, Cu and Mn profiles and their relation to redox status in lung cancer patients. J Trace Elem Med Biol 45:78–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2017.09.024
Rodrigues GP, Cozzolino SMF, Marreiro DDN, Caldas DRC, Silva KG, Sousa Almondes KG (2017) Mineral status and superoxide dismutase enzyme activity in Alzheimer’s disease. J Trace Elem Med Biol 44:83–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2017.06.005
Wang S, Liu X, Chen S, Liu Z, Zhang X, Liang XJ (2018) Regulation of Ca2+ signaling for drug-resistant breast cancer therapy with mesoporous silica nanocapsules encapsulated doxorubicin/siRNA cocktail. ACS Nano 13:274–281. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b05639
Subramanian VK, Deepe GS (2017) Metallothioneins: emerging modulators in immunity and infection. Int J Mol Sci 18:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102197
Evans ER, Bugga P, Asthana V, Drezek R (2018) Metallic nanoparticles for cancer immunotherapy. Mater Today 21:673–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2017.11.022
Meng Y, Sun J, Yu J, Wang C, Su J (2019) Dietary intakes of calcium, iron, magnesium, and potassium elements and the risk of colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. Biol Trace Elem Res 189:325–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1474-z
Bayer TA, Schafer S, Simons A, Kemmling A, KamerT TR (2003) Dietary Cu stabilizes brain superoxide dismutase 1 activity and reduces amyloid Abeta production in APP23 transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:14187–14192. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2332818100
Burkhead JL, Gray LW, Lutsenko S (2011) Systems biology approach to Wilson's disease. Biometals 24:455–466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-011-9430-9
Itazawa MK, Hsu HW, Medeiros R (2016) Copper exposure perturbs brain inflammatory responses and impairs clearance of amyloid-beta. Toxicol Sci 152:194–204. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfw081
Ahmed I, Ahmed R, Yang J, Law AWL, Zhang Y, Lau C (2017) Elemental analysis of the thyroid by laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Biomed Opt Express 8:4865–4871. https://doi.org/10.1364/BOE.8.004865
Ahmed SS, Santosh W (2010) Metallomic profiling and linkage map analysis of early Parkinson's disease: a new insight to aluminum marker for the possible diagnosis. PLoS One 5:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0011252
Tseng WY, Su MY, Tseng YH (2016) Introduction to cardiovascular magnetic resonance: Technical principles and clinical applications. Acta Cardiol Sin 32:129–144. https://doi.org/10.6515/ACS20150616A
Guevel LX, Henry M, Motto-Ros V, Longo E, Montanez MI, Pelascini F (2018) Elemental and optical imaging evaluation of zwitterionic gold nanoclusters in glioblastoma mouse models. Nanoscale 10:18657–18664. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NR05299A
Ghasemi F, Parvin P, Hosseini Motlagh NS, Amjadi A, Abachi S (2016) Laser induced breakdown spectroscopy and acoustic response techniques to discriminate healthy and cancerous breast tissues. Appl Opt 55:8227–8235. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.55.008227
Pozebon D, Scheffler GL, Dressler VL, Nunes MAG (2014) Review of the applications of laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) to the analysis of biological samples. J Anal At Spectrom 29:2204–2228. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4JA00250D
Aida S, Maryam B, Mohammad MHM, Seyed HT (2018) Feasibility study on discrimination of neo-plastic and non-neoplastic gastric tissues using spark discharge assisted laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. J Lasers Med Sci 10:64–69. https://doi.org/10.15171/jlms.2019.10
Busser B, Moncay S, Coll JL, Sancey L, Motto-Ros V (2018) Elemental imaging using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy: a new and promising approach for biological and medical applications. Coord Chem Rev 351:70–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2017.12.006
Gimenez Y, Busser B, Trichard F, Kulesza A, Laurent JM, Zaun V (2016) 3D imaging of nanoparticle distribution in biological tissue by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Sci Rep 6:29936–29945. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep29936
Gill RK, Smith ZJ, Panchal RR, Bishop JW, Gandour-Edwards R, Wachsmann-Hogiu S (2015) Preliminary fsLIBS study on bone tumors. Biomed Opt Express 6:4850–4858. https://doi.org/10.1364/BOE.6.004850
Rehse SJ, Salimnia H, Miziolek AW (2012) Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS): an overview of recent progress and future potential for biomedical applications. J Med Eng Technol 36:77–89. https://doi.org/10.3109/03091902.2011.645946
Wei HY, Zhao Z, Wang Y, Zou J, Lin Q, Duan YX (2019) One-step self-assembly of multifunctional DNA nanohydrogels: an enhanced and harmless strategy for guiding combined antitumor therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b15874
Moncayo S, Duponchel L, Mousavipak N, Panczer G, Trichard F, Bousquet B (2018) Exploration of megapixel hyperspectral LIBS images using principal component analysis. J Anal Atom Spectrom 33:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7JA00398F
Liu T, Liu W, Zhang M, Yu W, Gao F, Li C (2018) Ferrous-supply-regeneration nanoengineering for cancer-cell-specific ferroptosis in combination with imaging-guided photodynamic therapy. ACS Nano 12:121–128. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b05860
Nelson N (1999) Metal ion transporters and homeostasis. EMBO J 18:4361–4371. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/18.16.4361
Cemek M, Buyukokuroglu ME, Buyukben A, Aymelek F, Yilmaz F, Dogan M (2010) Bio-element status in children with acute rheumatic fever: before treatment and after clinical improvement. Pediatr Cardiol 31:1002–1007. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-010-9752-3
Puig S, Ramos-Alonso L, Romero AM, Martinez-Pastor MT (2017) The elemental role of iron in DNA synthesis and repair. Metallomics 9:1483–1500. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00116A
Baaij JH, Hoenderop JG, Bindels RJ (2015) Magnesium in man: implications for health and disease. Physiol Rev 95:1–46. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00012.2014
Seo JA, Kim B, Dhanasekaran DN, Tsang BK, Song YS (2015) Resveratrol triggers ER stress-mediated apoptosis by disrupting N-linked glycosylation of proteins in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Lett 371:347–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2015.11.032
Rizzuto R, Pinton P, Ferrari D, Chami M, Szabadkai G, Magalhaes PJ (2003) Calcium and apoptosis: facts and hypotheses. Oncogene 22:8619–8627. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207105
Feske S, Wulff H, Skolnik EY (2015) Ion channels in innate and adaptive immunity. Annu Rev Immunol 33:291–353. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-immunol-032414-112212
Maximilian B, Szilvia T, Balazs H, Balazs D, Andreas L (2017) FTIR-spectroscopic and LA-ICP-MS imaging for combined hyperspectral image analysis of tumor models. Anal Methods 9:5464–5471. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7AY01369H
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21874095, 61605134); Key Research and Development Project from Department of Science and Technology, Sichuan Province (2017SZ0013); Graduate Student’s Research and Innovation Fund of Sichuan University (No. 2018YJSY054); Chengdu Technological Innovation Project (2018-YF05-01184-SN); and Sichuan Applied Basic Research Project (2019YJ0078).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hongyan Wei finished the research, data analysis, and manuscript writing. Zhao Zhao gave some ideas about the methods. Prof. Qingyu Lin finished the LIBS test experiment and revised the article frame and contents. Prof. Yixiang Duan put forward ideas to design this research and amend the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable institutional and/or national guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 933 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, H., Zhao, Z., Lin, Q. et al. Study on the Molecular Mechanisms Against Human Breast Cancer from Insight of Elemental Distribution in Tissue Based on Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS). Biol Trace Elem Res 199, 1686–1692 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02292-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02292-8