Abstract
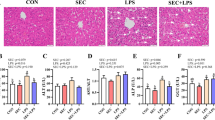
Selenium (Se) is important in many physiological processes, such as antioxidant processes and inflammation. The aim of our experiments was to investigate the molecular mechanism that selenomethionine could reduce the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation by inhibiting the TLR4-NF-κB-NLRP3 signaling pathway. Eighty broilers were randomly and evenly divided into two groups, giving normal Se content diets (Con group, 0.2 mg Se/kg diet) and Se-rich basal diets (Se group, 0.5 mg selenomethionine/kg diet) for 90 days. Se-rich basal diets were based on 0.2 mg/kg sodium selenite contained. Five hours before euthanized, 20 broilers were randomly selected from each group and given lipopolysaccharide (200 μg/kg BW) by intraperitoneal injection, Con+LPS group and Se+LPS group, respectively. The Con group and Se group were given equal saline by intraperitoneal injection. We observed the microscopic pathological changes of liver tissue detected oxidative stress by kit and detected the expression of inflammatory factors, heat shock protein (HSP), and nod-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3)–related genes by qRT-PCR and Western blot. With the microscope, we found the Con+LPS group had obvious inflammatory lesions such as sinusoidal congestion, but the damage was significantly alleviated in the Se+LPS group. In the Con+LPS group, the activity of GSH-Px and the content of GSH were significantly decreased compared with those in the Con group; however, they are increased in the Se group and in the Se + LPS group. Inflammatory factors (MyD88, NF-κB, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-12, IL-18, iNOS, and COX-2), heat shock proteins (HSP27, HSP60, HSP70, and HSP90), and the expression of NLRP3 and caspase-1 increased in the Con+LPS group compared with those in the Con group, while they were lower in the Se+LPS group than in the Con+LPS group. We concluded that selenomethionine inhibits the LPS-induced inflammation of liver tissue via suppressing the TLR4-NF-κB-NLRP3 signaling pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luo J, Li X, Li X, He Y, Zhang M, Cao C, Wang K (2018) Selenium-rich yeast protects against aluminum-induced peroxidation of lipide and inflammation in mice liver. Biometals 31(6):1051–1059
Li S, Tang T, Guo P, Zou Q, Ao X, Hu L, Tan L (2019) A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials: efficacy of selenium treatment for sepsis. Medicine (Baltimore) 98(9):e14733
Sun Z, Xu Z, Wang D, Yao H, Li S (2018) Selenium deficiency inhibits differentiation and immune function and imbalances the Th1/Th2 of dendritic cells. Metallomics 10(5):759–767
Chi Q, Luan Y, Zhang Y, Hu X, Li S (2019) The regulatory effects of miR-138-5p on selenium deficiency-induced chondrocyte apoptosis are mediated by targeting SelM. Metallomics 11(4):845–857
Gao X, Zhang Z, Xing H, Yu J, Zhang N, Xu S (2016) Selenium deficiency-induced inflammation and increased expression of regulating inflammatory cytokines in the chicken gastrointestinal tract. Biol Trace Elem Res 173(1):210–218
Gao X, Zhang Z, Li Y, Shen P, Hu X, Cao Y, Zhang N (2016) Selenium deficiency facilitates inflammation following S. aureus infection by regulating TLR2-related pathways in the mouse mammary gland. Biol Trace Elem Res 172(2):449–457
Zhang Z, Gao X, Cao Y, Jiang H, Wang T, Song X, Guo M, Zhang N (2015) Selenium deficiency facilitates inflammation through the regulation of TLR4 and TLR4-related signaling pathways in the mice uterus. Inflammation 38(3):1347–1356
Jin X, Jia T, Liu R, Xu S (2018) The antagonistic effect of selenium on cadmium-induced apoptosis via PPAR-gamma/PI3K/Akt pathway in chicken pancreas. J Hazard Mater 357:355–362
Yao HD, Wu Q, Zhang ZW, Zhang JL, Li S, Huang JQ, Ren FZ, Xu SW, Wang XL, Lei XG (2013) Gene expression of endoplasmic reticulum resident selenoproteins correlates with apoptosis in various muscles of se-deficient chicks. J Nutr 143(5):613–619
Yao HD, Wu Q, Zhang ZW, Li S, Wang XL, Lei XG, Xu SW (2013) Selenoprotein W serves as an antioxidant in chicken myoblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta 1830(4):3112–3120
Cao C, Li X, Qin L, Luo J, Zhang M, Ou Z, Wang K (2018) High selenium yeast mitigates aluminum-induced cerebral inflammation by increasing oxidative stress and blocking NO production. Biometals 31(5):835–843
Abu-El-Zahab HSH et al (2019) Antioxidant, antiapoptotic, antigenotoxic, and hepatic ameliorative effects of L-carnitine and selenium on cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity and alterations in liver cell structure in male mice. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 173:419–428
Rao SV et al (2016) Effect of supplementing organic forms of zinc, selenium and chromium on performance, anti-oxidant and immune responses in broiler chicken reared in tropical summer. Biol Trace Elem Res 172(2):511–520
Bruno P, Rafael S, Gerson F, et al (2018) NF-kappaB: Two Sides of the Same Coin. Genes 9(1):24
Shi Q, Wang W, Chen M, Zhang H, Xu S (2019) Ammonia induces Treg/Th1 imbalance with triggered NF-kappaB pathway leading to chicken respiratory inflammation response. Sci Total Environ 659:354–362
Afonina IS, Zhong Z, Karin M, Beyaert R (2017) Limiting inflammation-the negative regulation of NF-kappaB and the NLRP3 inflammasome. Nat Immunol 18(8):861–869
Zhong Z, Umemura A, Sanchez-Lopez E, Liang S, Shalapour S, Wong J, He F, Boassa D, Perkins G, Ali SR, McGeough MD, Ellisman MH, Seki E, Gustafsson AB, Hoffman HM, Diaz-Meco MT, Moscat J, Karin M (2016) NF-kappaB restricts inflammasome activation via elimination of damaged mitochondria. Cell 164(5):896–910
Baker RG, Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2011) NF-kappaB, inflammation, and metabolic disease. Cell Metab 13(1):11–22
Wu J, Niu P, Zhao Y, Cheng Y, Chen W, Lin L, Lu J, Cheng X, Xu Z (2019) Impact of miR-223-3p and miR-2909 on inflammatory factors IL-6, IL-1ss, and TNF-alpha, and the TLR4/TLR2/NF-kappaB/STAT3 signaling pathway induced by lipopolysaccharide in human adipose stem cells. PLoS One 14(2):e0212063
Kleinridders A, Schenten D, Könner AC, Belgardt BF, Mauer J, Okamura T, Wunderlich FT, Medzhitov R, Brüning JC (2009) MyD88 signaling in the CNS is required for development of fatty acid-induced leptin resistance and diet-induced obesity. Cell Metab 10(4):249–259
Chen M, Li X, Shi Q, Zhang Z, Xu S (2019) Hydrogen sulfide exposure triggers chicken trachea inflammatory injury through oxidative stress-mediated FOS/IL8 signaling. J Hazard Mater 368:243–254
Salari S, Seibert T, Chen YX, Hu T, Shi C, Zhao X, Cuerrier CM, Raizman JE, O’Brien ER (2013) Extracellular HSP27 acts as a signaling molecule to activate NF-kappaB in macrophages. Cell Stress Chaperones 18(1):53–63
Qi J et al (2015) Heat shock protein 90 inhibition by 17-dimethylaminoethylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin protects blood-brain barrier integrity in cerebral ischemic stroke. Am J Transl Res 7(10):1826–1837
Giffard RG, Han RQ, Emery JF, Duan M, Pittet JF (2008) Regulation of apoptotic and inflammatory cell signaling in cerebral ischemia: the complex roles of heat shock protein 70. Anesthesiology 109(2):339–348
Marker T, Sell H, Zillessen P, Glode A, Kriebel J, Ouwens DM, Pattyn P, Ruige J, Famulla S, Roden M, Eckel J, Habich C (2012) Heat shock protein 60 as a mediator of adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance. Diabetes 61(3):615–625
Shirato K et al (2017) Regular voluntary exercise potentiates interleukin-1beta and interleukin-18 secretion by increasing caspase-1 expression in murine macrophages. Mediators Inflamm 2017:9290416
Ohtsu A et al (2017) Advanced glycation end products and lipopolysaccharides stimulate interleukin-6 secretion via the RAGE/TLR4-NF-kappaB-ROS pathways and resveratrol attenuates these inflammatory responses in mouse macrophages. Exp Ther Med 14(5):4363–4370
Eun SH, Woo JT, Kim DH (2017) Tangeretin inhibits IL-12 expression and NF-kappaB Activation in dendritic cells and attenuates colitis in mice. Planta Med 83(6):527–533
Komada T, Muruve DA (2019) The role of inflammasomes in kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 15:501–520. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41581-019-0158-z
Matias ML, Gomes VJ, Romao-Veiga M, Ribeiro VR, Nunes PR & Romagnoli GG, et al. (2019) Silibinin downregulates the nf-κb pathway and nlrp1/nlrp3 inflammasomes in monocytes from pregnant women with preeclampsia. Molecules 24(8). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081548
Khakroo Abkenar, I., Rahmani-nia F & Lombardi G (2019) The Effects of Acute and Chronic Aerobic Activity on the Signaling Pathway of the Inflammasome NLRP3 Complex in Young Men. Medicina 55(4):105
Chen Y, Qian Q, Yu J (2019) Carbenoxolone ameliorates insulin sensitivity in obese mice induced by high fat diet via regulating the IkappaB-alpha/NF-kappaB pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome. Biomed Pharmacother 115:108868
Martine P, Chevriaux A, Derangère V, Apetoh L, Garrido C, Ghiringhelli F, Rébé C (2019) HSP70 is a negative regulator of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell Death Dis 10(4):256
He G, Karin M (2011) NF-kappaB and STAT3 - key players in liver inflammation and cancer. Cell Res 21(1):159–168
Yu L, Yang S, Sun L, Jiang YF, Zhu LY (2014) Effects of selenium-enriched Agaricus blazei Murill on liver metabolic dysfunction in mice, a comparison with selenium-deficient Agaricus blazei Murill and sodium selenite. Biol Trace Elem Res 160(1):79–84
Zhu C, Zhang S, Song C, Zhang Y, Ling Q, Hoffmann PR, Li J, Chen T, Zheng W, Huang Z (2017) Selenium nanoparticles decorated with Ulva lactuca polysaccharide potentially attenuate colitis by inhibiting NF-kappaB mediated hyper inflammation. J Nanobiotechnology 15(1):20
Wang W, Chen M, Jin X, Li X, Yang Z, Lin H, Xu S (2018) H2S induces Th1/Th2 imbalance with triggered NF-kappaB pathway to exacerbate LPS-induce chicken pneumonia response. Chemosphere 208:241–246
Zheng S, Jin X, Chen M, Shi Q, Zhang H, Xu S (2019) Hydrogen sulfide exposure induces jejunum injury via CYP450s/ROS pathway in broilers. Chemosphere 214:25–34
Kim Y, Kim DC, Cho ES, Ko SO, Kwon WY, Suh GJ, Shin HK (2014) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of selenium in oral buccal mucosa and small intestinal mucosa during intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Inflamm (Lond) 11(1):36
Wang J, Liu Z, He X, Lian S, Liang J, Yu D, Sun D, Wu R (2018) Selenium deficiency induces duodenal villi cell apoptosis via an oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial apoptosis pathway and an inflammatory signaling-induced death receptor pathway. Metallomics 10(10):1390–1400
Wei Z, Yao M, Li Y, Yang Z, Feng X (2015) Inhibition of Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory responses by selenium in bovine mammary epithelial cells in primary culture. Inflammation 38(1):152–158
Ma J, Zhu S, Guo Y, Hao M, Chen Y, Wang Y, Yang M, Chen J, Guo M (2018) Selenium attenuates Staphylococcus aureus mastitis in mice by inhibiting the activation of the NALP3 inflammasome and NF-kappaB/MAPK pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1591-8
Zhang WJ, Fang ZM, Liu WQ (2019) NLRP3 inflammasome activation from Kupffer cells is involved in liver fibrosis of Schistosoma japonicum-infected mice via NF-kappaB. Parasit Vectors 12(1):29
Xiao J et al (2018) Lycium barbarum polysaccharides improve hepatic injury through NFkappa-B and NLRP3/6 pathways in a methionine choline deficient diet steatohepatitis mouse model. Int J Biol Macromol 120(Pt B):1480–1489
Souza CF, Baldissera MD, Descovi SN, Diniz SLP, Henn AS, Flores EMM, da Silva AS, Baldisserotto B (2019) Diphenyl diselenide dietary supplementation protects against methylmercury-chloride-induced immunotoxicity in the head kidney and spleen of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) via regulation of purinergic signaling and the NLRP3 inflammasome. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 222:59–64
Lu Y, Xu S, Chen H, He M, Deng Y, Cao Z, Pi H, Chen C, Li M, Ma Q, Gao P, Ji Y, Zhang L, Yu Z, Zhou Z (2016) CdSe/ZnS quantum dots induce hepatocyte pyroptosis and liver inflammation via NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Biomaterials 90:27–39
Wang H, Li S, Teng X (2016) The Antagonistic Effect of Selenium on Lead-Induced Inflammatory Factors and Heat Shock Proteins mRNA Expression in Chicken Livers. Biol Trace Elem Res 171(2):437–444
Shi C, Ulke-Lemée A, Deng J, Batulan Z, O’Brien ER (2019) Characterization of heat shock protein 27 in extracellular vesicles: a potential anti-inflammatory therapy. FASEB J 33(2):1617–1630
Hu X, Chi Q, Wang D, Chi X, Teng X, Li S (2018) Hydrogen sulfide inhalation-induced immune damage is involved in oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis and the Th1/Th2 imbalance in broiler bursa of Fabricius. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 164:201–209
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their sincere thanks to the members of the veterinary internal medicine laboratory and key Laboratory for Laboratory Animals at the College of Veterinary Medicine, Northeast Agricultural University.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31872437).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, J., Wang, W., Zhang, Q. et al. Inhibition of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation of Chicken Liver Tissue by Selenomethionine via TLR4-NF-κB-NLRP3 Signaling Pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res 195, 205–214 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01841-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01841-0