Abstract
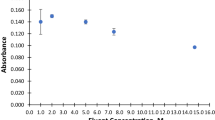
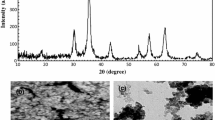
In this work, mesoporous strontium titanate nanoparticles (SrTiO3 NPs) were synthesized through a single-step combustion process and were characterized by FT-IR, XRD, SEM-EDX, and TEM. The effects of main parameters that may influence the extraction process (i.e., pH, sorbent amount, time of extraction, eluting agent, and the presence concomitant ions) were investigated. The optimum extraction was achieved at pH 6, 50 mg of sorbent, 20-min shaking time, and 4.0 mL of 0.1 mol L−1 thiourea as desorption agent. Under these conditions, the maximum adsorption capacity was 155.6 mg g−1 with a preconcentration factor of 250 (for a 1000 mL sample solution). The calibration graph was linear up to 1000 μg L−1 and the limit of detection was 1.75 μg L−1. The precision (as relative standard deviation) was 2.53% (n = 10). The procedure was employed for the preconcentration of Pb2+ from blood and urine samples of bladder cancer patients before its determination by FAAS.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu J, Goyer RA, Waalkes MP (2008) Toxic effects of metals. In: Klaassen CD (ed) Casarett and Doull’s toxicology, the basic science of poisons, 7th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 931–979
da Silva PAB, de Souza GC, da S. Leotério DM, Belian MF, Silva WE, Paim AP, Lavorante AF (2015) Synthesis and characterization of functionalized silica with 3, 6-ditia-1, 8-octanediol for the preconcentration and determination of lead in milk employing multicommuted flow system coupled to FAAS. J Food Compos Anal 40:177–184
Chen J, Xiao S, Wu X, Fang K, Liu W (2005) Determination of lead in water samples by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry after cloud point extraction. Talanta 67(5):992–996
dos Santos ÉJ, Herrmann AB, Prado SK, Fantin EB, dos Santos VW, de Oliveira AVM, Curtius AJ (2013) Determination of toxic elements in glass beads used for pavement marking by ICP OES. Microchem J 108:233–238
Cao Y, Deng B, Yan L, Huang H (2017) An environmentally-friendly, highly efficient, gas pressure-assisted sample introduction system for ICP-MS and its application to detection of cadmium and lead in human plasma. Talanta 167:520–525
das Graças AKM, de Andrade JB, de Jesus DS, Lemos VA, Bandeira ML, dos Santos WN, Bezerra MA, Amorim FA, Souza AS, Ferreira SL (2006) Separation and preconcentration procedures for the determination of lead using spectrometric techniques: a review. Talanta 69(1):16–24
Visser AE, Swatloski RP, Griffin ST, Hartman DH, Rogers RD (2001) Liquid/liquid extraction of metal ions in room temperature ionic liquids. Sep Sci Technol 36(5–6):785–804
Gouda AA (2016) A new coprecipitation method without carrier element for separation and preconcentration of some metal ions at trace levels in water and food samples. Talanta 146:435–441
Mortada W, Kenawy I, Abdel-Rhman M, El-Gamal G, Moalla S (2017) A new thiourea derivative [2-(3-ethylthioureido) benzoic acid] for cloud point extraction of some trace metals in water, biological and food samples. J Trace Elem Med Biol 44:266–273
Mortada W, Kenawy I, El-Reash YA, Mousa A (2017) Microwave assisted modification of cellulose by gallic acid and its application for removal of aluminium from real samples. Int J Biol Macromol 101:490–501
Hu B, He M, Chen B (2015) Nanometer-sized materials for solid-phase extraction of trace elements. Anal Bioanal Chem 407(10):2685–2710
Feist B (2016) Selective dispersive micro solid-phase extraction using oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes modified with 1, 10-phenanthroline for preconcentration of lead ions. Food Chem 209:37–42
Jiang H-m, Yang T, Wang Y-h, Lian H-z, Hu X (2013) Magnetic solid-phase extraction combined with graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry for speciation of Cr (III) and Cr (VI) in environmental waters. Talanta 116:361–367
Shirkhanloo H, Khaligh A, Mousavi HZ, Rashidi A (2016) Ultrasound assisted-dispersive-micro-solid phase extraction based on bulky amino bimodal mesoporous silica nanoparticles for speciation of trace manganese (II)/(VII) ions in water samples. Microchem J 124:637–645
Bicim T, Yaman M (2016) Sensitive determination of uranium in natural waters using UV-Vis spectrometry after preconcentration by ion-imprinted polymer-ternary complexes. J AOAC Int 99(4):1043–1048
Limchoowong N, Sricharoen P, Areerob Y, Nuengmatcha P, Sripakdee T, Techawongstien S, Chanthai S (2017) Preconcentration and trace determination of copper (II) in Thai food recipes using Fe3O4 @ Chi–GQDs nanocomposites as a new magnetic adsorbent. Food Chem 230:388–397
Mortada W, Moustafa A, Ismail A, Hassanien M, Aboud A (2015) Microwave assisted decoration of titanium oxide nanotubes with CuFe2O4 quantum dots for solid phase extraction of uranium. RSC Adv 5(77):62414–62423
Yavuz E, Tokalıoğlu Ş, Şahan H, Patat Ş (2014) Nano sponge Mn2O3 as a new adsorbent for the preconcentration of Pd (II) and Rh (III) ions in sea water, wastewater, rock, street sediment and catalytic converter samples prior to FAAS determinations. Talanta 128:31–37
Ghaedi M, Niknam K, Shokrollahi A, Niknam E, Rajabi HR, Soylak M (2008) Flame atomic absorption spectrometric determination of trace amounts of heavy metal ions after solid phase extraction using modified sodium dodecyl sulfate coated on alumina. J Hazard Mater 155(1):121–127
Pena M, Fierro J (2001) Chemical structures and performance of perovskite oxides. Chem Rev 101(7):1981–2018
Tsumura T, Sogabe K, Toyoda M (2009) Preparation of SrTiO3-supported TiO2 photocatalyst. Mater Sci Eng B 157(1):113–115
Johnson DC, Prieto AL (2011) Use of strontium titanate (SrTiO3) as an anode material for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 196(18):7736–7741
Thongnopkun P, Ekgasit S (2005) FTIR spectra of faceted diamonds and diamond simulants. Diam Relat Mater 14(10):1592–1599
Khajepour A, Rahmani F (2017) An approach to design a 90 Sr radioisotope thermoelectric generator using analytical and Monte Carlo methods with ANSYS, COMSOL, and MCNP. Appl Radiat Isot 119:51–59
Shiyong L, Jiayun Z (2007) Kinetics of strontium titanate formation from solid state reaction between strontium carbonate and anatase. High Temp Mater Processes 26(1):33–42
Barrett EP, Joyner LG, Halenda PP (1951) The determination of pore volume and area distributions in porous substances. I Computations from nitrogen isotherms. J Am Chem Soc 73(1):373–380
Brunauer S, Emmett PH, Teller E (1938) Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J Am Chem Soc 60(2):309–319
Kenawy I, El-Reash YA, Hassanien M, Alnagar N, Mortada W (2018) Use of microwave irradiation for modification of mesoporous silica nanoparticles by thioglycolic acid for removal of cadmium and mercury. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 258:217–227
Monsef Khoshhesab Z, Najafi N (2017) Magnetic solid-phase extraction to preconcentrate trace amounts of gold (III) using nickel ferrite magnetic nanoparticles. Int J Environ Anal Chem 97(13): 1–16
Afkhami A, Saber-Tehrani M, Bagheri H (2010) Simultaneous removal of heavy-metal ions in wastewater samples using nano-alumina modified with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine. J Hazard Mater 181(1–3):836–844
Soylak M, Acar D, Yilmaz E, El-Khodary SA, Morsy M, Ibrahim M (2017) Magnetic graphene oxide as an efficient adsorbent for the separation and preconcentration of Cu (II), Pb (II), and Cd (II) from environmental samples. J AOAC Int 100(5):1544–1550
Jin Z, Gao H, Hu L (2015) Removal of Pb (II) by nano-titanium oxide investigated by batch, XPS and model techniques. RSC Adv 5(107):88520–88528
Kenawy IM, Mortada WI, Abou El-Reash YG, Hawwas AH (2015) New modified cellulose nanoparticles for solid-phase extraction of some metal ions in biological and water samples. Can J Chem 94(3):221–228
Ren Y, Abbood HA, He F, Peng H, Huang K (2013) Magnetic EDTA-modified chitosan/SiO2/Fe3O4 adsorbent: preparation, characterization, and application in heavy metal adsorption. Chem Eng J 226:300–311
Dąbrowski A (2001) Adsorption—from theory to practice. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 93(1–3):135–224
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 40(9):1361–1403
Mckay G, Blair H, Gardner J (1982) Adsorption of dyes on chitin. I Equilibrium studies. J Appl Polym Sci 27(8):3043–3057
León M, Flores-Alamo N, Solache-Ríos MJ, Rosa-Gómez I, Díaz-Campos G (2017) Lead and copper adsorption behaviour by Lemna gibba: kinetic and equilibrium studies. CLEAN–Soil Air Water 45(8): 1600357
Wadhwa SK, Tuzen M, Kazi TG, Soylak M, Hazer B (2014) Polyhydroxybutyrate-b-polyethyleneglycol block copolymer for the solid phase extraction of lead and copper in water, baby foods, tea and coffee samples. Food Chem 152:75–80
Ghaedi M, Montazerozohori M, Rahimi N, Biysreh MN (2013) Chemically modified carbon nanotubes as efficient and selective sorbent for enrichment of trace amount of some metal ions. J Ind Eng Chem 19(5):1477–1482
Daşbaşi T, Muğlu H, Soykan C, Ülgen A (2018) SPE and determination by FAAS of heavy metals using a new synthesized polymer resin in various water and dried vegetables samples. J Macromol Sci A 55(3):288–295
Baghban N, Yilmaz E, Soylak M (2018) Vortex assisted solid-phase extraction of lead (II) using orthorhombic nanosized Bi2WO6 as a sorbent. Microchim Acta 185(1):34
Cândido Siqueira LM, de Sousa Neto JA, Coelho NMM, Alves VN (2017) Preconcentration system for determination of lead in chicken feed using Moringa oleifera husks as a biosorbent. Microchem J 133:327–332
Golabek T, Darewicz B, Borawska M, Markiewicz R, Socha K, Kudelski J (2009) Lead concentration in the bladder tissue and blood of patients with bladder cancer. Scand J Urol Nephrol 43(6):467–470
Chang CH, Liu CS, Liu HJ, Huang CP, Huang CY, Hsu HT, Liou SH, Chung CJ (2016) Association between levels of urinary heavy metals and increased risk of urothelial carcinoma. Int J Urol 23(3):233–239
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mortada, W.I., Abdelghany, A.M. Preconcentration of Lead in Blood and Urine Samples Among Bladder Cancer Patients Using Mesoporous Strontium Titanate Nanoparticles. Biol Trace Elem Res 193, 100–110 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01704-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01704-8