Abstract
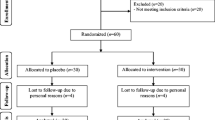
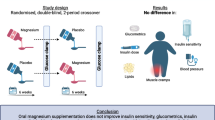
Low serum magnesium concentrations were associated with development of renal failure. We aimed to determine whether magnesium supplementation improves renal function, insulin resistance, and metabolic profiles in patients with diabetic nephropathy. A total of 80 hypomagnesemic patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes and early-stage nephropathy were recruited. Subjects received either daily magnesium oxide or placebo for 12 weeks. Biochemical and anthropometric variables were measured. Physical activity and dietary intakes were also recorded. This study was approved by the ethics committee of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences and was registered on the Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials website (IRCT registration no. IRCT201404271485N12). Serum magnesium levels were not changed significantly. Although the supplementation did not influence glycemic indices, patients in the magnesium group had greater insulin resistance compared with the placebo group after intervention (0.3 ± 2.3 μIU/mL vs. − 0.04 ± 2.05, P = 0.04). No significant changes were observed in serum total cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL, LDL, and total cholesterol/HDL cholesterol ratio. Furthermore, magnesium did not affect inflammation, serum levels of creatinine, and blood urine nitrogen. However, a marginal decrease in microalbuminuria (− 3.1 ± 2.2 mg/L vs. − 14 ± 9.9, P = 0.09) was observed. Oral magnesium supplementation slightly improved microalbuminuria but resulted in increased insulin resistance in patients with diabetic nephropathy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shaw JE, Sicree RA, Zimmet PZ (2010) Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 87(1):4–14
Esteghamati A, Gouya MM, Abbasi M, Delavari A, Alikhani S, Alaedini F, Safaie A, Forouzanfar M, Gregg EW (2008) Prevalence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in the adult population of Iran: National Survey of Risk Factors for Non-Communicable Diseases of Iran. Diabetes Care 31(1):96–98
Locatelli F, Pozzoni P, Del Vecchio L (2004) Renal replacement therapy in patients with diabetes and end-stage renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 15(Suppl 1):S25–S29
Krairittichai U, Mahannopkul R, Bunnag S (2012) An open label, randomized controlled study of oral calcitriol for the treatment of proteinuria in patients with diabetic kidney disease. J Med Assoc Thail 95(Suppl 3):S41–S47
Aperis G, Paliouras C, Zervos A, Arvanitis A, Alivanis P (2011) The role of paricalcitol on proteinuria. J Ren Care 37(2):80–84
Khan MI, Siddique KU, Ashfaq F, Ali W, Reddy HD, Mishra A (2013) Effect of high-dose zinc supplementation with oral hypoglycemic agents on glycemic control and inflammation in type-2 diabetic nephropathy patients. J Nat Sci Biol Med 4(2):336–340
Reinhart RA, Marx JJ Jr, Haas RG, Desbiens NA (1987) Intracellular magnesium of mononuclear cells from venous blood of clinically healthy subjects. J Nat Sci Biol Med 167(2):187–195
Ainsworth BE, Haskell WL, Herrmann SD, Meckes N, Bassett DR Jr, Tudor-Locke C et al (2011) Compendium of physical activities: a second update of codes and MET values. Med Sci Sports Exerc 43(8):1575–1581
Corsonello A, Ientile R, Buemi M, Cucinotta D, Mauro VN, Macaione S, Corica F (2000) Serum ionized magnesium levels in type 2 diabetic patients with microalbuminuria or clinical proteinuria. Am J Nephrol 20(3):187–192
Pickup JC, Chusney GD, Crook MA, Viberti GC (1994) Hypomagnesaemia in IDDM patients with microalbuminuria and clinical proteinuria. Diabetologia 37(6):639
Sakaguchi Y, Shoji T, Hayashi T, Suzuki A, Shimizu M, Mitsumoto K, Kawabata H, Niihata K, Okada N, Isaka Y, Rakugi H, Tsubakihara Y (2012) Hypomagnesemia in type 2 diabetic nephropathy: a novel predictor of end-stage renal disease. Diabetes Care 35(7):1591–1597
Xu J, Xu W, Yao H, Sun W, Zhou Q, Cai L (2013) Associations of serum and urinary magnesium with the pre-diabetes, diabetes and diabetic complications in the Chinese Northeast population. PLoS One 8(2):e56750. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0056750
Sales CH, Pedrosa LF, Lima JG, Lemos TM, Colli C (2011) Influence of magnesium status and magnesium intake on the blood glucose control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Clin Nutr 30(3):359–364
Rodriguez-Moran M, Guerrero-Romero F (2003) Oral magnesium supplementation improves insulin sensitivity and metabolic control in type 2 diabetic subjects: a randomized double-blind controlled trial. Diabetes Care 26(4):1147–1152
Lal J, Vasudev K, Kela AK, Jain SK (2003) Effect of oral magnesium supplementation on the lipid profile and blood glucose of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Assoc Physicians India 51:37–42
Pham PC, Pham PM, Pham PA, Pham SV, Pham HV, Miller JM et al (2005) Lower serum magnesium levels are associated with more rapid decline of renal function in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2. Clin Nephrol 63(6):429–436
Song Y, He K, Levitan EB, Manson JE, Liu S (2006) Effects of oral magnesium supplementation on glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized double-blind controlled trials. Diabet Med 23(10):1050–1056
Veronese N, Watutantrige-Fernando S, Luchini C, Solmi M, Sartore G, Sergi G, Manzato E, Barbagallo M, Maggi S, Stubbs B (2016) Effect of magnesium supplementation on glucose metabolism in people with or at risk of diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of double-blind randomized controlled trials. Eur J Clin Nutr 70(12):1354–1359
Matsuzaki H, Ohdachi J, Fuchigami M, Masuyama R, Uehara M, Nakamura K et al (2002) Changes in N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase activity in the urine and urinary albumin excretion in magnesium deficient rats. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 66(1):192–194
Grafton G, Bunce CM, Sheppard MC, Brown G, Baxter MA (1992) Effect of Mg2+ on Na(+)-dependent inositol transport. Role for Mg2+ in etiology of diabetic complications. Diabetes 41(1):35–39
de Lordes LM, Cruz T, Pousada JC, Rodrigues LE, Barbosa K, Cangucu V (1998) The effect of magnesium supplementation in increasing doses on the control of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 21(5):682–686
Farvid MS, Homayouni F, Amiri Z, Adelmanesh F (2011) Improving neuropathy scores in type 2 diabetic patients using micronutrients supplementation. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 93(1):86–94
A. Catharine Ross BC, Robert J. Cousins, Katherine L. Tucker, Thomas R. Ziegler. Modern nutrition in health and disease. 2014. 11th ed. Chapter 9: Magnesium; p.164
Song Y, Manson JE, Tinker L, Howard BV, Kuller LH, Nathan L, Rifai N, Liu S (2007) Insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion determined by homeostasis model assessment and risk of diabetes in a multiethnic cohort of women: the Women’s Health Initiative Observational Study. Diabetes Care 30(7):1747–1752
Yajnik CS, Smith RF, Hockaday TD, Ward NI (1984) Fasting plasma magnesium concentrations and glucose disposal in diabetes. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 288(6423):1032–1034
Xu B, Sun J, Deng X, Huang X, Sun W, Xu Y et al (2013) Low serum magnesium level is associated with microalbuminuria in Chinese diabetic patients. Int J Endocrinol 2013:580685
Pham PC, Pham PM, Pham PT, Pham SV, Pham PA, Pham PT (2009) The link between lower serum magnesium and kidney function in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2 deserves a closer look. Clin Nephrol 71(4):375–379
Allegra A, Corsonello A, Buemi M, D'Angelo R, di Benedetto A, Bonanzinga S et al (1997) Plasma, erythrocyte and platelet magnesium levels in type 1 diabetic patients with microalbuminuria and clinical proteinuria. J Trace Elem Med Biol 11(3):154–157
Simental-Mendia LE, Rodriguez-Moran M, Guerrero-Romero F (2014) Oral magnesium supplementation decreases C-reactive protein levels in subjects with prediabetes and hypomagnesemia: a clinical randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Arch Med Res 45(4):325–330
Walker AF, Marakis G, Christie S, Byng M (2003) Mg citrate found more bioavailable than other mg preparations in a randomised, double-blind study. Magnes Res 16(3):183–191
Kappeler D, Heimbeck I, Herpich C, Naue N, Höfler J, Timmer W, Michalke B (2017) Higher bioavailability of magnesium citrate as compared to magnesium oxide shown by evaluation of urinary excretion and serum levels after single-dose administration in a randomized cross-over study. BMC Nutr 3(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40795-016-0121-3
Zghoul N, Alam-Eldin N, Mak IT, Silver B, Weglicki WB (2018) Hypomagnesemia in diabetes patients: comparison of serum and intracellular measurement of responses to magnesium supplementation and its role in inflammation. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 11:389–400
Paolisso G, Scheen A, D'Onofrio F, Lefebvre P (1990) Magnesium and glucose homeostasis. Diabetologia 33(9):511–514
Alzaid AA, Dinneen SF, Moyer TP, Rizza RA (1995) Effects of insulin on plasma magnesium in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: evidence for insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 80(4):1376–1381
Bhattacharyya AK, Thera C, Anderson JT et al (1969) Dietary calcium and fat. Effect on serum lipids and fecal excretion of cholesterol and its degradation products in man. Am J Clin Nutr 22:1161–1174
Gacs G, Barltrop D (1977) Significance of Ca-soap formation for calcium absorption in the rat. Gut 18:64–68
Buse JB, Tan MH, Prince MJ, Erickson PP (2004) The effects of oral anti-hyperglycaemic medications on serum lipid profiles in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 6(2):133–156
Saris NE, Mervaala E, Karppanen H, Khawaja JA, Lewenstam A (2000) Magnesium. An update on physiological, clinical and analytical aspects. Clin Chim Acta 294(1–2):1–26
Ryan MP, Ryan MF, Counihan TB (1981) The effect of diuretics on lymphocyte magnesium and potassium. Acta Med Scand Suppl 647:153–161
Acknowledgments
This study was extracted from a MSc dissertation which was approved by the School of Nutrition and Food Sciences, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences (no. 193012). We wish to thank all individuals who kindly participated in our study.
Funding
The financial support for this study comes from the Food Security Research Center, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MS, PS, FS, and AE contributed in the conception, design, statistical analyses, data interpretation, and manuscript drafting. All authors approved the final manuscript for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Transparency Declaration
The lead author affirms that this manuscript is an honest, accurate, and transparent account of the study being reported. The reporting of this work is compliant with CONSORT guidelines. The lead author affirms that no important aspects of the study have been omitted and that any discrepancies from the study as planned (IRCT registration no. IRCT201404271485N12) have been explained.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Novelty Statement
To manage renal function in diabetic nephropathy, several strategies included have been applied, but this is the first study which examined the effect of magnesium supplementation on renal function, insulin resistance, and metabolic profiles in patients with diabetic nephropathy.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sadeghian, M., Azadbakht, L., Khalili, N. et al. Oral Magnesium Supplementation Improved Lipid Profile but Increased Insulin Resistance in Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy: a Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Biol Trace Elem Res 193, 23–35 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01687-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01687-6