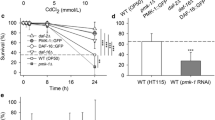
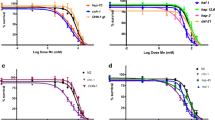
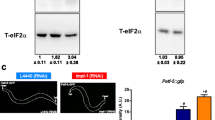
Abstract
Rare earth (RE) ions at high concentrations are toxic to many organisms as they induce oxidative stress and cause improper incorporation of the ions into calcium-binding proteins. Although the mechanism of action underlying the toxicity of REs has been identified, intracellular signaling pathways involved in stress responses against RE ions still remain unclear. In Caenorhabditis elegans, cellular responses against heavy metal stresses are primarily regulated by the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)-like mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway with a minor contribution of the p38-like MAPK pathway. In this study, we found that both JNK- and p38-like MAPK pathways were involved in stress responses against RE. Unlike heavy metal responses, mutations in both the JNK and p38 pathways caused similar hypersensitivity to RE ions. Although the signaling pathways used for these stress responses were found to be similar, the degree of their respective contribution slightly differed between heavy metal and RE ions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tchounwou PB, Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, Sutton DJ (2012) Heavy metals toxicity and the environment. Mol Clin Environ Toxicol:133–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7643-8340-4_6
Beyersmann D, Hartwig A (2008) Carcinogenic metal compounds: recent insight into molecular and cellular mechanisms. Arch Toxicol 82:493–512. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-008-0313-y
Xia Q, Feng X, Huang H, du L, Yang X, Wang K (2011) Gadolinium-induced oxidative stress triggers endoplasmic reticulum stress in rat cortical neurons. J Neurochem 117:38–47. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07162.x
Jiang N, Wang L, Lu T, Huang X (2011) Toxic effect of terbium ion on horseradish cell. Biol Trace Elem Res 143:1722–1728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-011-8968-2
Hong J, Yu X, Pan X, Zhao X, Sheng L, Sang X, Lin A, Zhang C, Zhao Y, Gui S, Sun Q, Wang L, Hong F (2014) Pulmonary toxicity in mice following exposure to cerium chloride. Biol Trace Elem Res 159:269–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-9953-3
Pagano G, Guida M, Siciliano A, Oral R, Koçbaş F, Palumbo A, Castellano I, Migliaccio O, Thomas PJ, Trifuoggi M (2016) Comparative toxicities of selected rare earth elements: sea urchin embryogenesis and fertilization damage with redox and cytogenetic effects. Environ Res 147:453–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2016.02.031
Burroughs SE, Horrocks WD, Ren H, Klee CB (1994) Characterization of the lanthanide ion-binding properties of calcineurin-B using laser-induced luminescence spectroscopy. Biochemistry 33:10428–10436
Pidcock E, Moore GR (2001) Structural characteristics of protein binding sites for calcium and lanthanide ions. JBIC. J Biol Inorg Chem 6:479–489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s007750100214
McLarnon SJ, Riccardi D (2002) Physiological and pharmacological agonists of the extracellular Ca2+-sensing receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 447:271–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-2999(02)01849-6
Roh J-Y, Lee J, Choi J (2006) Assessment of stress-related gene expression in the heavy metal-exposed nematode Caenorhabditis elegans: a potential biomarker for metal-induced toxicity monitoring and environmental risk assessment. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:2946–2956. https://doi.org/10.1897/05-676R.1
Shen L, Xiao J, Ye H, Wang D (2009) Toxicity evaluation in nematode Caenorhabditis elegans after chronic metal exposure. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 28:125–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2009.03.009
Chang L, Karin M (2001) Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature 410:37–40. https://doi.org/10.1038/35065000
Mizuno T, Hisamoto N, Terada T, Kondo T, Adachi M, Nishida E, Kim DH, Ausubel FM, Matsumoto K (2004) The Caenorhabditis elegans MAPK phosphatase pathway in stress response. EMBO J 23:2226–2234. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600226
Inoue H, Hisamoto N, An JH, Oliveira RP, Nishida E, Blackwell TK, Matsumoto K (2005) The C. elegans p38 MAPK pathway regulates nuclear localization of the transcription factor SKN-1 in oxidative stress response. Genes Dev 19:2278–2283. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1324805
Wakabayashi T, Ymamoto A, Kazaana A, Nakano Y, Nojiri Y, Kashiwazaki M (2016) Antibacterial, antifungal and nematicidal activities of rare earth ions. Biol Trace Elem Res 174:464–470. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0727-y
Brenner S (1974) The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 77:71–94
Kawai K, Wang G, Okamoto S, Ochi K (2007) The rare earth, scandium, causes antibiotic overproduction in Streptomyces spp. FEMS Microbiol Lett 274:311–315. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00846.x
Inaoka T, Ochi K (2012) Undecaprenyl pyrophosphate involvement in susceptibility of Bacillus subtilis to rare earth elements. J Bacteriol 194:5632–5637. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.01147-12
Jenkins W, Perone P, Walker K, Bhagavathula N, Aslam MN, DaSilva M, Dame MK, Varani J (2011) Fibroblast response to lanthanoid metal ion stimulation: potential contribution to fibrotic tissue injury. Biol Trace Elem Res 144:621–635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-011-9041-x
Pagano G, Guida M, Tommasi F, Oral R (2015) Health effects and toxicity mechanisms of rare earth elements—knowledge gaps and research prospects. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 115:40–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.01.030
Liu P, Xiao H, Li X, Zhang C, Liu Y (2006) Study on the toxic mechanism of La3+ to Escherichia coli. Biol Trace Elem Res 114:293–299
Mu K, Zhao X, Hu L, Zhang F, Zhang W, Cui J (2006) Toxicity of lanthanum to pathogenic fungi and its morphological characteristics. J Rare Earths 24:607–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0721(06)60173-7
Tai P, Zhao Q, Su D, Li P, Stagnitti F (2010) Biological toxicity of lanthanide elements on algae. Chemosphere 80:1031–1035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.05.030
Oral R, Bustamante P, Warnau M, D’Ambra A, Guida M, Pagano G (2010) Cytogenetic and developmental toxicity of cerium and lanthanum to sea urchin embryos. Chemosphere 81:194–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.06.057
Thomas PJ, Carpenter D, Boutin C, Allison JE (2014) Rare earth elements (REEs): effects on germination and growth of selected crop and native plant species. Chemosphere 96:57–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.07.020
Hattori A, Mizuno T, Akamatsu M, Hisamoto N, Matsumoto K (2013) The Caenorhabditis elegans JNK signaling pathway activates expression of stress response genes by derepressing the Fos/HDAC repressor complex. PLoS Genet 9:e1003315. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003315
Barsyte D, Lovejoy DA, Lithgow GJ (2001) Longevity and heavy metal resistance in daf-2 and age-1 long-lived mutants of Caenorhabditis elegans. FASEB J 15:627–634. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.99-0966com
Acknowledgements
Nematode strains were provided by the Caenorhabditis Genetics Center, which is funded by the NIH Office of Research Infrastructure Programs (P40 OD010440). We thank Dr. Naoki Hisamoto and Dr. Kunihiro Mtsumoto of the Nagoya University for providing us mutant strains.
Funding
This study was supported in part by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI with a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) (B264207180) to TW.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wakabayashi, T., Nakano, Y. Stress Responses Against Rare Earth Ions Are Mediated by the JNK and p38 MAPK Pathways in Caenorhabditis elegans. Biol Trace Elem Res 190, 550–555 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1577-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1577-6